Halogen headlights emit a warm, yellowish light and are generally more affordable but consume more energy and have a shorter lifespan compared to LED headlights. LED headlights offer brighter, whiter light with better energy efficiency, improved durability, and longer service life, enhancing nighttime visibility and safety. While initial costs for LEDs are higher, their longevity and performance benefits make them a cost-effective upgrade for modern vehicles.
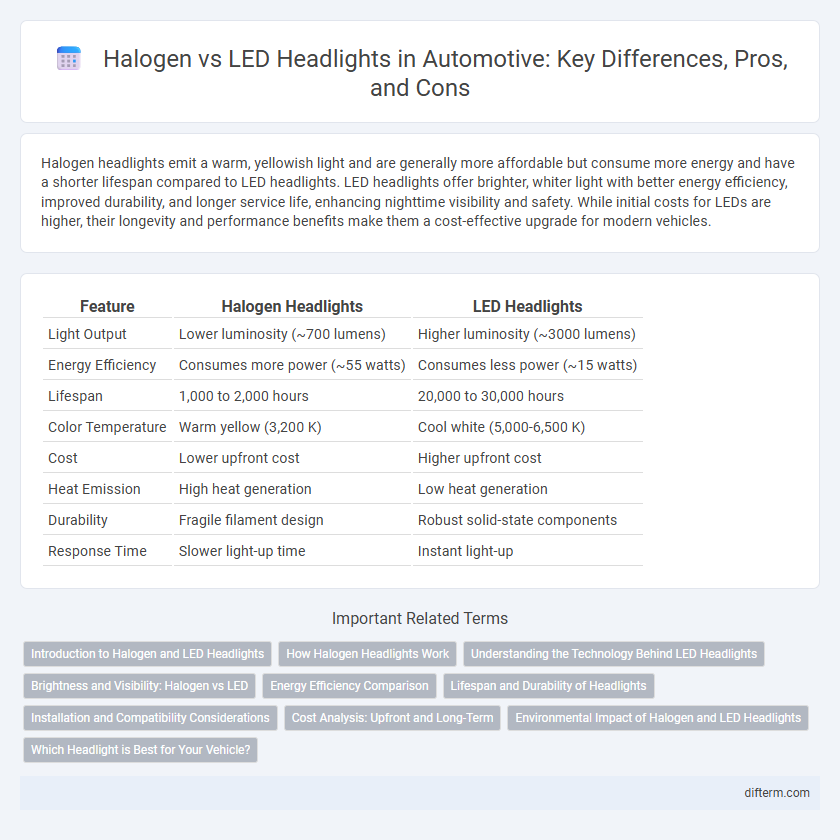
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Halogen Headlights | LED Headlights |
|---|---|---|
| Light Output | Lower luminosity (~700 lumens) | Higher luminosity (~3000 lumens) |
| Energy Efficiency | Consumes more power (~55 watts) | Consumes less power (~15 watts) |
| Lifespan | 1,000 to 2,000 hours | 20,000 to 30,000 hours |
| Color Temperature | Warm yellow (3,200 K) | Cool white (5,000-6,500 K) |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher upfront cost |
| Heat Emission | High heat generation | Low heat generation |
| Durability | Fragile filament design | Robust solid-state components |
| Response Time | Slower light-up time | Instant light-up |
Introduction to Halogen and LED Headlights
Halogen headlights use tungsten filaments enclosed in halogen gas, providing warm, yellowish light with moderate brightness and affordability. LED headlights employ semiconductor diodes that emit bright, white light, offering higher energy efficiency, longer lifespan, and improved visibility. The transition from halogen to LED technology reflects advancements in automotive lighting for enhanced safety and performance.
How Halogen Headlights Work
Halogen headlights operate using a tungsten filament encased in a glass bulb filled with halogen gas, which increases the filament's lifespan and brightness by enabling higher operating temperatures. When electric current passes through the filament, it heats up and emits light through incandescence, producing a warm, yellowish beam. The halogen gas inside the bulb helps prevent tungsten evaporation, maintaining clarity and consistent illumination in automotive lighting systems.
Understanding the Technology Behind LED Headlights
LED headlights use light-emitting diodes that produce brighter, more focused illumination with lower energy consumption compared to halogen headlights, which rely on heated tungsten filaments. The semiconductor technology in LEDs allows for faster response times and longer lifespan, enhancing vehicle safety and efficiency. Advanced thermal management in LED systems prevents overheating, ensuring consistent light output and durability under various driving conditions.
Brightness and Visibility: Halogen vs LED
LED headlights provide significantly higher brightness levels compared to halogen headlights, emitting a more intense and focused beam that enhances visibility during nighttime driving. The color temperature of LED lights, typically around 5000-6000 Kelvin, closely mimics natural daylight, improving contrast and reducing eye strain for drivers. Halogen headlights, with lower brightness and a warmer color temperature of approximately 3200 Kelvin, offer less illumination and a shorter effective range, which can impact overall driving safety in low-light conditions.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Halogen headlights consume significantly more energy, typically around 55 watts per bulb, compared to LED headlights which use only 15-20 watts, making LEDs up to 70% more energy-efficient. This reduced power consumption in LED headlights contributes to lower fuel consumption in gasoline vehicles and extends battery life in electric cars. The enhanced efficiency of LED headlights also results in less heat generation, minimizing energy loss and improving overall vehicle energy management.
Lifespan and Durability of Headlights
Halogen headlights typically last around 450 to 1,000 hours, whereas LED headlights offer significantly longer lifespans, often exceeding 25,000 hours. Due to their solid-state design, LED headlights are more resistant to vibrations and impact, enhancing overall durability compared to the fragile filaments of halogen bulbs. This extended lifespan and increased durability make LED headlights a cost-effective and reliable choice for modern automotive lighting systems.
Installation and Compatibility Considerations
Halogen headlights offer simple installation and broad compatibility with most vehicle electrical systems, requiring minimal modifications or adapters. LED headlights, while providing improved energy efficiency and brightness, often necessitate specific wiring harnesses, CAN bus adapters, or additional resistors to prevent error codes and ensure proper function. Compatibility should be verified with vehicle models to address potential issues like dashboard warnings or flickering when upgrading to LED systems.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term
Halogen headlights typically cost between $15 to $30 per bulb, offering a lower initial investment compared to LED headlights, which range from $50 to $200 per bulb. LED headlights consume less power and last up to 25,000 hours, significantly reducing replacement and energy costs over time compared to halogen bulbs, which average around 1,000 hours of use. Long-term savings from LED technology include lower maintenance expenses and enhanced fuel efficiency due to reduced electrical load, despite the higher upfront cost.
Environmental Impact of Halogen and LED Headlights
LED headlights consume significantly less energy than halogen headlights, reducing the overall carbon footprint of vehicles. Halogen bulbs generate more heat and require frequent replacements, contributing to increased waste and resource consumption. The longer lifespan and higher efficiency of LED technology make it a more environmentally sustainable choice in automotive lighting.
Which Headlight is Best for Your Vehicle?
LED headlights offer superior brightness, energy efficiency, and longer lifespan compared to halogen headlights, making them ideal for modern vehicles seeking enhanced visibility and reduced maintenance. Halogen headlights remain a cost-effective option with easier replacement and compatibility for older models, but they consume more power and provide less clarity in low-light conditions. Choosing the best headlight depends on your vehicle's compatibility, lighting needs, and budget considerations.
halogen headlights vs LED headlights Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com