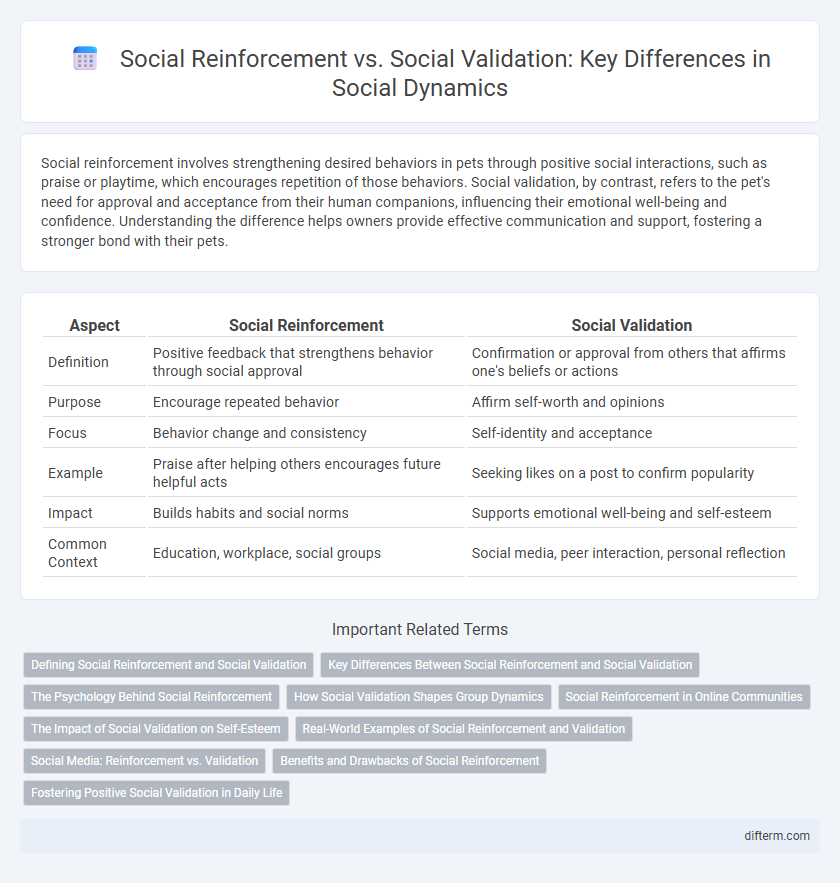
Social reinforcement involves strengthening desired behaviors in pets through positive social interactions, such as praise or playtime, which encourages repetition of those behaviors. Social validation, by contrast, refers to the pet's need for approval and acceptance from their human companions, influencing their emotional well-being and confidence. Understanding the difference helps owners provide effective communication and support, fostering a stronger bond with their pets.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Social Reinforcement | Social Validation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Positive feedback that strengthens behavior through social approval | Confirmation or approval from others that affirms one's beliefs or actions |
| Purpose | Encourage repeated behavior | Affirm self-worth and opinions |
| Focus | Behavior change and consistency | Self-identity and acceptance |
| Example | Praise after helping others encourages future helpful acts | Seeking likes on a post to confirm popularity |
| Impact | Builds habits and social norms | Supports emotional well-being and self-esteem |
| Common Context | Education, workplace, social groups | Social media, peer interaction, personal reflection |
Defining Social Reinforcement and Social Validation
Social reinforcement involves the process where behaviors are encouraged or increased through positive feedback, such as praise or rewards, fostering a sense of acceptance within a group. Social validation refers to the acknowledgment and affirmation individuals receive from others, confirming that their feelings, opinions, or actions are valued and understood. Both concepts play crucial roles in shaping social interactions and personal self-esteem in community and relationship dynamics.
Key Differences Between Social Reinforcement and Social Validation
Social reinforcement involves receiving positive feedback or rewards that encourage specific behaviors, whereas social validation centers on feeling accepted and acknowledged by a group. Reinforcement drives behavior modification through external stimuli, while validation addresses internal needs for belonging and self-worth. The key difference lies in reinforcement's focus on behavior change versus validation's emphasis on emotional and social acceptance.
The Psychology Behind Social Reinforcement
Social reinforcement stems from behavioral psychology, where positive feedback increases the likelihood of repeated actions by satisfying intrinsic needs for belonging and approval. It differs from social validation, which centers on external affirmation that shapes self-esteem and identity through comparison with others. The psychological mechanism behind social reinforcement involves dopamine release, strengthening neural pathways that encourage behaviors endorsed by social groups.
How Social Validation Shapes Group Dynamics
Social validation significantly influences group dynamics by reinforcing shared beliefs and behaviors, creating a sense of belonging and mutual acceptance among members. It drives individuals to conform to group norms to gain approval, which strengthens social bonds and promotes cohesion. This process can both stabilize group identity and limit diversity by discouraging dissenting opinions or alternative perspectives.
Social Reinforcement in Online Communities
Social reinforcement in online communities enhances user engagement by promoting positive behaviors through likes, comments, and shares, strengthening group cohesion and individual motivation. This mechanism relies on consistent feedback from peers, which encourages repeated participation and fosters a supportive environment. Effective social reinforcement directly contributes to the growth of vibrant, interactive digital spaces that sustain long-term user commitment.
The Impact of Social Validation on Self-Esteem
Social validation significantly influences self-esteem by providing external approval that individuals often interpret as a measure of their worth. Positive social validation from peers, family, or social media boosts confidence and reinforces a sense of belonging, while lack of validation can contribute to self-doubt and decreased self-esteem. Understanding the psychological mechanisms behind social validation offers critical insights into human motivation and the need for acceptance.
Real-World Examples of Social Reinforcement and Validation
Social reinforcement occurs when positive feedback, such as praise for teamwork on a project, encourages continued collaborative behavior in professional settings. Social validation is exemplified by individuals seeking approval through social media likes and comments to affirm their identity and choices. Community recognition programs, like employee of the month awards, integrate both social reinforcement and validation by rewarding desired behavior while acknowledging individual contributions.
Social Media: Reinforcement vs. Validation
Social media platforms often blur the lines between social reinforcement and social validation by rewarding users through likes, shares, and comments that reinforce certain behaviors and content styles. Social reinforcement fosters repeated engagement by encouraging conformity to group norms or popular trends, boosting dopamine responses linked to social approval. Social validation, however, primarily serves as an external confirmation of identity or worth, influencing self-esteem and perceived social status within virtual communities.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Social Reinforcement
Social reinforcement strengthens desired behaviors through positive feedback, increasing motivation and fostering a supportive environment. However, overreliance on social reinforcement may lead to dependency on external approval and undermine intrinsic motivation. Balancing social reinforcement with personal validation ensures sustainable behavior change and psychological well-being.
Fostering Positive Social Validation in Daily Life
Fostering positive social validation in daily life enhances self-esteem and strengthens interpersonal relationships by encouraging genuine recognition of individual efforts and qualities. Emphasizing authentic feedback over superficial praise creates a supportive environment that promotes emotional well-being and mutual respect. Consistent positive social validation contributes to building resilience and a meaningful sense of belonging within social groups.
social reinforcement vs social validation Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com