Container image scanning analyzes container images for vulnerabilities before deployment, ensuring security at the build stage by detecting known flaws and compliance issues. Runtime scanning monitors containers during execution, identifying threats and anomalous behavior in real time to protect running applications from emerging risks. Combining image scanning and runtime scanning strengthens overall container security by preventing vulnerabilities early and actively defending against attacks in production environments.
Table of Comparison
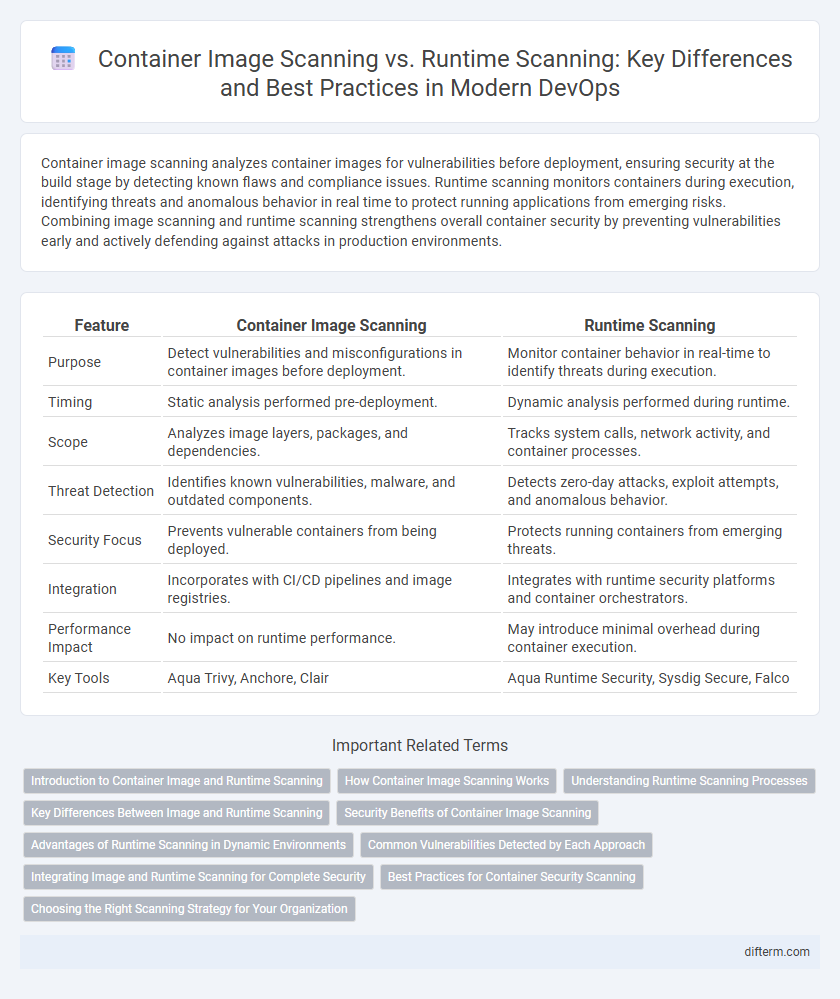
| Feature | Container Image Scanning | Runtime Scanning |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detect vulnerabilities and misconfigurations in container images before deployment. | Monitor container behavior in real-time to identify threats during execution. |
| Timing | Static analysis performed pre-deployment. | Dynamic analysis performed during runtime. |
| Scope | Analyzes image layers, packages, and dependencies. | Tracks system calls, network activity, and container processes. |
| Threat Detection | Identifies known vulnerabilities, malware, and outdated components. | Detects zero-day attacks, exploit attempts, and anomalous behavior. |
| Security Focus | Prevents vulnerable containers from being deployed. | Protects running containers from emerging threats. |
| Integration | Incorporates with CI/CD pipelines and image registries. | Integrates with runtime security platforms and container orchestrators. |
| Performance Impact | No impact on runtime performance. | May introduce minimal overhead during container execution. |
| Key Tools | Aqua Trivy, Anchore, Clair | Aqua Runtime Security, Sysdig Secure, Falco |
Introduction to Container Image and Runtime Scanning
Container image scanning analyzes the contents of container images before deployment, detecting vulnerabilities, malware, and configuration issues to ensure secure and compliant software releases. Runtime scanning continuously monitors running containers, identifying suspicious behaviors, unauthorized changes, and real-time threats that may bypass initial image scans. Combining both methods enhances container security by addressing risks at different stages of the software lifecycle.
How Container Image Scanning Works
Container image scanning works by analyzing the container image before deployment to detect vulnerabilities, malware, and misconfigurations within the software layers, libraries, and dependencies. It uses static analysis tools to compare the image's content against known vulnerability databases such as CVEs (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) and policy rules to ensure compliance with security standards. By identifying risks early in the software supply chain, container image scanning reduces the attack surface and prevents vulnerable containers from entering production environments.
Understanding Runtime Scanning Processes
Runtime scanning processes involve continuously monitoring containerized applications during execution to detect vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and anomalous behaviors in real-time. This dynamic approach complements container image scanning by identifying threats that manifest only at runtime, such as zero-day exploits and runtime privilege escalations. Effective runtime scanning leverages behavior analysis, system call monitoring, and integration with security orchestration tools to enhance container security posture throughout the application lifecycle.
Key Differences Between Image and Runtime Scanning
Container image scanning analyzes static container images for vulnerabilities before deployment, identifying outdated libraries, misconfigurations, and embedded secrets. Runtime scanning continuously monitors running containers to detect real-time threats, anomalous behavior, and zero-day exploits that manifest during execution. Image scanning ensures baseline security posture, while runtime scanning provides dynamic protection against evolving attacks in production environments.
Security Benefits of Container Image Scanning
Container image scanning enhances security by detecting vulnerabilities, malware, and misconfigurations before deployment, ensuring only safe images enter the production environment. It identifies outdated libraries and insecure dependencies within container images, reducing the attack surface and compliance risks. Early detection of security flaws in container images minimizes runtime threats and supports continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines with improved risk management.
Advantages of Runtime Scanning in Dynamic Environments
Runtime scanning offers real-time threat detection by monitoring container behavior dynamically, identifying vulnerabilities that static image scanning may miss. It provides enhanced protection against zero-day exploits and runtime attacks such as privilege escalation or in-memory exploits. This continuous security approach adapts to changing workloads and environment conditions, ensuring robust defense in dynamic cloud-native infrastructures.
Common Vulnerabilities Detected by Each Approach
Container image scanning primarily detects vulnerabilities such as outdated libraries, misconfigurations, and known CVEs (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) present in the static container image before deployment. Runtime scanning identifies risks including zero-day exploits, unauthorized process activity, and abnormal network connections by monitoring the container's behavior during execution. Combining both methods enhances security by covering both static vulnerabilities in the image and dynamic risks in live container environments.
Integrating Image and Runtime Scanning for Complete Security
Integrating container image scanning with runtime scanning provides a comprehensive security approach by addressing vulnerabilities both before deployment and during active operation. Image scanning analyzes container layers for known security flaws, misconfigurations, and compliance issues, ensuring a secure foundation, while runtime scanning continuously monitors container behavior for anomalous activity and zero-day threats. Combining these methods enhances threat detection accuracy, reduces risk exposure in dynamic environments, and supports DevSecOps practices through continuous, automated security validation.
Best Practices for Container Security Scanning
Container image scanning identifies vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and outdated packages within the container image before deployment, ensuring security compliance at the build stage. Runtime scanning monitors container behavior and system calls in real-time, detecting anomalies and threats that emerge during container execution. Best practices for container security scanning integrate both static image scanning and dynamic runtime analysis, continuously updating vulnerability databases and automating scans within CI/CD pipelines for proactive threat mitigation.
Choosing the Right Scanning Strategy for Your Organization
Container image scanning analyzes container images for vulnerabilities before deployment, ensuring security compliance and reducing risk from known exploits. Runtime scanning monitors running containers in real-time to detect unusual behavior or zero-day threats that static scans might miss. Choosing the right scanning strategy depends on your organization's risk tolerance, deployment frequency, and resource availability to balance proactive vulnerability management with dynamic threat detection.
Container image scanning vs Runtime scanning Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com