Social norms are the unwritten rules guiding behavior within a community, while social values represent the deep-rooted beliefs driving those norms. In social pet interactions, norms dictate acceptable conduct like sharing toys or respecting space, whereas values emphasize care, trust, and companionship. Understanding the distinction enhances harmonious relationships between pets and their social environment.
Table of Comparison
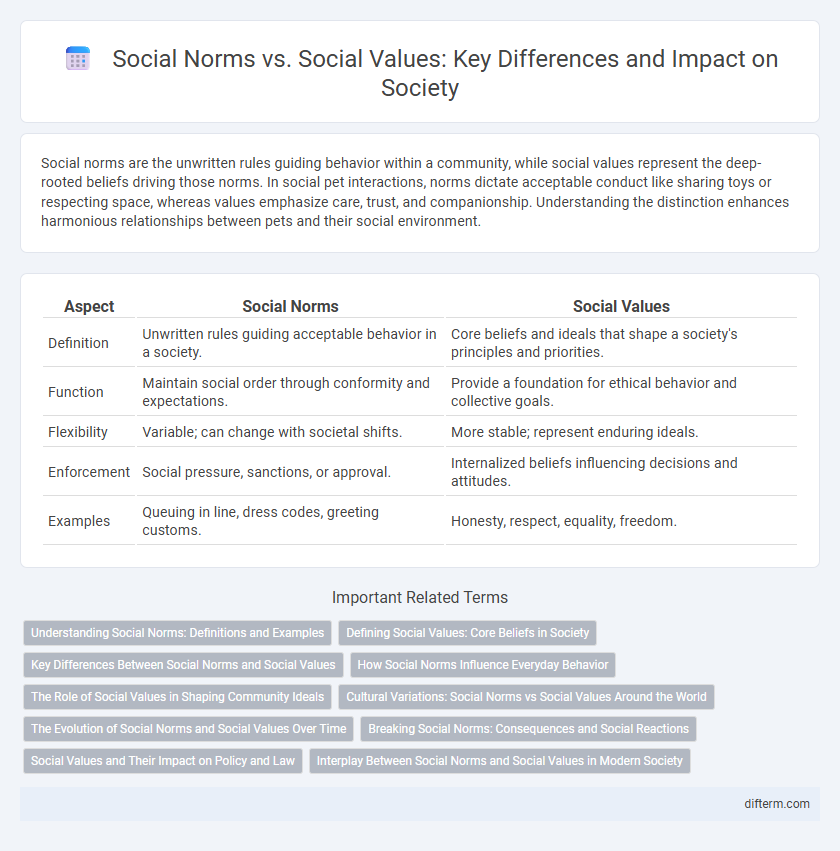
| Aspect | Social Norms | Social Values |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unwritten rules guiding acceptable behavior in a society. | Core beliefs and ideals that shape a society's principles and priorities. |
| Function | Maintain social order through conformity and expectations. | Provide a foundation for ethical behavior and collective goals. |
| Flexibility | Variable; can change with societal shifts. | More stable; represent enduring ideals. |
| Enforcement | Social pressure, sanctions, or approval. | Internalized beliefs influencing decisions and attitudes. |
| Examples | Queuing in line, dress codes, greeting customs. | Honesty, respect, equality, freedom. |
Understanding Social Norms: Definitions and Examples
Social norms are unwritten rules that govern behavior within a group, guiding what is considered acceptable or unacceptable conduct. Examples include customs like queuing in public spaces or polite greetings, reflecting collective expectations without formal enforcement. These norms differ from social values, which are core principles like honesty and respect that underpin societal beliefs and influence the creation of norms.
Defining Social Values: Core Beliefs in Society
Social values represent the fundamental beliefs and principles that guide behavior and judgment within a community, shaping what is considered morally important or desirable. These core beliefs influence social norms, which are the specific rules and expectations for behavior derived from the broader value system. Understanding social values is crucial for analyzing cultural identity, social cohesion, and the evolution of collective attitudes in society.
Key Differences Between Social Norms and Social Values
Social norms are unwritten rules guiding everyday behavior, while social values represent deeply held beliefs about what is important in a society. Norms regulate actions and maintain social order through external expectations, whereas values shape internal motivations and influence priorities across cultures. Understanding these distinctions helps clarify how societal behaviors and principles interact to form cohesive communities.
How Social Norms Influence Everyday Behavior
Social norms shape everyday behavior by establishing unwritten rules that guide acceptable actions within a community. These norms influence decisions ranging from communication styles to personal space, reinforcing conformity and social cohesion. Deviations from established norms often result in social sanctions, highlighting their role in maintaining order and predictability in daily interactions.
The Role of Social Values in Shaping Community Ideals
Social values serve as foundational beliefs that inform and guide the collective behavior within a community, significantly influencing the establishment of social norms. These values, such as respect, equality, and cooperation, create a shared vision of what is considered desirable and acceptable, thereby shaping community ideals and expectations. Through the reinforcement of social values, communities cultivate cohesive environments that foster mutual understanding and collective well-being.
Cultural Variations: Social Norms vs Social Values Around the World
Social norms vary significantly across cultures, reflecting specific behaviors and rules deemed acceptable within each society, while social values represent deeper, more enduring beliefs that shape those behaviors globally. For example, collectivist cultures emphasize social harmony and conformity as norms, guided by values such as community and interdependence, whereas individualist cultures prioritize personal freedom and self-expression, influencing different normative behaviors. Understanding these cultural variations is essential for navigating cross-cultural interactions and fostering mutual respect in a globalized world.
The Evolution of Social Norms and Social Values Over Time
Social norms and social values have continuously evolved, reflecting changes in cultural, economic, and technological contexts. Norms often adapt more rapidly through shifts in behaviors and practices, while values tend to change gradually, influenced by deeper societal reflection and collective experiences. Historical events, globalization, and digital communication have accelerated the transformation of both, reshaping expectations and moral priorities across generations.
Breaking Social Norms: Consequences and Social Reactions
Breaking social norms often triggers negative social reactions, including ostracism, criticism, and loss of reputation, as these norms guide acceptable behavior within a community. Social values underpin these norms, shaping perceptions of legitimacy and morality, which intensifies the consequences when norms are violated. Understanding this dynamic reveals how conformity preserves social cohesion and why deviance faces resistance within societies.
Social Values and Their Impact on Policy and Law
Social values serve as foundational principles shaping societal expectations, directly influencing the development and implementation of policies and laws that reflect collective ethical standards. Legal frameworks often embody social values such as justice, equality, and human rights, ensuring that laws promote fairness and social cohesion. The alignment between social values and policy outcomes fosters legitimacy and public trust in governance systems.
Interplay Between Social Norms and Social Values in Modern Society
Social norms and social values interact dynamically in modern society, shaping behaviors and collective expectations. Social values represent foundational beliefs such as equality and freedom, while social norms dictate acceptable actions aligned with these values. This interplay influences cultural evolution, policy-making, and individual identity formation.
social norms vs social values Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com