Bitmap images consist of pixels, making them ideal for rich, detailed photographs but prone to quality loss when scaled. Vector images use mathematical paths, ensuring crisp lines and scalability without degradation, perfect for logos and illustrations. Choosing between bitmap and vector depends on the need for resolution independence and the type of graphic content.
Table of Comparison
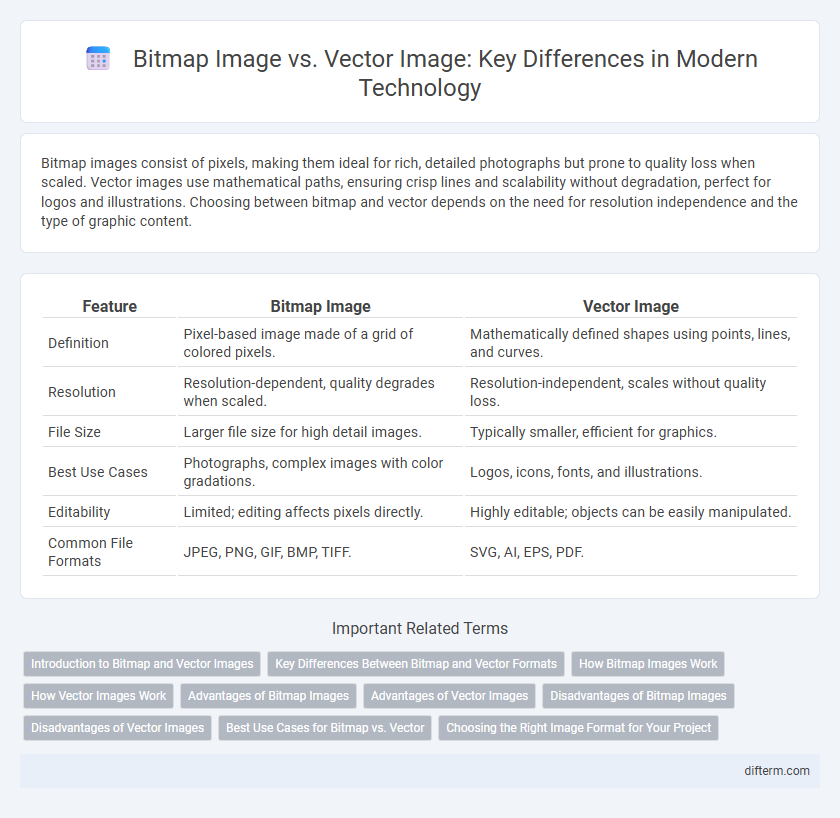
| Feature | Bitmap Image | Vector Image |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pixel-based image made of a grid of colored pixels. | Mathematically defined shapes using points, lines, and curves. |
| Resolution | Resolution-dependent, quality degrades when scaled. | Resolution-independent, scales without quality loss. |
| File Size | Larger file size for high detail images. | Typically smaller, efficient for graphics. |
| Best Use Cases | Photographs, complex images with color gradations. | Logos, icons, fonts, and illustrations. |
| Editability | Limited; editing affects pixels directly. | Highly editable; objects can be easily manipulated. |
| Common File Formats | JPEG, PNG, GIF, BMP, TIFF. | SVG, AI, EPS, PDF. |
Introduction to Bitmap and Vector Images
Bitmap images consist of pixels arranged in a grid, each pixel representing a specific color, making them ideal for detailed photographs but prone to quality loss when scaled. Vector images use mathematical equations to create shapes and lines, allowing infinite scalability without losing clarity, making them perfect for logos and graphic designs. Understanding the differences between bitmap and vector formats is crucial for selecting the appropriate image type based on project requirements and output needs.
Key Differences Between Bitmap and Vector Formats
Bitmap images consist of pixels arranged in a grid, making them resolution-dependent and ideal for detailed, complex images like photographs. Vector images use mathematical equations and geometric shapes, enabling infinite scalability without loss of quality, which suits logos and illustrations. Bitmap formats include JPEG and PNG, while vector formats commonly include SVG and AI, highlighting distinct uses based on image clarity and resizing needs.
How Bitmap Images Work
Bitmap images consist of a grid of individual pixels, each storing color information, which collectively form a detailed image. The resolution of a bitmap image is fixed, meaning that scaling up can cause pixelation and loss of clarity. Common bitmap formats include JPEG, PNG, and GIF, which are widely used for photographs and complex digital artwork due to their rich color depth.
How Vector Images Work
Vector images work by using mathematical equations and geometric primitives such as points, lines, and shapes to create scalable graphics. This allows them to maintain crisp edges and quality regardless of resizing, making them ideal for logos, icons, and illustrations. Unlike bitmap images that rely on pixels, vector graphics store information as paths, enabling efficient file sizes and resolution independence.
Advantages of Bitmap Images
Bitmap images excel in displaying complex color variations and subtle gradients, making them ideal for detailed photographs and rich textures. Their pixel-based nature allows for precise editing at the pixel level, providing control over fine image details. Common file formats like JPEG, PNG, and GIF support bitmap images with widespread compatibility across digital platforms and software.
Advantages of Vector Images
Vector images offer significant advantages over bitmap images by maintaining crisp quality at any scaling level, ensuring perfect clarity for logos and illustrations across various display sizes. Their smaller file sizes result from storing mathematical formulas for shapes instead of pixel data, optimizing storage and load times. Vector graphics also allow easy editing and manipulation without loss of detail, making them ideal for design projects requiring frequent adjustments.
Disadvantages of Bitmap Images
Bitmap images suffer from significant quality loss when resized, leading to pixelation and blurriness due to fixed resolution. These files typically require larger storage space compared to vector images, resulting in slower loading times and increased bandwidth consumption. Furthermore, bitmap formats struggle with scalability and are less suitable for high-resolution displays or print media where sharp detail is critical.
Disadvantages of Vector Images
Vector images often struggle with rendering complex color gradients and detailed photographic elements, resulting in less realistic visuals compared to bitmap images. Their reliance on mathematical equations makes them incompatible with certain pixel-based editing tools, limiting flexibility in photo manipulation. File sizes can increase significantly when storing highly intricate vector designs, impacting storage and performance efficiency.
Best Use Cases for Bitmap vs. Vector
Bitmap images excel in detailed photo editing, digital painting, and complex color gradients, making them ideal for photographs and realistic artwork due to their pixel-based structure. Vector images are best suited for logos, icons, and scalable graphics that require infinite resizing without loss of quality, as they use mathematical paths rather than pixels. Choosing the appropriate format depends on the project's need for detail, scalability, and file size efficiency.
Choosing the Right Image Format for Your Project
Bitmap images consist of pixels, making them ideal for detailed photographs but prone to quality loss when scaled. Vector images use mathematical paths, ensuring crisp, scalable graphics perfect for logos and illustrations. Selecting the right format depends on project requirements: detailed photo realism favors bitmap, while scalability and clean lines demand vector graphics.
Bitmap image vs Vector image Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com