Hydraulic steering systems deliver consistent feedback and robust performance, especially in heavy-duty vehicles, by relying on pressurized fluid to assist the driver's input. Electric power steering (EPS) systems offer improved fuel efficiency and customizable steering feel through electronic control units that adjust assistance based on driving conditions. Choosing between the two depends on factors like vehicle type, desired responsiveness, maintenance preferences, and overall efficiency goals.
Table of Comparison
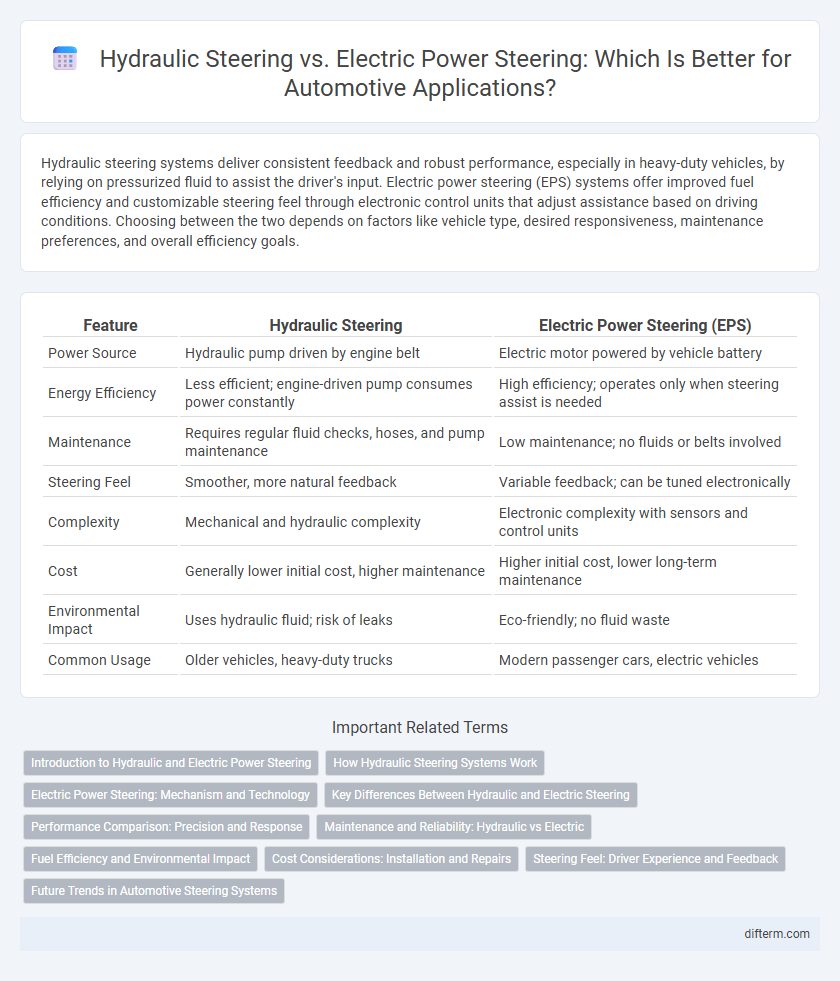
| Feature | Hydraulic Steering | Electric Power Steering (EPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Hydraulic pump driven by engine belt | Electric motor powered by vehicle battery |
| Energy Efficiency | Less efficient; engine-driven pump consumes power constantly | High efficiency; operates only when steering assist is needed |
| Maintenance | Requires regular fluid checks, hoses, and pump maintenance | Low maintenance; no fluids or belts involved |
| Steering Feel | Smoother, more natural feedback | Variable feedback; can be tuned electronically |
| Complexity | Mechanical and hydraulic complexity | Electronic complexity with sensors and control units |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost, higher maintenance | Higher initial cost, lower long-term maintenance |
| Environmental Impact | Uses hydraulic fluid; risk of leaks | Eco-friendly; no fluid waste |
| Common Usage | Older vehicles, heavy-duty trucks | Modern passenger cars, electric vehicles |
Introduction to Hydraulic and Electric Power Steering
Hydraulic steering systems utilize a pump driven by the engine to provide fluid pressure, enhancing steering effort and feedback for heavier vehicles. Electric power steering (EPS) replaces hydraulic components with an electric motor and sensors, offering improved fuel efficiency and customizable steering assistance. Advancements in EPS technology enable precise control, reduced maintenance, and integration with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
How Hydraulic Steering Systems Work
Hydraulic steering systems operate by using fluid pressure generated by a pump, typically driven by the engine, to assist the driver in turning the steering wheel. A hydraulic fluid is directed through valves to a piston or cylinder within the steering gear, amplifying the force applied and reducing driver effort. This mechanism provides consistent steering feedback and durability, especially in heavy-duty automotive applications.
Electric Power Steering: Mechanism and Technology
Electric Power Steering (EPS) utilizes an electric motor to assist the driver's steering input, enhancing fuel efficiency by reducing engine load compared to traditional hydraulic systems. EPS systems incorporate sensors, electronic control units (ECUs), and torque sensors to precisely modulate steering assistance based on vehicle speed and driving conditions. This advanced technology improves maneuverability, reduces maintenance requirements, and enables integration with autonomous driving and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
Key Differences Between Hydraulic and Electric Steering
Hydraulic steering systems rely on a pump driven by the engine to provide steering assistance, resulting in higher energy consumption and maintenance requirements, whereas electric power steering (EPS) uses an electric motor, offering improved fuel efficiency and lower operational costs. EPS systems deliver precise steering control with customizable assistance levels, while hydraulic systems typically provide a consistent but less adaptable steering feel. Integration of EPS with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) enhances vehicle safety and performance, a feature not commonly achievable with traditional hydraulic steering.
Performance Comparison: Precision and Response
Hydraulic steering systems deliver strong feedback and robust performance in heavy-duty and off-road vehicles, offering consistent precision under varying conditions. Electric power steering (EPS) provides faster response times and enhanced control accuracy through advanced sensors and real-time adjustments, improving fuel efficiency by reducing engine load. EPS systems enable customizable steering feel and adaptive assistance, making them superior in precision and responsiveness for modern automotive applications.
Maintenance and Reliability: Hydraulic vs Electric
Hydraulic steering systems require regular maintenance, including fluid checks and hose inspections, to prevent leaks and ensure consistent performance, while electric power steering (EPS) systems reduce maintenance needs by eliminating hydraulic components and fluid. EPS offers improved reliability due to fewer moving parts and reduced susceptibility to wear and leaks, contributing to longer service intervals and lower overall maintenance costs. However, hydraulic systems remain robust in heavy-duty applications, where high steering loads demand durable mechanical components despite increased upkeep.
Fuel Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Electric power steering (EPS) significantly improves fuel efficiency by reducing engine load since it only consumes energy when steering assistance is needed, unlike hydraulic steering systems that continuously run the pump driven by the engine. This decreased fuel consumption directly lowers CO2 emissions, making EPS a more environmentally friendly option in automotive design. Hydraulic steering systems' constant energy draw results in higher fuel consumption and an increased environmental footprint compared to the more efficient electric alternative.
Cost Considerations: Installation and Repairs
Hydraulic steering systems generally have higher installation and repair costs due to complex components like pumps, hoses, and fluid reservoirs requiring regular maintenance. Electric power steering (EPS) reduces long-term expenses with simpler installation procedures and fewer mechanical parts, leading to lower labor and replacement costs. EPS also eliminates the need for hydraulic fluid changes, further minimizing overall maintenance expenses.
Steering Feel: Driver Experience and Feedback
Hydraulic steering offers a more natural, tactile feedback due to its direct mechanical linkage, allowing drivers to feel road texture and resistance precisely. Electric power steering (EPS) provides variable assistance and can be tuned for different driving conditions but often sacrifices some of the nuanced road feel. Drivers valuing dynamic feedback typically prefer hydraulic systems, while EPS prioritizes efficiency and adaptability.
Future Trends in Automotive Steering Systems
Electric power steering (EPS) is rapidly becoming the dominant technology in automotive steering systems due to its superior energy efficiency, precise control, and seamless integration with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). Future trends emphasize the development of more sophisticated EPS variants featuring adaptive torque feedback and enhanced connectivity for autonomous driving capabilities. Hydraulic steering systems are increasingly phased out in favor of EPS, which supports eco-friendly initiatives and reduces vehicle weight, contributing to improved fuel economy and lower emissions.
hydraulic steering vs electric power steering Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com