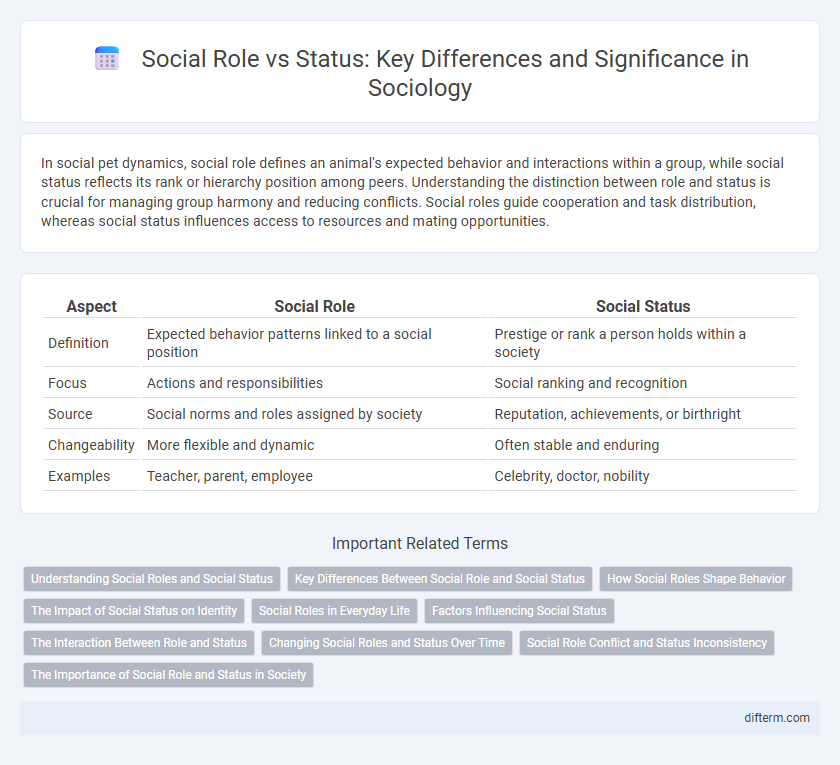
In social pet dynamics, social role defines an animal's expected behavior and interactions within a group, while social status reflects its rank or hierarchy position among peers. Understanding the distinction between role and status is crucial for managing group harmony and reducing conflicts. Social roles guide cooperation and task distribution, whereas social status influences access to resources and mating opportunities.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Social Role | Social Status |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expected behavior patterns linked to a social position | Prestige or rank a person holds within a society |
| Focus | Actions and responsibilities | Social ranking and recognition |
| Source | Social norms and roles assigned by society | Reputation, achievements, or birthright |
| Changeability | More flexible and dynamic | Often stable and enduring |
| Examples | Teacher, parent, employee | Celebrity, doctor, nobility |
Understanding Social Roles and Social Status
Social roles define expected behaviors and responsibilities associated with a particular position in a group, while social status reflects the relative prestige or rank an individual holds within a community. Understanding social roles helps clarify how people navigate interactions and fulfill societal functions, as these roles guide behavior in diverse social contexts. Social status influences access to resources and shapes interpersonal dynamics, making it a critical factor in examining social structure and individual identity.
Key Differences Between Social Role and Social Status
Social roles refer to the expected behaviors and responsibilities associated with a specific position within a social structure, while social status denotes the relative rank or prestige an individual holds in society. Social roles are dynamic and can change depending on the context, whereas social status is more fixed and reflects long-term social hierarchy. Understanding these distinctions highlights how social roles drive interaction patterns whereas social status influences access to resources and power.
How Social Roles Shape Behavior
Social roles act as behavioral blueprints that guide individuals' actions within specific contexts, influencing their decisions, interactions, and expectations. These roles are tied to societal norms and help maintain social order by promoting predictable behavior patterns. The fulfillment of social roles also reinforces one's social status, affecting both self-identity and external perceptions.
The Impact of Social Status on Identity
Social status significantly shapes individual identity by influencing self-perception and social interactions within various communities. Higher social status often correlates with increased access to resources, social capital, and opportunities, reinforcing a sense of belonging and self-worth. Identity formation is thus deeply intertwined with one's perceived status, affecting behavior, aspirations, and group dynamics.
Social Roles in Everyday Life
Social roles define expected behaviors and responsibilities associated with a particular status in everyday life. These roles guide interactions and help maintain social order by providing predictable patterns of conduct. Understanding social roles is essential for navigating complex social environments and fostering effective communication.
Factors Influencing Social Status
Social status is influenced by factors such as wealth, occupation, education, and family background, which collectively determine an individual's position within social hierarchies. Cultural norms and societal values play a crucial role in defining what attributes are considered prestigious or valuable, further shaping social roles. Interpersonal relationships and network connections also significantly impact social status by providing access to resources and opportunities.
The Interaction Between Role and Status
Social role and status interact dynamically within societal structures, where status provides a hierarchical position and role entails the expected behaviors associated with that position. The negotiation of social interactions depends on the alignment or conflict between an individual's role expectations and their status in the social hierarchy. Role strain or role conflict often arises when incompatible demands are placed on individuals, influenced by their varying statuses in different social contexts.
Changing Social Roles and Status Over Time
Social roles and status evolve significantly due to cultural shifts, technological advancements, and changing economic conditions. Individuals often experience role transitions as society redefines expectations, such as the increasing participation of women in leadership positions altering traditional gender roles. Status can fluctuate with these changes, reflecting new norms and values that reshape social hierarchies over time.
Social Role Conflict and Status Inconsistency
Social role conflict occurs when an individual faces incompatible demands from multiple social roles, generating stress and reducing role performance. Status inconsistency arises when a person's social positions have conflicting levels of prestige or power, leading to social tension and identity confusion. Both phenomena disrupt social cohesion by challenging individuals' expectations within social hierarchies and role sets.
The Importance of Social Role and Status in Society
Social role and status fundamentally shape individual behavior and societal expectations, guiding interactions within communities. Status, derived from factors like occupation, education, and cultural background, determines one's relative position and influence, while social roles define specific duties and norms associated with these positions. Understanding the interplay between social role and status enhances social cohesion and facilitates structured, functional relationships across diverse groups.
social role vs status Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com