A VPN encrypts all internet traffic, providing enhanced security and privacy by routing data through a secure server, making it ideal for protecting personal information and bypassing geo-restrictions. In contrast, a proxy only masks your IP address for specific applications or browsers without encrypting traffic, offering limited privacy and security benefits. Choosing between a VPN and a proxy depends on the level of protection needed and the intended online activities.
Table of Comparison
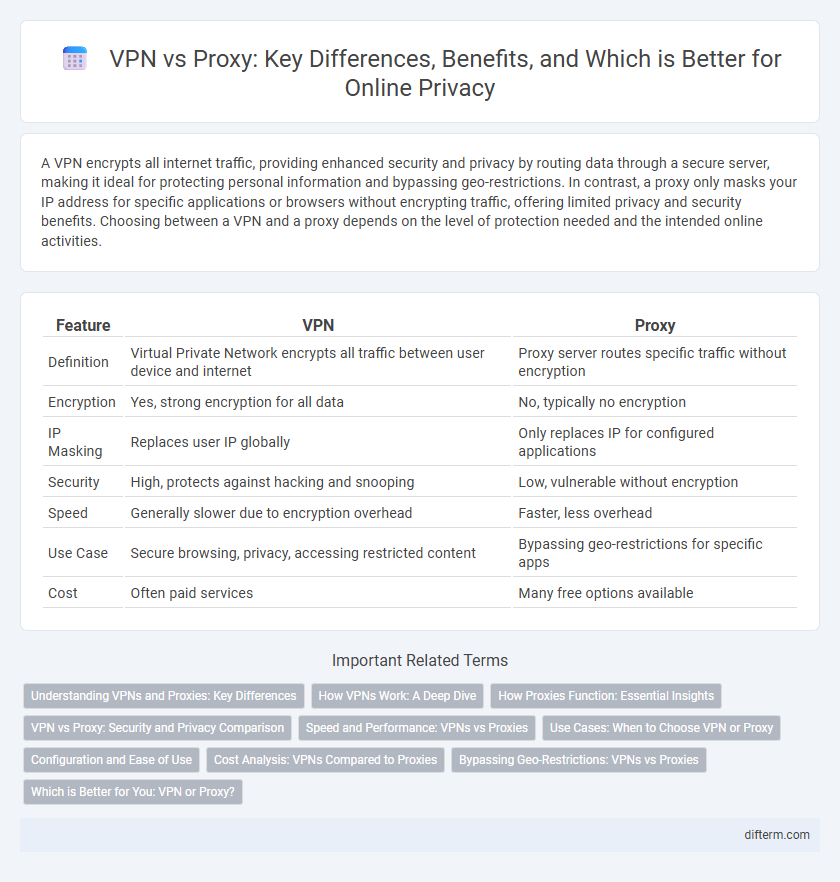
| Feature | VPN | Proxy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual Private Network encrypts all traffic between user device and internet | Proxy server routes specific traffic without encryption |
| Encryption | Yes, strong encryption for all data | No, typically no encryption |
| IP Masking | Replaces user IP globally | Only replaces IP for configured applications |
| Security | High, protects against hacking and snooping | Low, vulnerable without encryption |
| Speed | Generally slower due to encryption overhead | Faster, less overhead |
| Use Case | Secure browsing, privacy, accessing restricted content | Bypassing geo-restrictions for specific apps |
| Cost | Often paid services | Many free options available |
Understanding VPNs and Proxies: Key Differences
VPNs encrypt internet traffic, creating a secure tunnel between the user and the destination server, which ensures privacy and protection from cyber threats. Proxies act as intermediaries by routing requests through different servers but do not provide encryption, leaving data vulnerable to interception. Understanding these distinctions helps users select VPNs for comprehensive security and proxies for basic IP masking or content access.
How VPNs Work: A Deep Dive
VPNs encrypt internet traffic through secure tunnels, masking IP addresses and enhancing online privacy by routing data via remote servers. This encryption prevents third parties from intercepting sensitive information, ensuring confidentiality and security on public or unsecured networks. Unlike proxies, VPNs provide comprehensive protection for all internet activities across devices, supporting anonymous browsing and bypassing geo-restrictions seamlessly.
How Proxies Function: Essential Insights
Proxies function as intermediaries between a user's device and the internet, routing requests through a server to mask the original IP address and enhance privacy. By forwarding web traffic, proxies enable access to geo-restricted content and filter malicious sites, improving security. Unlike VPNs, proxies typically do not encrypt data, making them faster but less secure for sensitive communications.
VPN vs Proxy: Security and Privacy Comparison
VPNs encrypt internet traffic with protocols like OpenVPN and WireGuard, offering robust security and protecting user privacy by masking IP addresses and preventing data interception. Proxies only route specific traffic through an intermediary server without encryption, leaving data vulnerable to monitoring and exposing the user's real IP address. For enhanced security and privacy, VPNs provide comprehensive protection across all applications, while proxies offer limited anonymity primarily for web browsing.
Speed and Performance: VPNs vs Proxies
VPNs encrypt all internet traffic, which can slightly reduce connection speed due to the overhead of encryption protocols like OpenVPN or WireGuard. Proxies typically offer faster speeds because they only reroute specific application traffic without encryption, minimizing latency. However, VPNs provide more consistent performance across different network conditions by optimizing routing and security simultaneously.
Use Cases: When to Choose VPN or Proxy
VPNs provide comprehensive security by encrypting all internet traffic, making them ideal for protecting sensitive data during online banking or accessing geo-restricted streaming services. Proxies are suitable for lightweight tasks like bypassing content filters or managing multiple social media accounts without requiring full traffic encryption. Choosing a VPN is essential for privacy-focused users needing robust security, while proxies are preferred for faster, less secure browsing and simple IP masking.
Configuration and Ease of Use
VPNs require installation of dedicated software and straightforward configuration processes, often with one-click connection options, making them user-friendly for both beginners and advanced users. Proxies generally involve manual setup in browser or application settings, which can be less intuitive and more time-consuming for average users. VPNs also provide system-wide protection, whereas proxies typically only route specific application traffic, influencing ease of use and overall configuration complexity.
Cost Analysis: VPNs Compared to Proxies
VPNs typically involve subscription fees ranging from $5 to $15 per month, providing robust encryption and comprehensive security features, while proxies often offer free or low-cost services with limited protection and slower speeds. The total cost of VPNs reflects their ability to secure entire internet traffic and access geo-restricted content, making them suitable for privacy-focused users and businesses. Proxies serve well for basic tasks like anonymous browsing but may incur hidden costs related to data leaks or compromised connections.
Bypassing Geo-Restrictions: VPNs vs Proxies
VPNs encrypt all internet traffic and route it through servers in different countries, effectively bypassing geo-restrictions on streaming platforms and websites while maintaining user privacy and security. Proxies only reroute specific browser or app traffic without encryption, making them less effective for bypassing geo-blocks on multiple applications or protecting data from interception. VPN services like ExpressVPN or NordVPN offer broader access and enhanced security compared to free proxy servers, which are often slower and vulnerable to data leaks.
Which is Better for You: VPN or Proxy?
Choosing between a VPN and a proxy depends on your specific needs for online privacy, security, and speed. VPNs encrypt your internet traffic, providing robust security and anonymity suitable for sensitive activities like banking or accessing geo-restricted content, while proxies handle only web traffic without encryption, offering faster speeds but less protection. For comprehensive privacy and secure browsing, a VPN is better; for simple IP masking and speed, a proxy may suffice.
VPN vs Proxy Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com