Social interaction in pets involves direct behaviors such as playing, grooming, or physical contact that foster companionship and bonding. Social communication refers to the exchange of signals like vocalizations, body language, and scent marking that convey emotions or intentions between animals. Understanding both aspects is essential for promoting healthy relationships and reducing stress in social pets.
Table of Comparison
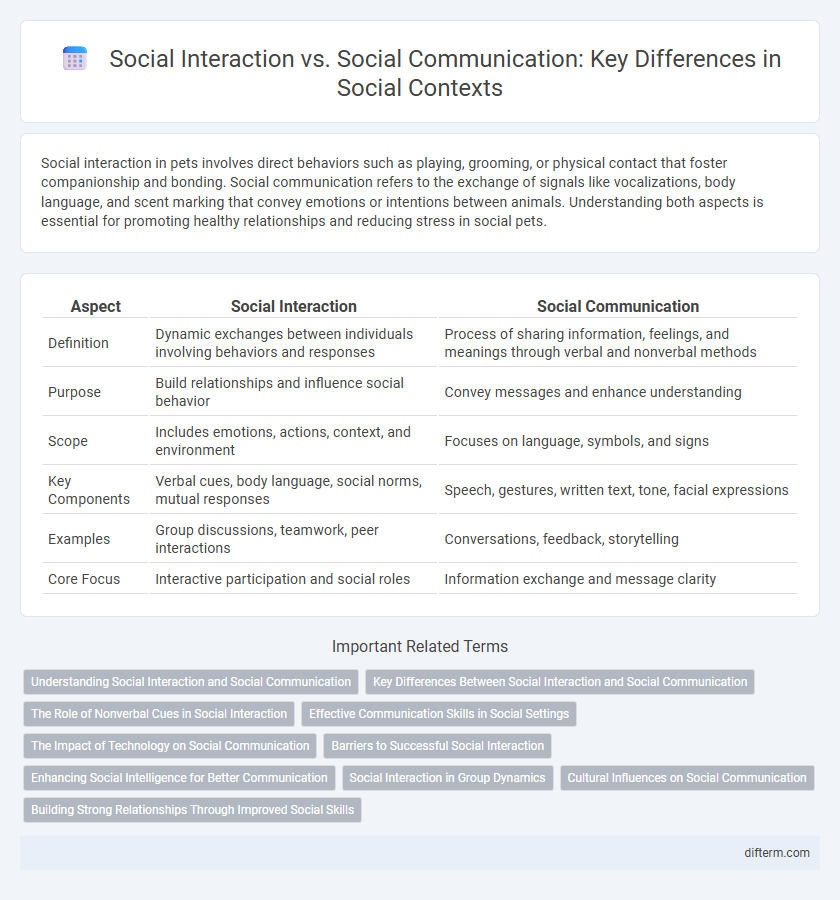
| Aspect | Social Interaction | Social Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dynamic exchanges between individuals involving behaviors and responses | Process of sharing information, feelings, and meanings through verbal and nonverbal methods |
| Purpose | Build relationships and influence social behavior | Convey messages and enhance understanding |
| Scope | Includes emotions, actions, context, and environment | Focuses on language, symbols, and signs |
| Key Components | Verbal cues, body language, social norms, mutual responses | Speech, gestures, written text, tone, facial expressions |
| Examples | Group discussions, teamwork, peer interactions | Conversations, feedback, storytelling |
| Core Focus | Interactive participation and social roles | Information exchange and message clarity |
Understanding Social Interaction and Social Communication
Understanding social interaction involves recognizing the dynamic, reciprocal exchange of behaviors and cues between individuals in various contexts, which shapes relationships and social norms. Social communication specifically refers to the use of verbal and non-verbal language skills to convey messages effectively and interpret others' intentions, emotions, and responses. Distinguishing between these concepts is crucial for developing social competence and improving interpersonal connections across diverse social environments.
Key Differences Between Social Interaction and Social Communication
Social interaction involves reciprocal actions between individuals, emphasizing behavioral exchanges like gestures, eye contact, and shared activities that build and maintain relationships. Social communication, however, focuses on the use of language, symbols, and nonverbal cues to convey messages, express emotions, and understand others' intents in various contexts. Key differences highlight that social interaction is broader, encompassing social behaviors, while social communication is specifically the process of information exchange within those interactions.
The Role of Nonverbal Cues in Social Interaction
Nonverbal cues such as facial expressions, body language, and eye contact play a crucial role in social interaction by conveying emotions and intentions beyond spoken words. These subtle signals enhance understanding and foster trust, often shaping the outcome of conversations in both personal and professional contexts. Effective interpretation of nonverbal communication improves empathy, social bonding, and conflict resolution.
Effective Communication Skills in Social Settings
Effective communication skills in social settings enhance meaningful interactions by combining verbal and nonverbal cues to convey emotions and intentions clearly. Mastering active listening, empathy, and clarity fosters stronger social bonds and reduces misunderstandings. These abilities are essential for building trust and facilitating collaboration in diverse social environments.
The Impact of Technology on Social Communication
Technology has transformed social communication by enabling instant, multimedia interactions across global networks, enhancing connectivity beyond traditional face-to-face social interaction boundaries. Digital platforms and social media facilitate diverse expressive modes, yet they can also reduce nonverbal cue transmission, affecting empathy and relationship depth. The evolving landscape of social communication integrates asynchronous messaging and real-time video calls, reshaping social dynamics and influencing communication effectiveness in personal and professional contexts.
Barriers to Successful Social Interaction
Barriers to successful social interaction often stem from miscommunication, differing social norms, and emotional misunderstandings. Social communication requires not only verbal expression but also nonverbal cues such as body language and tone, which can be easily misinterpreted or overlooked. Addressing these barriers involves enhancing active listening skills and fostering empathy to bridge gaps between individuals in diverse social contexts.
Enhancing Social Intelligence for Better Communication
Enhancing social intelligence involves improving the ability to understand and manage social interactions, which directly strengthens social communication skills. Effective social communication depends on recognizing social cues, interpreting emotional expressions, and adapting responses appropriately in diverse contexts. Developing these competencies leads to more meaningful connections, reduces misunderstandings, and fosters positive interpersonal relationships.
Social Interaction in Group Dynamics
Social interaction in group dynamics involves the patterns of behavior, roles, and communication exchanges that shape relationships and influence group cohesion. It encompasses nonverbal cues, shared norms, and collaborative problem-solving processes that drive collective decision-making and conflict resolution. Effective social interaction fosters trust, cooperation, and mutual understanding, essential for group performance and social identity formation.
Cultural Influences on Social Communication
Cultural influences play a crucial role in shaping social communication by determining the norms, values, and language styles used during interactions. Variations in nonverbal cues, such as eye contact, gestures, and personal space, reflect cultural differences in interpreting social messages. Understanding these cultural nuances enhances effective cross-cultural communication and reduces misunderstandings in diverse social settings.
Building Strong Relationships Through Improved Social Skills
Building strong relationships relies on mastering both social interaction and social communication, which encompass verbal and non-verbal cues essential for meaningful connections. Enhanced social skills promote empathy, active listening, and clear expression, fostering trust and mutual understanding in personal and professional settings. Prioritizing these competencies leads to deeper bonds and more effective collaboration across diverse social environments.
social interaction vs social communication Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com