Power over Ethernet (PoE) delivers both data and electrical power through a single cable, reducing installation complexity and costs compared to traditional Ethernet, which requires separate power sources. PoE enhances network flexibility, enabling devices like IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless access points to be easily deployed in locations without nearby power outlets. This integrated approach supports efficient network management and scalability, making it ideal for modern smart building and IoT applications.
Table of Comparison
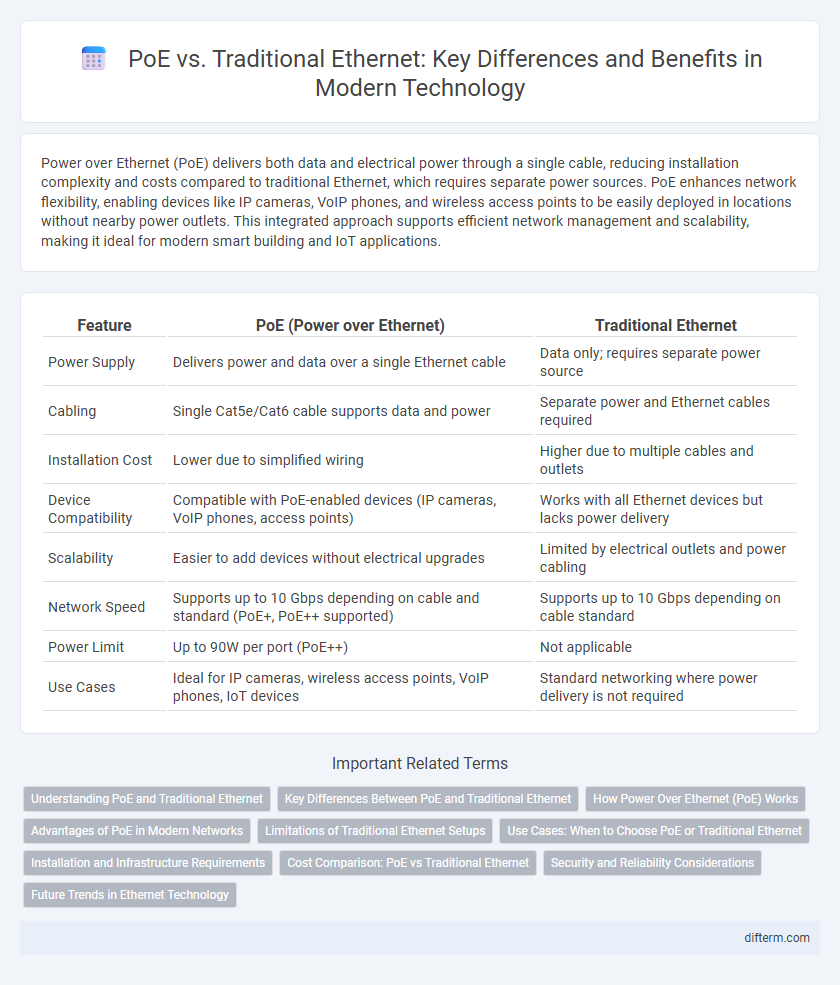
| Feature | PoE (Power over Ethernet) | Traditional Ethernet |
|---|---|---|
| Power Supply | Delivers power and data over a single Ethernet cable | Data only; requires separate power source |
| Cabling | Single Cat5e/Cat6 cable supports data and power | Separate power and Ethernet cables required |
| Installation Cost | Lower due to simplified wiring | Higher due to multiple cables and outlets |
| Device Compatibility | Compatible with PoE-enabled devices (IP cameras, VoIP phones, access points) | Works with all Ethernet devices but lacks power delivery |
| Scalability | Easier to add devices without electrical upgrades | Limited by electrical outlets and power cabling |
| Network Speed | Supports up to 10 Gbps depending on cable and standard (PoE+, PoE++ supported) | Supports up to 10 Gbps depending on cable standard |
| Power Limit | Up to 90W per port (PoE++) | Not applicable |
| Use Cases | Ideal for IP cameras, wireless access points, VoIP phones, IoT devices | Standard networking where power delivery is not required |
Understanding PoE and Traditional Ethernet
Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology enables both data transmission and electrical power delivery over a single Ethernet cable, reducing the need for separate power supplies. Traditional Ethernet transmits only data signals, requiring independent power sources for connected devices such as IP cameras or access points. PoE enhances network efficiency and deployment flexibility by simplifying cable management and lowering installation costs.
Key Differences Between PoE and Traditional Ethernet
Power over Ethernet (PoE) integrates data transmission and electrical power delivery over a single Ethernet cable, reducing the need for separate power supplies and simplifying installation. Traditional Ethernet transmits only data, requiring separate power sources for devices such as IP cameras and wireless access points. PoE provides enhanced flexibility in device placement and reduces infrastructure costs by combining power and connectivity in one cable.
How Power Over Ethernet (PoE) Works
Power over Ethernet (PoE) delivers electrical power alongside data over standard Ethernet cables, eliminating the need for separate power supplies in connected devices like IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless access points. It utilizes two methods: endspan, where power is supplied by PoE-enabled network switches, and midspan, which involves PoE injectors adding power between the switch and the device. By leveraging the existing twisted-pair cabling infrastructure, PoE simplifies installation, reduces costs, and enhances network flexibility compared to traditional Ethernet setups requiring separate power sources.
Advantages of PoE in Modern Networks
Power over Ethernet (PoE) simplifies modern network installations by delivering both data and electrical power through a single Ethernet cable, reducing the need for separate power supplies and outlets. This integration enhances network scalability and flexibility, enabling easier deployment of devices like IP cameras, wireless access points, and VoIP phones in various locations. PoE also improves energy efficiency and centralizes power management, contributing to lower operational costs and streamlined maintenance in complex network environments.
Limitations of Traditional Ethernet Setups
Traditional Ethernet setups require separate power sources and data cables, increasing installation complexity and costs. They lack the ability to deliver power over the same cable, limiting deployment flexibility for devices like IP cameras and wireless access points. This separation often results in more extensive infrastructure and higher maintenance requirements compared to Power over Ethernet (PoE) solutions.
Use Cases: When to Choose PoE or Traditional Ethernet
PoE (Power over Ethernet) is ideal for deploying devices like IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless access points where simultaneous power and data delivery simplify installations and reduce cabling costs. Traditional Ethernet is preferred in high-bandwidth applications such as data centers or enterprise networks where power delivery is managed separately and maximum network performance is critical. Choosing PoE or traditional Ethernet depends on device power needs, infrastructure complexity, and scalability requirements in the specific technology environment.
Installation and Infrastructure Requirements
PoE (Power over Ethernet) simplifies installation by combining data and power transmission over a single Ethernet cable, reducing the need for separate electrical wiring and outlets. Traditional Ethernet requires dedicated power sources for connected devices, increasing the complexity and cost of infrastructure setup. PoE also minimizes cable clutter and supports easier scalability in IP camera, VoIP phone, and wireless access point deployments.
Cost Comparison: PoE vs Traditional Ethernet
PoE (Power over Ethernet) reduces installation costs by eliminating the need for separate power cables, lowering material and labor expenses compared to Traditional Ethernet setups. Traditional Ethernet requires additional electrical wiring and outlets, increasing overall infrastructure costs and complexity. Over time, PoE systems deliver significant savings in maintenance and energy efficiency, making them a cost-effective choice for modern network deployments.
Security and Reliability Considerations
Power over Ethernet (PoE) enhances security by minimizing potential vulnerabilities through centralized power management and reduced cabling, lowering physical tampering risks. Traditional Ethernet relies on separate power sources, which can introduce points of failure and increase susceptibility to power interruptions, impacting reliability. PoE ensures consistent network uptime and simplifies secure device deployment by integrating data and power delivery over a single Ethernet cable.
Future Trends in Ethernet Technology
Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology is rapidly evolving with advancements like higher power delivery standards such as PoE++ and the integration of intelligent power management systems, positioning it as the future backbone for smart buildings and IoT ecosystems. Traditional Ethernet continues to improve in speed and efficiency, with developments like 400GbE and greater adoption of optical fiber infrastructure enhancing data transmission capabilities. Emerging trends include seamless convergence of data, power, and control signals over a single Ethernet cable, driving innovations in automation, security, and edge computing within enterprise and industrial networks.
PoE vs Traditional Ethernet Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com