GitOps streamlines application deployment by using Git repositories as the single source of truth for infrastructure and application code, enabling automated, version-controlled updates. DevOps combines development and operations teams to enhance collaboration, continuous integration, and continuous delivery processes, fostering faster software delivery. While DevOps emphasizes culture and processes, GitOps focuses on automation and declarative infrastructure through Git workflows.
Table of Comparison
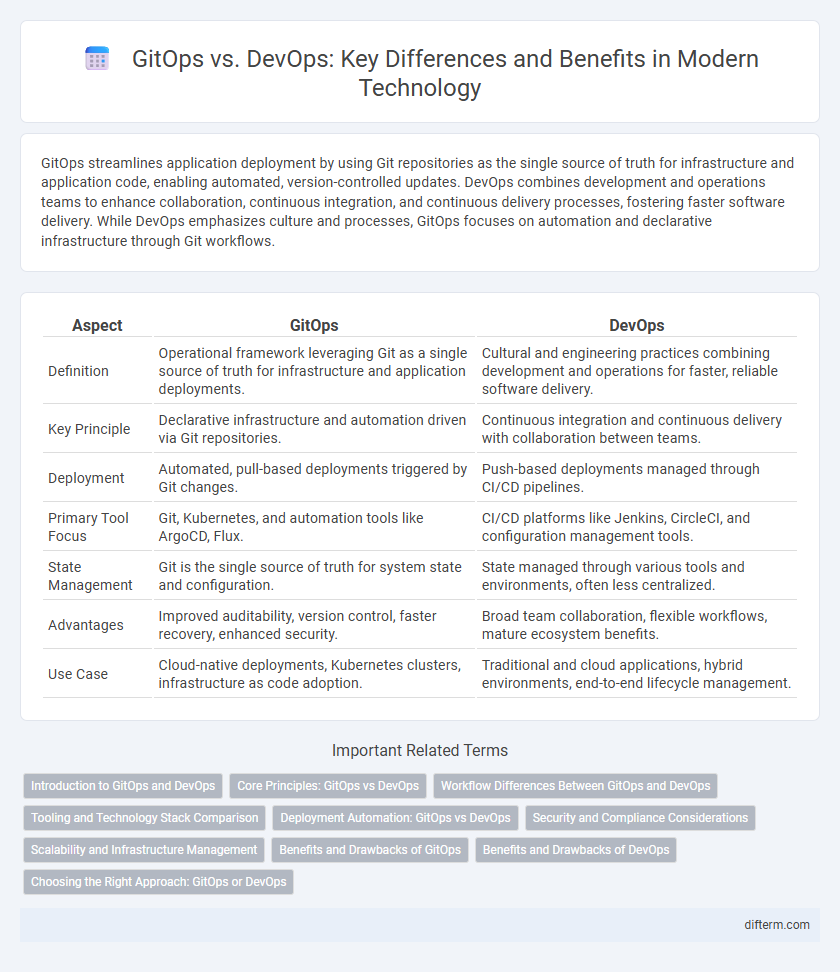
| Aspect | GitOps | DevOps |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Operational framework leveraging Git as a single source of truth for infrastructure and application deployments. | Cultural and engineering practices combining development and operations for faster, reliable software delivery. |
| Key Principle | Declarative infrastructure and automation driven via Git repositories. | Continuous integration and continuous delivery with collaboration between teams. |
| Deployment | Automated, pull-based deployments triggered by Git changes. | Push-based deployments managed through CI/CD pipelines. |
| Primary Tool Focus | Git, Kubernetes, and automation tools like ArgoCD, Flux. | CI/CD platforms like Jenkins, CircleCI, and configuration management tools. |
| State Management | Git is the single source of truth for system state and configuration. | State managed through various tools and environments, often less centralized. |
| Advantages | Improved auditability, version control, faster recovery, enhanced security. | Broad team collaboration, flexible workflows, mature ecosystem benefits. |
| Use Case | Cloud-native deployments, Kubernetes clusters, infrastructure as code adoption. | Traditional and cloud applications, hybrid environments, end-to-end lifecycle management. |
Introduction to GitOps and DevOps
GitOps is an operational framework that uses Git repositories as the single source of truth for declarative infrastructure and application deployment, enhancing automation and consistency in software delivery. DevOps combines software development and IT operations to shorten the development lifecycle while delivering high-quality software through continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. Both methodologies emphasize collaboration and automation, but GitOps leverages Git's version control advantages to improve transparency and rollback capabilities in cloud-native environments.
Core Principles: GitOps vs DevOps
GitOps centers on using Git as the single source of truth for declarative infrastructure and application state, enabling automated deployments and continuous reconciliation. DevOps emphasizes collaboration between development and operations teams to streamline software delivery through practices like continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD). Core principles of GitOps include version-controlled infrastructure, automated rollbacks, and enhanced observability, while DevOps prioritizes culture, automation, and monitoring across the software lifecycle.
Workflow Differences Between GitOps and DevOps
GitOps centers its workflow on declarative configurations stored in Git repositories, enabling automated deployment and continuous reconciliation through Kubernetes controllers. In contrast, DevOps encompasses a broader workflow integrating collaboration, continuous integration, and continuous delivery pipelines that may rely on various tools beyond Git. The GitOps workflow emphasizes version-controlled infrastructure automation, whereas DevOps workflows typically focus on cross-functional team practices and toolchain orchestration for software delivery.
Tooling and Technology Stack Comparison
GitOps relies heavily on Kubernetes-native tools such as Flux and Argo CD for continuous deployment, emphasizing declarative configuration and automation through Git repositories. DevOps employs a broader technology stack, including Jenkins, Ansible, and Terraform, supporting diverse environments and integrating various CI/CD pipelines, infrastructure as code, and configuration management tools. The GitOps approach streamlines operations with Git as a single source of truth, whereas DevOps tools offer flexibility across multiple platforms and technology stacks.
Deployment Automation: GitOps vs DevOps
Deployment automation in GitOps is driven by declarative infrastructure as code stored in Git repositories, enabling automatic synchronization between the desired state and actual cluster state through continuous reconciliation loops. DevOps deployment automation relies on scripted pipelines and CI/CD tools that manage deployments via imperative commands, often requiring manual intervention or additional orchestration for consistency. GitOps enhances deployment reliability and auditability by using version-controlled Git commits as the single source of truth, reducing configuration drift compared to traditional DevOps automation practices.
Security and Compliance Considerations
GitOps enhances security and compliance by enforcing declarative infrastructure through version-controlled Git repositories, ensuring auditable and immutable change histories. DevOps integrates continuous security practices but often relies on manual configurations, increasing risks of misconfigurations and compliance gaps. Automating policy enforcement and using Git as a single source of truth makes GitOps a robust approach for maintaining regulatory compliance and reducing security vulnerabilities.
Scalability and Infrastructure Management
GitOps enhances scalability by leveraging declarative configurations and automated workflows, enabling consistent infrastructure management across multiple environments. It simplifies infrastructure changes through version-controlled repositories, promoting rapid and reliable deployments. DevOps integrates continuous integration and delivery but can face complexities in scaling without unified infrastructure-as-code practices.
Benefits and Drawbacks of GitOps
GitOps offers enhanced deployment consistency and improved collaboration by leveraging Git as the single source of truth for infrastructure and application code, enabling automated and declarative continuous delivery. It reduces human error and accelerates rollback processes but may introduce complexity in managing multiple Git repositories and requires a steep learning curve for teams unfamiliar with Git workflows. In contrast, traditional DevOps practices provide flexibility and broader tool adoption but often lack the strict version control and automation governance that GitOps enforces.
Benefits and Drawbacks of DevOps
DevOps accelerates software delivery by fostering collaboration between development and operations teams, improving deployment frequency and reducing failure rates. However, the approach can introduce complexity due to toolchain integration challenges and requires a cultural shift that may face resistance within organizations. Despite these drawbacks, DevOps enhances continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) processes, making it essential for agile software development.
Choosing the Right Approach: GitOps or DevOps
Choosing the right approach between GitOps and DevOps hinges on organizational needs and infrastructure complexity. GitOps emphasizes declarative infrastructure and automated deployments through Git repositories, enhancing traceability and rollback capabilities. DevOps focuses on cultural collaboration and continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines, fostering faster development cycles and flexible operational practices.
GitOps vs DevOps Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com