Blockchain relies on a decentralized ledger technology that records transactions in sequential blocks secured by cryptographic hashes, ensuring transparency and immutability. Hashgraph uses a directed acyclic graph (DAG) structure with a gossip protocol to achieve faster consensus, higher throughput, and reduced latency compared to traditional blockchain systems. While blockchain prioritizes security and widespread adoption, hashgraph focuses on scalability and efficiency for real-time applications.
Table of Comparison
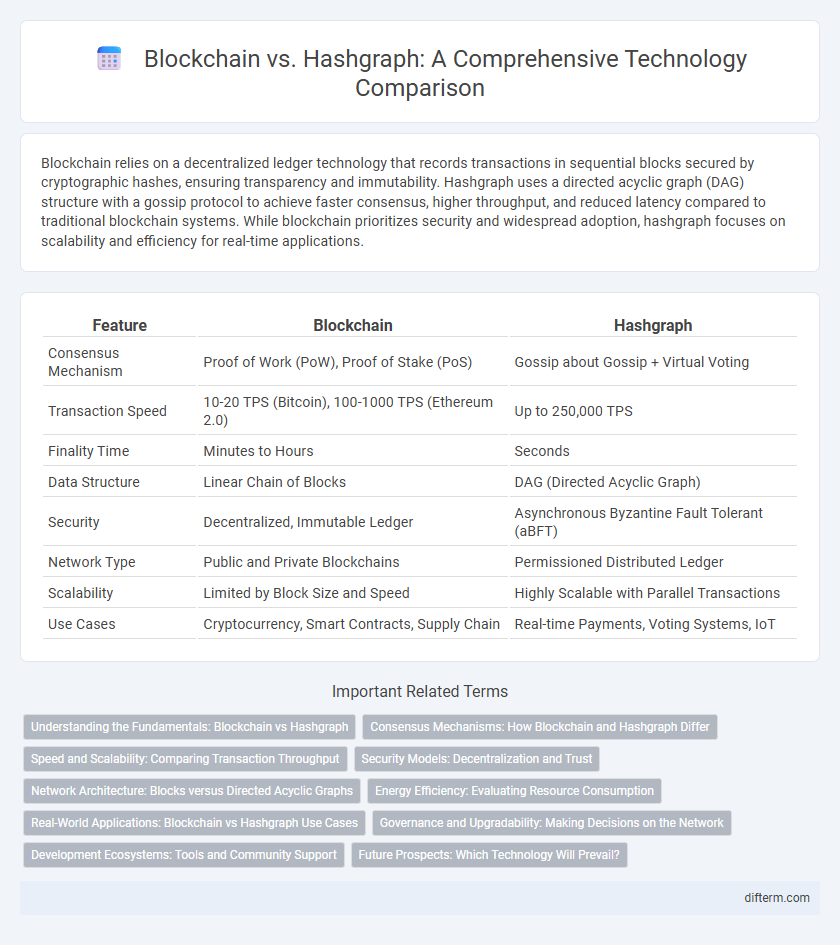
| Feature | Blockchain | Hashgraph |
|---|---|---|
| Consensus Mechanism | Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS) | Gossip about Gossip + Virtual Voting |
| Transaction Speed | 10-20 TPS (Bitcoin), 100-1000 TPS (Ethereum 2.0) | Up to 250,000 TPS |
| Finality Time | Minutes to Hours | Seconds |
| Data Structure | Linear Chain of Blocks | DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) |
| Security | Decentralized, Immutable Ledger | Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerant (aBFT) |
| Network Type | Public and Private Blockchains | Permissioned Distributed Ledger |
| Scalability | Limited by Block Size and Speed | Highly Scalable with Parallel Transactions |
| Use Cases | Cryptocurrency, Smart Contracts, Supply Chain | Real-time Payments, Voting Systems, IoT |
Understanding the Fundamentals: Blockchain vs Hashgraph
Blockchain operates as a decentralized ledger using a chain of cryptographic blocks to ensure data integrity and transparency. Hashgraph employs a directed acyclic graph structure with a gossip protocol and virtual voting to achieve faster consensus and higher throughput. Both technologies prioritize security and decentralization, yet Hashgraph offers enhanced scalability and efficiency compared to traditional blockchain systems.
Consensus Mechanisms: How Blockchain and Hashgraph Differ
Blockchain relies on Proof of Work or Proof of Stake consensus mechanisms that validate transactions through mining or staking, ensuring security but often leading to slower transaction speeds. Hashgraph uses a Gossip about Gossip protocol combined with virtual voting to achieve asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance, allowing faster and more energy-efficient consensus. This fundamental difference results in Hashgraph offering higher throughput and lower latency compared to traditional Blockchain systems.
Speed and Scalability: Comparing Transaction Throughput
Blockchain technology typically processes between 5 to 20 transactions per second (TPS), constrained by its consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work. Hashgraph leverages a gossip protocol and virtual voting, enabling speeds of up to 250,000 TPS, significantly outperforming traditional blockchains. This vast difference in transaction throughput highlights Hashgraph's enhanced scalability for high-demand applications.
Security Models: Decentralization and Trust
Blockchain relies on a decentralized network of nodes to validate transactions through consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake, enhancing trust through transparency and immutability. Hashgraph employs a gossip protocol with virtual voting that enables fast, asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance, offering high security without the need for energy-intensive mining. Both systems prioritize decentralization, but Hashgraph's consensus model enables greater scalability and faster finality while maintaining robust security guarantees.
Network Architecture: Blocks versus Directed Acyclic Graphs
Blockchain employs a linear sequence of blocks linked cryptographically, ensuring immutability and transparency through its consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake. Hashgraph utilizes a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) structure, enabling asynchronous, parallel processing of transactions that increases throughput and reduces latency. The architectural distinction impacts scalability, data ordering, and fault tolerance, with DAG offering potential advantages in speed and efficiency over traditional blockchains.
Energy Efficiency: Evaluating Resource Consumption
Blockchain technology typically consumes significantly more energy due to its proof-of-work consensus mechanism, requiring extensive computational power for transaction validation. In contrast, Hashgraph utilizes a gossip-about-gossip protocol with virtual voting, drastically reducing energy consumption while maintaining high throughput and security. This efficient resource usage makes Hashgraph a more sustainable option for scalable decentralized applications.
Real-World Applications: Blockchain vs Hashgraph Use Cases
Blockchain dominates supply chain management by ensuring transparent product provenance and secure transaction ledgers across industries like pharmaceuticals and food. Hashgraph excels in high-frequency trading and real-time gaming applications due to its asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance and faster consensus mechanisms. Both technologies innovate digital identity verification and decentralized finance, with Hashgraph offering lower latency and Blockchain providing greater adoption and developer support.
Governance and Upgradability: Making Decisions on the Network
Blockchain governance typically relies on decentralized consensus mechanisms such as proof-of-work or proof-of-stake to validate proposed changes, often requiring majority agreement among network participants. Hashgraph employs a gossip-about-gossip protocol with virtual voting, enabling faster and more efficient decision-making processes while maintaining fairness through asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (aBFT). Upgradability in blockchain networks can be slower due to hard forks or community coordination challenges, whereas Hashgraph's governance model supports more seamless updates by leveraging its consensus algorithm's inherent efficiency and speed.
Development Ecosystems: Tools and Community Support
Blockchain development ecosystems benefit from extensive tooling such as Ethereum's Solidity, Truffle, and Web3.js, supported by a large global developer community fostering innovation. Hashgraph offers robust SDKs like Hedera Hashgraph's Java, JavaScript, and Go libraries, with a growing but smaller community focused on enterprise-grade applications. Both platforms provide powerful development resources, but Blockchain's mature ecosystem delivers broader third-party integrations and community-driven support.
Future Prospects: Which Technology Will Prevail?
Blockchain, established as the backbone of cryptocurrencies, offers a decentralized and secure ledger system with widespread adoption and extensive developer support. Hashgraph presents a faster, energy-efficient consensus algorithm using gossip protocols, promising higher scalability and lower latency for real-time applications. Future prospects indicate blockchain's dominance may persist in established financial sectors, while hashgraph could disrupt industries requiring rapid transaction finality and microtransactions, potentially leading to complementary coexistence rather than outright replacement.
Blockchain vs Hashgraph Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com