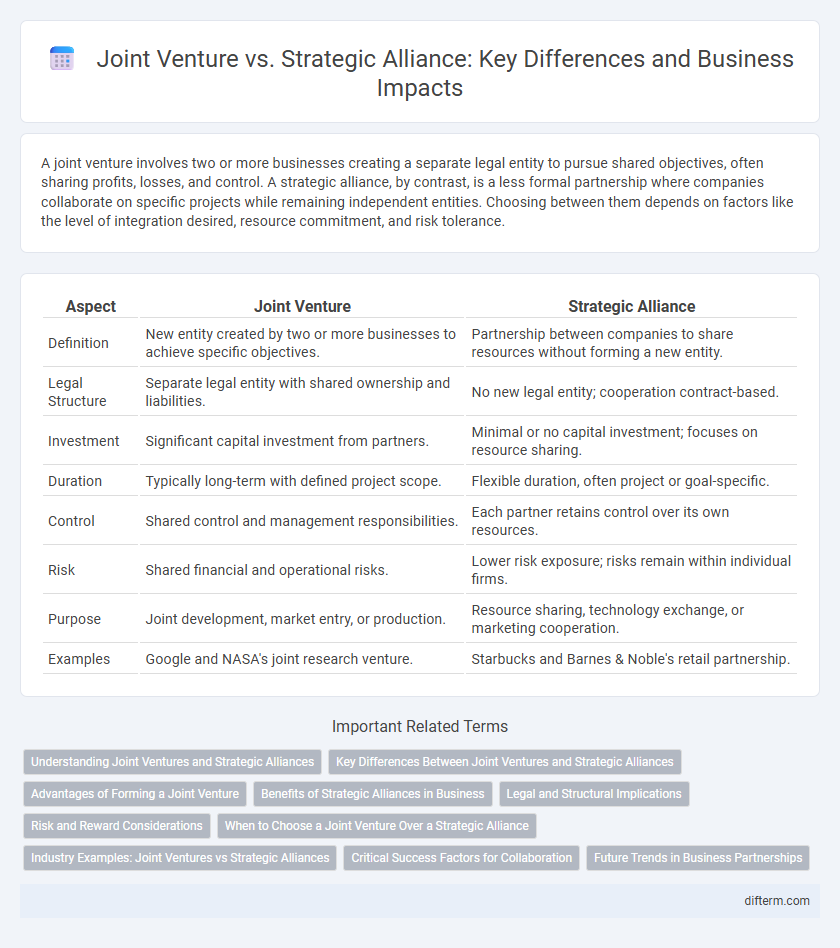
A joint venture involves two or more businesses creating a separate legal entity to pursue shared objectives, often sharing profits, losses, and control. A strategic alliance, by contrast, is a less formal partnership where companies collaborate on specific projects while remaining independent entities. Choosing between them depends on factors like the level of integration desired, resource commitment, and risk tolerance.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Joint Venture | Strategic Alliance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | New entity created by two or more businesses to achieve specific objectives. | Partnership between companies to share resources without forming a new entity. |
| Legal Structure | Separate legal entity with shared ownership and liabilities. | No new legal entity; cooperation contract-based. |
| Investment | Significant capital investment from partners. | Minimal or no capital investment; focuses on resource sharing. |
| Duration | Typically long-term with defined project scope. | Flexible duration, often project or goal-specific. |
| Control | Shared control and management responsibilities. | Each partner retains control over its own resources. |
| Risk | Shared financial and operational risks. | Lower risk exposure; risks remain within individual firms. |
| Purpose | Joint development, market entry, or production. | Resource sharing, technology exchange, or marketing cooperation. |
| Examples | Google and NASA's joint research venture. | Starbucks and Barnes & Noble's retail partnership. |
Understanding Joint Ventures and Strategic Alliances
Joint ventures involve creating a new legal entity where partners share ownership, risks, and profits, promoting deep collaboration for specific business objectives. Strategic alliances allow businesses to cooperate while remaining independent, leveraging each other's strengths without forming a separate entity. Understanding these structures helps companies choose between shared control and flexible collaboration to optimize market entry, resource sharing, and competitive advantage.
Key Differences Between Joint Ventures and Strategic Alliances
Joint ventures create a separate legal entity jointly owned by the partnering companies, while strategic alliances remain contractual agreements without forming a new entity. In joint ventures, partners share equity, risks, and profits proportionally, whereas strategic alliances involve cooperation without equity stakes or shared ownership. Joint ventures often require a longer-term commitment with integrated operations, while strategic alliances allow more flexibility and less formal collaboration focused on specific projects or objectives.
Advantages of Forming a Joint Venture
Forming a joint venture offers access to shared resources and capital, enabling businesses to undertake larger projects and enter new markets with reduced financial risk. This collaboration fosters deep integration of expertise and technology, enhancing innovation and competitive advantage. Joint ventures also benefit from shared profits and losses, aligning partner interests and promoting long-term commitment.
Benefits of Strategic Alliances in Business
Strategic alliances enable businesses to share resources and expertise without the complexities of forming a separate legal entity, allowing for greater flexibility and lower financial risk compared to joint ventures. These collaborations enhance market access, innovation capacity, and competitive advantage by leveraging complementary strengths of partner companies. Strategic alliances also facilitate faster response to market changes and foster long-term relationships beneficial for sustainable growth.
Legal and Structural Implications
A joint venture involves creating a new legal entity with shared ownership, liabilities, and governance structures defined by contractual agreements, often requiring regulatory approvals and compliance with corporate laws. In contrast, a strategic alliance maintains the independence of each partner without forming a separate entity, relying on contractual collaborations that outline roles, responsibilities, and intellectual property rights without combining assets or liabilities. The choice impacts risk distribution, decision-making authority, and legal obligations, making due diligence and clear agreements essential for mitigating potential disputes and ensuring alignment with business objectives.
Risk and Reward Considerations
Joint ventures involve shared ownership, leading to higher financial risk but also the potential for greater rewards through combined resources and profits. Strategic alliances typically carry lower risk since partners remain independent, but the rewards are often limited to mutual benefits such as market access or technology exchange. Assessing risk tolerance and desired control levels is crucial for businesses when choosing between joint ventures and strategic alliances.
When to Choose a Joint Venture Over a Strategic Alliance
Choose a joint venture over a strategic alliance when companies seek to create a new, legally separate entity to share resources, risks, and profits for a specific business objective. Joint ventures are ideal for long-term collaborations involving significant investment and operational integration, such as entering new markets or developing new products. Strategic alliances suit less formal partnerships with limited resource sharing and more flexibility for short-term projects or exploratory cooperation.
Industry Examples: Joint Ventures vs Strategic Alliances
Joint ventures in the automotive industry, such as the collaboration between Toyota and Subaru to develop sports cars, demonstrate deep integration with shared equity and joint risk. In contrast, strategic alliances like the partnership between Microsoft and Intel emphasize collaborative technology development while maintaining independent operations. These industry-specific examples highlight how joint ventures typically involve combined resources and profits, whereas strategic alliances focus on mutual benefits without equity sharing.
Critical Success Factors for Collaboration
Effective communication and aligned objectives are critical success factors in both joint ventures and strategic alliances, ensuring smooth collaboration and goal clarity. Trust-building mechanisms and shared resource management enhance partnership resilience and operational efficiency. Clear governance structures and performance measurement systems drive accountability and continuous improvement in joint business efforts.
Future Trends in Business Partnerships
Future trends in business partnerships emphasize increased use of hybrid models that combine elements of joint ventures and strategic alliances, fostering agility and resource sharing. Digital transformation and AI integration will drive deeper collaboration, enhancing data exchange and innovation capabilities. Cross-border partnerships are expected to rise, leveraging global markets and diverse expertise to navigate complex regulatory landscapes effectively.
Joint Venture vs Strategic Alliance Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com