Port fuel injection delivers fuel into the intake manifold, ensuring better mixing with air before entering the combustion chamber, which enhances throttle response and reduces carbon buildup on intake valves. Direct injection sprays fuel directly into the combustion chamber, offering superior fuel atomization, increased power output, and improved fuel efficiency while potentially causing more carbon deposits on intake valves. Choosing between port fuel injection and direct injection depends on balancing performance needs, fuel economy goals, and maintenance considerations.
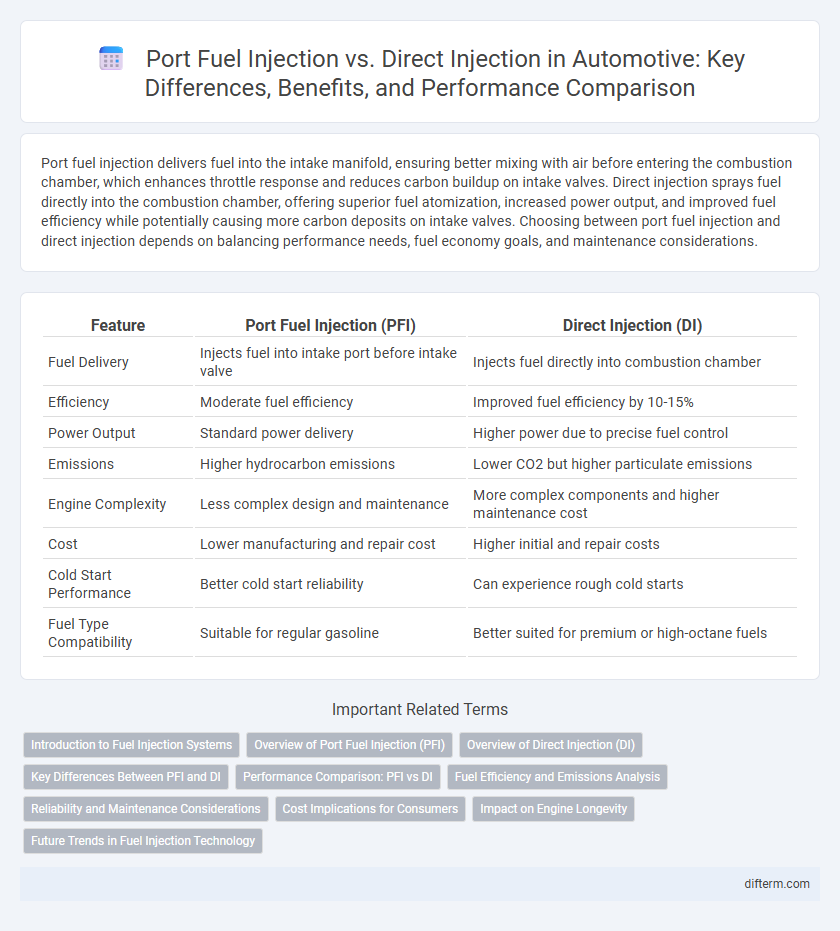
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Port Fuel Injection (PFI) | Direct Injection (DI) |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Delivery | Injects fuel into intake port before intake valve | Injects fuel directly into combustion chamber |
| Efficiency | Moderate fuel efficiency | Improved fuel efficiency by 10-15% |
| Power Output | Standard power delivery | Higher power due to precise fuel control |
| Emissions | Higher hydrocarbon emissions | Lower CO2 but higher particulate emissions |
| Engine Complexity | Less complex design and maintenance | More complex components and higher maintenance cost |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing and repair cost | Higher initial and repair costs |
| Cold Start Performance | Better cold start reliability | Can experience rough cold starts |
| Fuel Type Compatibility | Suitable for regular gasoline | Better suited for premium or high-octane fuels |
Introduction to Fuel Injection Systems
Fuel injection systems, including Port Fuel Injection (PFI) and Direct Injection (DI), play a critical role in modern automotive engine performance and efficiency. PFI delivers fuel into the intake port, mixing with air before entering the combustion chamber, while DI injects fuel directly into the combustion chamber for precise fuel delivery. Understanding the differences between these technologies helps optimize combustion, improve fuel economy, and reduce emissions in internal combustion engines.
Overview of Port Fuel Injection (PFI)
Port Fuel Injection (PFI) delivers fuel directly into the intake manifold, ensuring thorough mixing of air and fuel before entering the combustion chamber. This method provides better fuel atomization, reduced carbon buildup on intake valves, and improved emissions control compared to older carburetor systems. PFI technology remains widely used in modern vehicles due to its balance of performance, fuel efficiency, and lower manufacturing costs.
Overview of Direct Injection (DI)
Direct Injection (DI) in automotive engines delivers fuel directly into the combustion chamber, enhancing fuel atomization and combustion efficiency compared to Port Fuel Injection (PFI). This method improves power output, reduces fuel consumption, and lowers emissions due to precise fuel delivery and better air-fuel mixture control. DI technology supports advanced engine designs with higher compression ratios, enabling improved performance and adherence to stringent environmental regulations.
Key Differences Between PFI and DI
Port Fuel Injection (PFI) delivers fuel into the intake manifold, allowing better mixing with air before entering the combustion chamber, which results in smoother engine performance and reduced carbon buildup. Direct Injection (DI) sprays fuel directly into the combustion chamber, offering higher fuel efficiency, increased power output, and precise control of the air-fuel mixture, but it can lead to higher particulate emissions. PFI systems tend to have lower complexity and cost, while DI engines require advanced calibration and components to manage combustion dynamics effectively.
Performance Comparison: PFI vs DI
Direct Injection (DI) delivers superior performance by injecting fuel directly into the combustion chamber, resulting in better atomization and more precise fuel-air mixture control compared to Port Fuel Injection (PFI). DI engines typically achieve higher power output and improved fuel efficiency due to increased combustion pressure and reduced fuel wastage. However, PFI systems offer lower complexity and reduced risk of carbon buildup, making them more reliable over time despite slightly lower performance metrics.
Fuel Efficiency and Emissions Analysis
Port Fuel Injection systems typically provide better fuel atomization at lower engine speeds, resulting in more complete combustion and reduced hydrocarbon emissions. Direct Injection technology enhances fuel efficiency by delivering precise fuel quantity directly into the combustion chamber, optimizing air-fuel mixture and enabling higher compression ratios. However, Direct Injection can produce higher particulate emissions, requiring advanced aftertreatment systems to meet stringent environmental standards.
Reliability and Maintenance Considerations
Port Fuel Injection (PFI) systems generally offer higher reliability and easier maintenance due to simpler design and fewer issues with carbon buildup compared to Direct Injection (DI) systems. Direct Injection engines, while delivering better fuel efficiency and performance, often require more frequent maintenance such as intake valve cleaning to prevent carbon deposits. Repair costs for DI engines tend to be higher, making PFI a preferable choice for drivers prioritizing long-term reliability and lower maintenance expenses.
Cost Implications for Consumers
Port fuel injection systems generally have lower upfront costs due to simpler design and easier maintenance, making them more affordable for consumers. Direct injection engines, while offering better fuel efficiency and performance, often come with higher manufacturing and repair expenses that impact long-term ownership costs. Consumers should weigh initial price differences against potential fuel savings and increased maintenance to determine the best value.
Impact on Engine Longevity
Port fuel injection systems generally contribute to longer engine life by reducing carbon buildup on intake valves and maintaining cleaner combustion chambers. Direct injection improves fuel efficiency and power but may increase the risk of carbon deposits on valves, potentially leading to more frequent maintenance. Engine longevity depends on usage patterns and maintenance practices, with proper care mitigating risks associated with either injection system.
Future Trends in Fuel Injection Technology
Future trends in fuel injection technology emphasize the integration of advanced direct injection systems with higher pressure capabilities to improve fuel atomization and combustion efficiency. Emerging innovations include dual-injection setups combining port fuel injection (PFI) and direct injection (DI) to optimize power output and reduce emissions while enabling compatibility with alternative fuels. Electrification and AI-driven engine management systems are expected to further enhance precision fuel delivery, contributing to stringent emissions regulations and improved performance in next-generation internal combustion engines.
Port Fuel Injection vs Direct Injection Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com