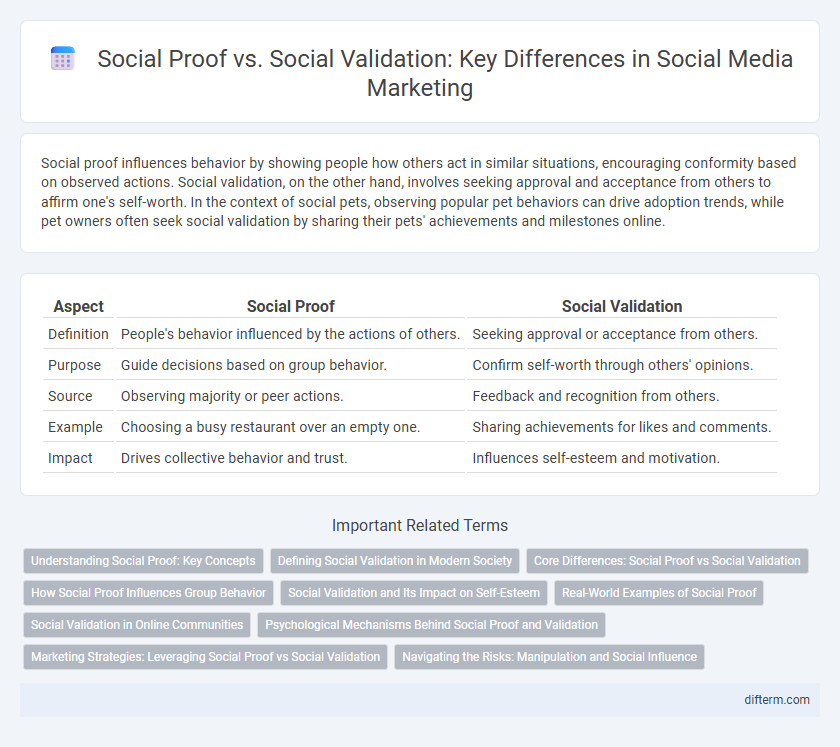
Social proof influences behavior by showing people how others act in similar situations, encouraging conformity based on observed actions. Social validation, on the other hand, involves seeking approval and acceptance from others to affirm one's self-worth. In the context of social pets, observing popular pet behaviors can drive adoption trends, while pet owners often seek social validation by sharing their pets' achievements and milestones online.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Social Proof | Social Validation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | People's behavior influenced by the actions of others. | Seeking approval or acceptance from others. |
| Purpose | Guide decisions based on group behavior. | Confirm self-worth through others' opinions. |
| Source | Observing majority or peer actions. | Feedback and recognition from others. |
| Example | Choosing a busy restaurant over an empty one. | Sharing achievements for likes and comments. |
| Impact | Drives collective behavior and trust. | Influences self-esteem and motivation. |
Understanding Social Proof: Key Concepts
Social proof is the psychological phenomenon where individuals mirror the actions of others to reflect correct behavior in ambiguous situations, often observed in consumer decisions and online reviews. It relies on perceived consensus and popularity, influencing trust and preference without direct personal validation. Understanding social proof involves recognizing its impact on decision-making through observable social cues, distinct from social validation, which centers on personal affirmation and acceptance by specific groups.
Defining Social Validation in Modern Society
Social validation in modern society refers to the psychological need to receive approval and acceptance from others to reinforce one's self-worth and social identity. It differs from social proof, which relies on the behavior of the majority as a guide for correctness, whereas social validation involves emotional and personal affirmation from peers or influential figures. This concept plays a critical role in shaping individual behavior, especially through social media platforms where likes, comments, and shares act as measurable indicators of acceptance and approval.
Core Differences: Social Proof vs Social Validation
Social proof refers to the influence people experience when observing others' actions, behaviors, or endorsements, often driving conformity and decision-making based on perceived popularity or correctness. Social validation centers on personal affirmation through acceptance, recognition, or approval from peers, emphasizing emotional validation and social belonging. The core difference lies in social proof being external behavior-driven evidence influencing choices, whereas social validation relates to internal emotional reassurance from social acceptance.
How Social Proof Influences Group Behavior
Social proof significantly shapes group behavior by encouraging individuals to mirror the actions and decisions of the majority, reinforcing collective norms. It operates through observable cues such as peer endorsements, ratings, and testimonials, which reduce uncertainty and foster conformity within social contexts. This phenomenon enhances trust and cohesion, driving group alignment and influencing decision-making processes.
Social Validation and Its Impact on Self-Esteem
Social validation significantly influences self-esteem by reinforcing an individual's sense of worth through external affirmation from peers, family, or social groups. Positive social validation activates neural pathways associated with reward and motivation, thereby enhancing confidence and emotional well-being. Chronic absence of social validation may contribute to feelings of insecurity and low self-esteem, highlighting its crucial role in psychological development.
Real-World Examples of Social Proof
Social proof influences behavior by showcasing real-world examples such as crowded restaurants, positive online reviews, and celebrity endorsements, which demonstrate how individuals rely on others' actions to guide their own decisions. Platforms like Amazon and Yelp leverage social proof through user ratings and testimonials to build trust and encourage purchases. Social validation, in contrast, involves personal acceptance and approval, often seen in peer recognition or social media likes, emphasizing individual social acceptance rather than collective influence.
Social Validation in Online Communities
Social validation in online communities plays a crucial role in shaping individual behavior by affirming members' beliefs and contributions through likes, comments, and shares. This reinforcement creates a sense of belonging and trust, enhancing engagement and loyalty within digital platforms. Unlike social proof, which relies on observing others' actions, social validation emphasizes personal recognition and acceptance from peers in virtual social environments.
Psychological Mechanisms Behind Social Proof and Validation
Social proof relies on the psychological mechanism of conformity, where individuals mimic the behavior of others to reduce uncertainty in decision-making. Social validation operates through self-affirmation and the need for acceptance, enhancing self-esteem by confirming one's choices or beliefs are socially approved. Both mechanisms leverage the brain's sensitivity to social cues, influencing behavior and perception in group dynamics.
Marketing Strategies: Leveraging Social Proof vs Social Validation
Marketing strategies leveraging social proof focus on showcasing user-generated content, reviews, and testimonials to build trust and influence potential customers. Social validation strategies emphasize aligning brand messaging with audience identity and values to enhance emotional connection and loyalty. Combining both approaches maximizes conversion rates by balancing credibility with personal relevance in consumer decision-making.
Navigating the Risks: Manipulation and Social Influence
Social proof and social validation often blur, but understanding their differences is crucial to navigate manipulation risks in social influence. Social proof relies on observed behaviors, while social validation depends on approval from others, making individuals vulnerable to inauthentic conformity and peer pressure. Recognizing these dynamics safeguards against deceptive tactics in marketing, online communities, and social media platforms.
social proof vs social validation Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com