Blue-green deployment involves maintaining two identical production environments, where one serves live traffic while the other is updated and tested before switching roles. Canary deployment releases new features to a small subset of users, gradually increasing exposure to monitor performance and catch issues early. Both strategies minimize downtime and risk, but blue-green offers instant rollback while canary allows progressive validation.
Table of Comparison
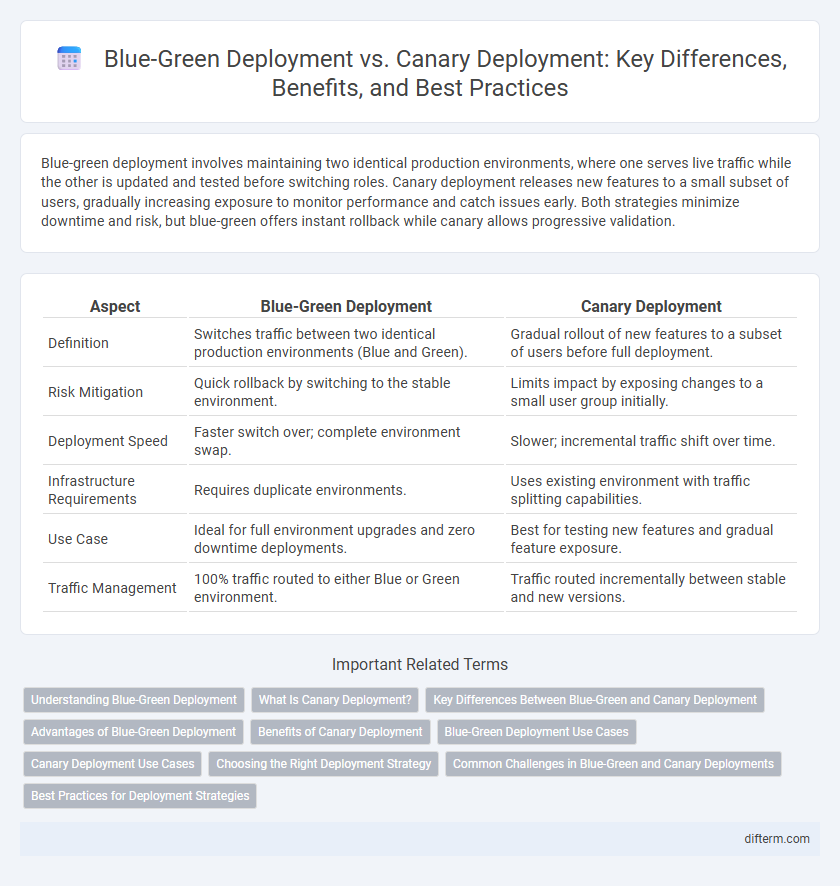
| Aspect | Blue-Green Deployment | Canary Deployment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Switches traffic between two identical production environments (Blue and Green). | Gradual rollout of new features to a subset of users before full deployment. |
| Risk Mitigation | Quick rollback by switching to the stable environment. | Limits impact by exposing changes to a small user group initially. |
| Deployment Speed | Faster switch over; complete environment swap. | Slower; incremental traffic shift over time. |
| Infrastructure Requirements | Requires duplicate environments. | Uses existing environment with traffic splitting capabilities. |
| Use Case | Ideal for full environment upgrades and zero downtime deployments. | Best for testing new features and gradual feature exposure. |
| Traffic Management | 100% traffic routed to either Blue or Green environment. | Traffic routed incrementally between stable and new versions. |
Understanding Blue-Green Deployment
Blue-green deployment is a release management strategy that reduces downtime and risk by running two identical production environments labeled blue and green. One environment serves all live production traffic while the other is updated with the new version, allowing seamless switching between versions. This method ensures quick rollback and minimal disruption during software updates.
What Is Canary Deployment?
Canary deployment is a software release strategy that gradually rolls out new features to a small subset of users before wider distribution, minimizing risk and allowing real-time monitoring of potential issues. This technique leverages automated testing, traffic routing, and real user feedback to ensure stability and performance in production environments. Compared to blue-green deployment, canary deployment provides more granular control over the release process and faster detection of defects.
Key Differences Between Blue-Green and Canary Deployment
Blue-green deployment involves running two identical production environments where one is active while the other is idle, allowing seamless traffic switching during releases, minimizing downtime. Canary deployment gradually releases new software to a small subset of users before full rollout, enabling real-time performance monitoring and risk mitigation. Key differences include the scope of user exposure, with blue-green switching all traffic at once versus canary's incremental user rollout, and the complexity of implementation, where blue-green requires duplicating environments while canary demands sophisticated traffic routing and monitoring tools.
Advantages of Blue-Green Deployment
Blue-green deployment minimizes downtime by running two identical production environments, enabling seamless switching between the current and new versions. This approach enhances rollback speed and reliability by isolating changes, reducing risk during updates. It simplifies infrastructure management and improves overall deployment safety in continuous delivery pipelines.
Benefits of Canary Deployment
Canary deployment offers precise risk mitigation by gradually releasing new software versions to a small subset of users, allowing early detection of issues without affecting the entire user base. It enables targeted performance monitoring and user feedback collection, facilitating quick rollback if problems arise. This technique supports continuous delivery by minimizing downtime and enhancing overall system stability.
Blue-Green Deployment Use Cases
Blue-green deployment is ideal for applications requiring zero downtime during updates, such as e-commerce platforms and financial services, where uninterrupted availability is critical. It allows seamless switchovers between identical environments, minimizing risk by enabling immediate rollback to the stable version if issues occur. This method is particularly effective in large-scale production systems and infrastructure-as-code environments where stability and rapid deployment are priorities.
Canary Deployment Use Cases
Canary deployment is ideal for testing new features with a small subset of users, minimizing risk by gradually rolling out changes while monitoring system performance and user feedback. This approach suits applications requiring real-time validation, such as e-commerce platforms and mobile apps, where quick rollback capabilities are crucial. It also supports continuous delivery pipelines by enabling incremental updates without disrupting the entire user base.
Choosing the Right Deployment Strategy
Selecting the appropriate deployment strategy depends on application complexity and risk tolerance; blue-green deployment offers seamless rollback through parallel environments, ideal for high-availability systems requiring minimal downtime. Canary deployment enables gradual feature rollout to a subset of users, facilitating real-time monitoring and risk mitigation for incremental updates. Evaluating traffic patterns, infrastructure costs, and team agility ensures optimal alignment between deployment strategy and business objectives.
Common Challenges in Blue-Green and Canary Deployments
Blue-green and canary deployments both face challenges in maintaining consistent database schema versions across environments, which can lead to data integrity issues. Monitoring and rollback complexities arise due to traffic splitting in canary deployments and environment switching in blue-green setups, increasing operational overhead. Ensuring seamless user experience while managing resource duplication in blue-green deployments and gradual exposure risks in canary strategies remains a significant hurdle.
Best Practices for Deployment Strategies
Blue-green deployment ensures zero-downtime by maintaining two identical production environments, allowing seamless traffic switching during updates. Canary deployment gradually releases new features to a subset of users, enabling real-time monitoring and minimizing risk from potential issues. Implementing robust monitoring, automated rollback mechanisms, and thorough testing are best practices to enhance reliability and user experience in both deployment strategies.
Blue-green deployment vs Canary deployment Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com