OAuth and SAML serve distinct purposes in digital authentication, with OAuth primarily designed for authorization, enabling secure delegated access to resources without sharing credentials. SAML, on the other hand, focuses on single sign-on (SSO) in enterprise environments, allowing identity providers to pass authorization credentials to service providers seamlessly. Understanding these protocols helps businesses enhance security and streamline user access across various applications and services.
Table of Comparison
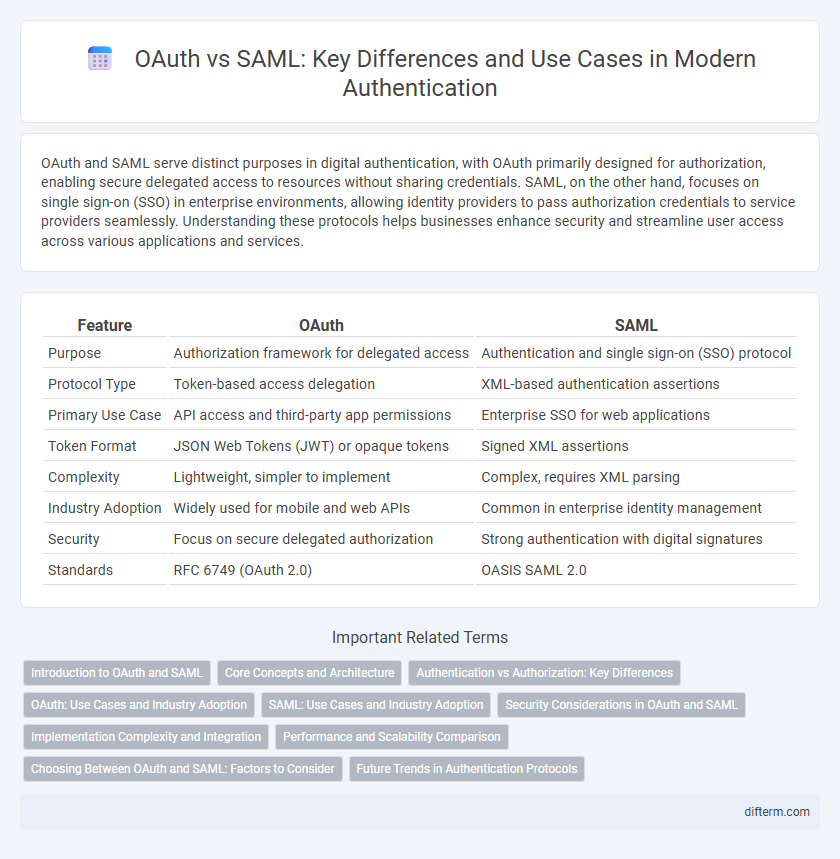
| Feature | OAuth | SAML |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Authorization framework for delegated access | Authentication and single sign-on (SSO) protocol |
| Protocol Type | Token-based access delegation | XML-based authentication assertions |
| Primary Use Case | API access and third-party app permissions | Enterprise SSO for web applications |
| Token Format | JSON Web Tokens (JWT) or opaque tokens | Signed XML assertions |
| Complexity | Lightweight, simpler to implement | Complex, requires XML parsing |
| Industry Adoption | Widely used for mobile and web APIs | Common in enterprise identity management |
| Security | Focus on secure delegated authorization | Strong authentication with digital signatures |
| Standards | RFC 6749 (OAuth 2.0) | OASIS SAML 2.0 |
Introduction to OAuth and SAML
OAuth is an open standard for access delegation commonly used to grant websites or applications limited access to user information without exposing credentials, primarily designed for authorization. SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) is an XML-based framework used for exchanging authentication and authorization data between parties, typically employed for single sign-on (SSO) in enterprise environments. Both protocols enhance security in identity management but serve distinct purposes: OAuth focuses on authorization, while SAML emphasizes authentication.
Core Concepts and Architecture
OAuth is an open standard for access delegation primarily used to grant third-party applications limited access to user resources without exposing credentials, utilizing tokens such as access tokens and refresh tokens within a RESTful architecture. SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) is an XML-based framework for exchanging authentication and authorization data between identity providers and service providers, leveraging assertions for single sign-on (SSO) in enterprise environments. OAuth focuses on authorization with resource owner consent, while SAML emphasizes authentication and identity federation through secure assertion statements.
Authentication vs Authorization: Key Differences
OAuth primarily handles authorization by granting third-party applications limited access to user resources without sharing credentials, while SAML focuses on authentication by enabling single sign-on (SSO) through the exchange of security assertions between identity providers and service providers. OAuth issues access tokens to define and manage user permissions, whereas SAML authenticates users via XML-based assertions to establish identity trust. Understanding these core differences helps organizations choose the appropriate protocol based on whether identity verification or delegated access control is the priority.
OAuth: Use Cases and Industry Adoption
OAuth is widely adopted for secure API authorization, enabling third-party applications to access user data without exposing credentials. Prominent use cases include social media platforms, cloud services, and mobile apps where seamless user authentication and delegated access are critical. Major technology firms like Google, Microsoft, and Facebook leverage OAuth protocols to enhance security and user experience across their platforms.
SAML: Use Cases and Industry Adoption
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) is widely adopted in enterprise environments for Single Sign-On (SSO) applications, particularly in sectors like healthcare, finance, and government due to its robust security and interoperability with legacy systems. It enables secure exchange of authentication and authorization data between identity providers and service providers, making it ideal for organizations requiring strong access control and compliance. Major industry players such as Microsoft, Google, and Amazon Web Services support SAML, reinforcing its position as a trusted protocol for federated identity management.
Security Considerations in OAuth and SAML
OAuth employs token-based authentication with limited lifespan tokens, reducing exposure risk from credential theft, but it requires secure token management to prevent replay or interception attacks. SAML uses XML-based assertions with strong support for encryption and digital signatures, providing robust identity verification and protection against tampering or impersonation. Security considerations in OAuth focus on securing access tokens and scopes, while SAML emphasizes assertion integrity and trust between identity and service providers.
Implementation Complexity and Integration
OAuth involves simpler implementation with RESTful APIs and JSON, making it ideal for modern web and mobile applications requiring lightweight authorization. SAML, relying on XML schemas and SOAP-based protocols, presents higher integration complexity but excels in enterprise environments demanding robust single sign-on and identity federation. Organizations prioritize OAuth for ease of integration with APIs, while SAML remains preferred for legacy systems and comprehensive security assertions.
Performance and Scalability Comparison
OAuth offers superior scalability due to its lightweight token-based authentication, enabling faster performance in distributed and cloud environments. SAML relies on XML-based assertions, which are more resource-intensive and can lead to increased latency in large-scale deployments. Enterprises prioritizing high throughput and responsive user access often prefer OAuth for its efficiency in handling numerous authentication requests concurrently.
Choosing Between OAuth and SAML: Factors to Consider
Choosing between OAuth and SAML depends on the authentication needs and use case scenarios; OAuth is ideal for delegated access in mobile and web applications, enabling secure authorization without sharing credentials. SAML suits enterprise environments requiring single sign-on (SSO) with robust identity federation between organizations. Consider factors like protocol complexity, token format, supported platforms, and integration requirements when deciding the best fit for secure authentication workflows.
Future Trends in Authentication Protocols
OAuth is evolving to support more granular permissions and decentralized identity management, enhancing security for API-driven ecosystems. SAML faces challenges adapting to mobile-first and cloud-native environments, prompting a gradual shift towards more flexible, token-based authentication methods. Future trends emphasize hybrid models combining OAuth's scalability with SAML's robust enterprise-grade security for seamless multi-factor and adaptive authentication experiences.
OAuth vs SAML Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com