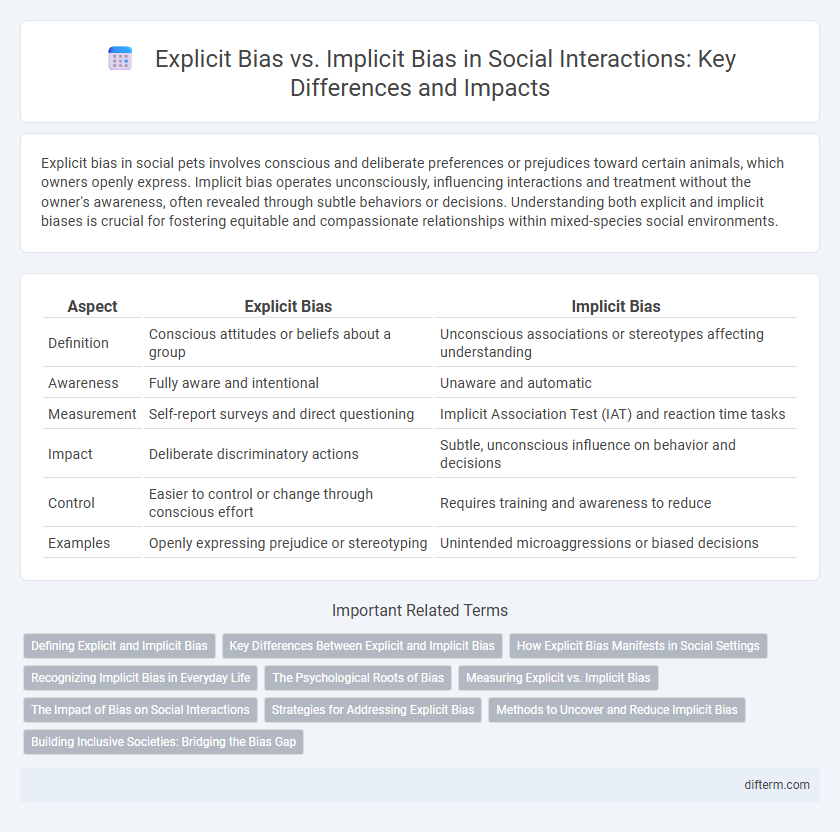
Explicit bias in social pets involves conscious and deliberate preferences or prejudices toward certain animals, which owners openly express. Implicit bias operates unconsciously, influencing interactions and treatment without the owner's awareness, often revealed through subtle behaviors or decisions. Understanding both explicit and implicit biases is crucial for fostering equitable and compassionate relationships within mixed-species social environments.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Explicit Bias | Implicit Bias |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Conscious attitudes or beliefs about a group | Unconscious associations or stereotypes affecting understanding |
| Awareness | Fully aware and intentional | Unaware and automatic |
| Measurement | Self-report surveys and direct questioning | Implicit Association Test (IAT) and reaction time tasks |
| Impact | Deliberate discriminatory actions | Subtle, unconscious influence on behavior and decisions |
| Control | Easier to control or change through conscious effort | Requires training and awareness to reduce |
| Examples | Openly expressing prejudice or stereotyping | Unintended microaggressions or biased decisions |
Defining Explicit and Implicit Bias
Explicit bias refers to the conscious attitudes and beliefs individuals hold about certain social groups, often expressed openly and deliberately. Implicit bias operates unconsciously, influencing perceptions and behaviors without intentional awareness or control. Understanding the distinction between explicit and implicit bias is crucial for addressing prejudice and promoting social equity.
Key Differences Between Explicit and Implicit Bias
Explicit bias involves conscious attitudes and beliefs that individuals are aware of and can intentionally express, often measured through self-report surveys. Implicit bias operates unconsciously, influencing behavior and decisions without awareness, typically assessed via implicit association tests (IAT). The key difference lies in awareness and control: explicit bias is deliberate and controllable, while implicit bias is automatic and often contradicts declared beliefs.
How Explicit Bias Manifests in Social Settings
Explicit bias manifests in social settings through overt actions and statements that reveal prejudiced attitudes, such as discriminatory language or exclusionary behaviors. People displaying explicit bias openly express stereotypes or negative judgments based on race, gender, or other social categories, often leading to direct marginalization. These behaviors can create hostile environments and reinforce social inequalities by signaling clear intolerance to affected individuals.
Recognizing Implicit Bias in Everyday Life
Implicit bias affects everyday decisions through unconscious attitudes and stereotypes that influence behavior without awareness. Recognizing implicit bias requires self-reflection, awareness of automatic judgments, and exposure to diverse perspectives to challenge ingrained assumptions. Tools like the Implicit Association Test (IAT) help individuals identify hidden biases and promote more equitable social interactions.
The Psychological Roots of Bias
The psychological roots of bias stem from cognitive shortcuts known as heuristics, which help the brain process vast amounts of information quickly but can lead to explicit and implicit biases. Explicit bias involves conscious attitudes and beliefs, whereas implicit bias operates subconsciously, influencing perceptions and behavior without conscious awareness. Both forms of bias originate in social categorization and in-group/out-group dynamics, deeply embedded in cognitive processes shaped by evolution and experience.
Measuring Explicit vs. Implicit Bias
Measuring explicit bias involves self-report surveys and questionnaires where individuals consciously acknowledge their attitudes or beliefs toward a group. Implicit bias is assessed through indirect methods like the Implicit Association Test (IAT), which reveals unconscious associations by analyzing reaction times in pairing concepts. Combining both measures provides a comprehensive understanding of bias, highlighting discrepancies between conscious attitudes and underlying automatic preferences.
The Impact of Bias on Social Interactions
Explicit bias involves conscious attitudes and beliefs that directly influence social interactions, leading to overt discrimination and prejudice. Implicit bias operates unconsciously, subtly affecting behavior and decisions, often reinforcing stereotypes without awareness. Both biases distort social perceptions, hinder trust-building, and contribute to inequitable treatment across diverse social groups.
Strategies for Addressing Explicit Bias
Explicit bias can be effectively addressed through targeted diversity training programs that promote awareness and accountability among individuals and organizations. Implementing clear anti-discrimination policies alongside regular bias assessments helps to identify and mitigate overt prejudices in workplace and social environments. Encouraging open dialogue and cultural competency education fosters a more inclusive atmosphere where explicit biases are recognized and actively challenged.
Methods to Uncover and Reduce Implicit Bias
Methods to uncover implicit bias include the Implicit Association Test (IAT), which measures automatic associations between concepts, and behavioral assessments analyzing decision-making patterns. Reducing implicit bias involves strategies like bias training programs, promoting diverse environments, and implementing structured decision-making processes to minimize subjective judgments. Continuous self-reflection and feedback loops enhance awareness and support long-term reduction of unconscious prejudices.
Building Inclusive Societies: Bridging the Bias Gap
Explicit bias involves conscious attitudes and beliefs that individuals openly express, while implicit bias operates subconsciously, influencing decisions without awareness. Building inclusive societies requires targeted interventions such as bias training and policy reforms that address both explicit prejudices and implicit stereotypes embedded in social structures. Bridging the bias gap fosters equitable opportunities and promotes diverse, harmonious communities where all members feel valued.
explicit bias vs implicit bias Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com