Flex fuel vehicles are designed to run on ethanol-blended fuels, typically E85, offering greater fuel flexibility and often lower emissions compared to premium fuel engines. Premium fuel contains a higher octane rating, enhancing engine performance and efficiency in vehicles that require or recommend it, but it is generally more expensive. Choosing between flex fuel and premium fuel depends on vehicle compatibility, cost efficiency, and environmental considerations.
Table of Comparison
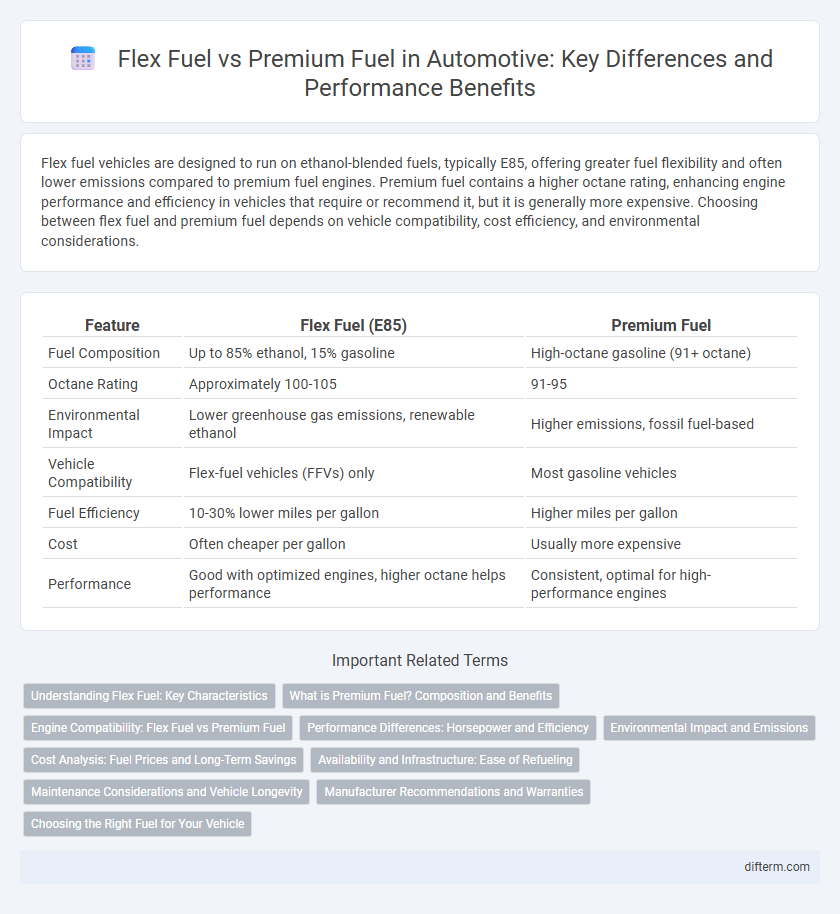
| Feature | Flex Fuel (E85) | Premium Fuel |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Composition | Up to 85% ethanol, 15% gasoline | High-octane gasoline (91+ octane) |
| Octane Rating | Approximately 100-105 | 91-95 |
| Environmental Impact | Lower greenhouse gas emissions, renewable ethanol | Higher emissions, fossil fuel-based |
| Vehicle Compatibility | Flex-fuel vehicles (FFVs) only | Most gasoline vehicles |
| Fuel Efficiency | 10-30% lower miles per gallon | Higher miles per gallon |
| Cost | Often cheaper per gallon | Usually more expensive |
| Performance | Good with optimized engines, higher octane helps performance | Consistent, optimal for high-performance engines |
Understanding Flex Fuel: Key Characteristics
Flex fuel vehicles are engineered to run on varying ethanol blends, typically E85, a mix of 85% ethanol and 15% gasoline, enhancing fuel flexibility and reducing reliance on traditional fossil fuels. These vehicles feature specialized fuel systems and engine calibrations designed to optimize performance and emissions across different ethanol concentrations. Understanding the chemical properties and combustion characteristics of ethanol is essential for maximizing efficiency and ensuring compatibility with flex fuel technology.
What is Premium Fuel? Composition and Benefits
Premium fuel is a high-octane gasoline, typically rated at 91 to 93 octane, designed to provide better engine performance and efficiency in high-compression engines. Its composition includes higher levels of anti-knock additives and fewer impurities, which help prevent engine knocking and improve combustion stability. The benefits of premium fuel include improved acceleration, enhanced fuel economy, and reduced emissions, making it ideal for luxury and performance vehicles requiring optimal engine protection.
Engine Compatibility: Flex Fuel vs Premium Fuel
Flex fuel vehicles (FFVs) are engineered to operate on varying ethanol blends, up to E85, without compromising engine performance or durability due to specialized fuel system components and engine calibrations. In contrast, premium fuel engines are designed for regular gasoline with a higher octane rating, emphasizing resistance to engine knocking rather than compatibility with ethanol blends. Understanding the differences in engine compatibility is crucial for optimizing efficiency, emissions, and overall vehicle longevity in flex fuel versus premium fuel applications.
Performance Differences: Horsepower and Efficiency
Flex fuel vehicles running on E85 ethanol blend typically generate slightly lower horsepower compared to premium gasoline due to ethanol's lower energy content per gallon. However, E85 can offer increased octane ratings, allowing for higher compression ratios and potential performance gains in specifically tuned engines. Premium fuel generally delivers more consistent fuel efficiency and power output in standard engines optimized for gasoline combustion.
Environmental Impact and Emissions
Flex fuel vehicles, which use ethanol-blended fuels such as E85, produce lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to premium gasoline by reducing carbon monoxide and particulate matter. Premium fuel vehicles, relying solely on high-octane gasoline, typically emit higher levels of carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxides, contributing more to air pollution and climate change. The renewable nature of ethanol in flex fuels supports decreased fossil fuel dependency, promoting a cleaner and more sustainable transportation sector.
Cost Analysis: Fuel Prices and Long-Term Savings
Flex fuel vehicles use ethanol-blended fuels that typically cost less per gallon than premium gasoline, resulting in immediate fuel expense savings. However, the lower energy content of ethanol can reduce miles per gallon, potentially offsetting initial cost advantages over time. Long-term savings depend on fluctuating fuel prices, regional ethanol availability, and vehicle fuel efficiency, making thorough cost analysis essential for optimal fuel choice.
Availability and Infrastructure: Ease of Refueling
Flex fuel vehicles benefit from a growing network of E85 ethanol blend stations, primarily concentrated in the Midwest and parts of the United States, providing moderate ease of refueling. Premium fuel, consisting of higher-octane gasoline, enjoys widespread availability at nearly all fuel stations across urban and rural areas, ensuring superior accessibility. The established infrastructure for premium fuel supports consistent refueling convenience, whereas flex fuel stations remain regionally limited, impacting refueling ease for flex fuel vehicle owners outside key markets.
Maintenance Considerations and Vehicle Longevity
Flex fuel vehicles require less frequent maintenance on the fuel system due to ethanol-compatible components that resist corrosion, but spark plugs and fuel filters may need more regular inspection because of ethanol's higher solvent properties. Premium fuel usage in conventional engines can improve combustion efficiency and reduce carbon deposits, potentially extending engine life and reducing maintenance costs. Choosing the appropriate fuel based on manufacturer recommendations is critical to optimizing vehicle longevity and minimizing costly repairs.
Manufacturer Recommendations and Warranties
Automakers recommend using the specified fuel type in the owner's manual to maintain optimal engine performance and avoid warranty issues. Flex-fuel vehicles are designed to run on any blend of ethanol and gasoline up to E85, ensuring warranty coverage when proper flex fuel is used. Using premium fuel in a non-premium-rated engine may not provide benefits and could void warranties if manufacturer specifications are not followed.
Choosing the Right Fuel for Your Vehicle
Choosing the right fuel for your vehicle depends on compatibility and performance requirements; flex fuel vehicles are designed to run on either E85 ethanol blend or regular gasoline, offering flexibility and often lower emissions. Premium fuel, with a higher octane rating (usually 91 or above), is essential for high-compression engines to prevent knocking and maintain optimal power output. Understanding your vehicle manufacturer's recommendations ensures maximum efficiency, engine longevity, and fuel economy.
flex fuel vs premium fuel Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com