Social welfare programs provide essential services and support to improve individuals' quality of life, addressing needs such as healthcare, education, and housing. Social security focuses on financial protection by offering income support through pensions, disability benefits, and unemployment insurance. Both systems aim to reduce poverty and promote social stability, yet social welfare emphasizes direct aid, while social security ensures economic safety nets.
Table of Comparison
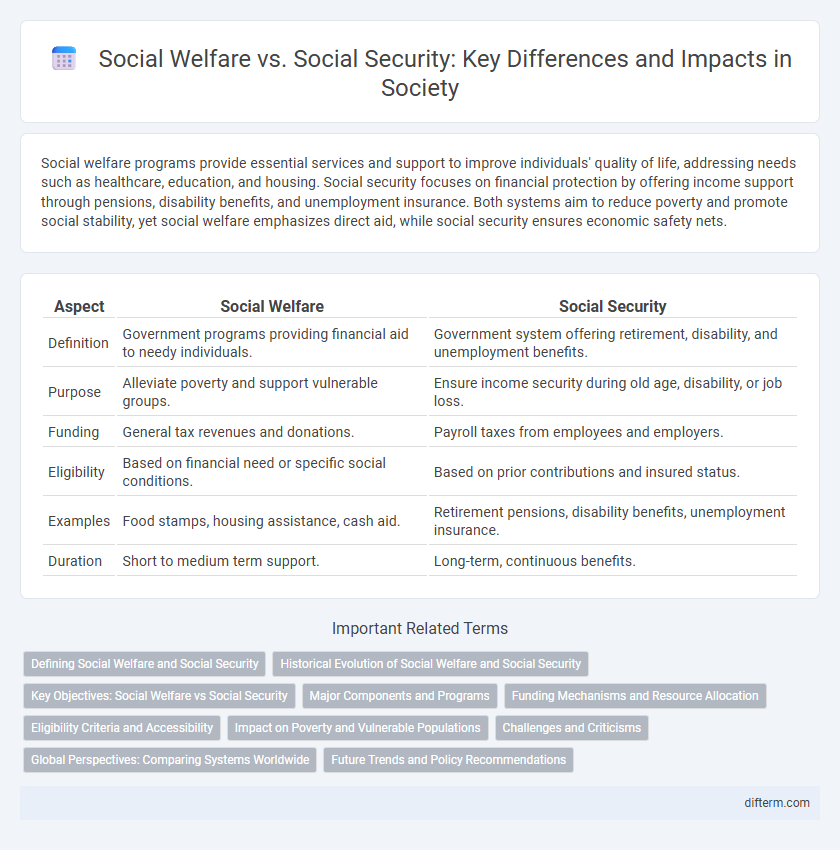
| Aspect | Social Welfare | Social Security |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government programs providing financial aid to needy individuals. | Government system offering retirement, disability, and unemployment benefits. |
| Purpose | Alleviate poverty and support vulnerable groups. | Ensure income security during old age, disability, or job loss. |
| Funding | General tax revenues and donations. | Payroll taxes from employees and employers. |
| Eligibility | Based on financial need or specific social conditions. | Based on prior contributions and insured status. |
| Examples | Food stamps, housing assistance, cash aid. | Retirement pensions, disability benefits, unemployment insurance. |
| Duration | Short to medium term support. | Long-term, continuous benefits. |
Defining Social Welfare and Social Security
Social welfare encompasses a broad range of government programs aimed at ensuring basic living standards, such as healthcare, education, housing, and income support for vulnerable populations. Social security specifically refers to government-managed financial programs providing retirement benefits, disability income, and survivor benefits to eligible workers and their families. While social welfare addresses overall quality of life, social security is designed to offer financial protection against life's uncertainties like old age, unemployment, and disability.
Historical Evolution of Social Welfare and Social Security
The historical evolution of social welfare and social security reveals distinct yet interconnected development paths; social welfare originated in charitable and community-based efforts addressing poverty and social needs, whereas social security emerged in the 20th century as government-administered programs designed to provide financial protection against life's risks such as unemployment, disability, and old age. Key milestones include Germany's introduction of the first social insurance system under Otto von Bismarck in the 1880s and the expansion of social welfare policies during the New Deal era in the United States, which laid the groundwork for modern social safety nets. The institutionalization of social security systems globally has transformed social welfare from voluntary aid to legally mandated rights ensuring economic security for vulnerable populations.
Key Objectives: Social Welfare vs Social Security
Social welfare aims to enhance general well-being by addressing social inequalities and providing support services such as healthcare, education, and housing. Social security primarily focuses on financial protection by offering income replacement through pensions, unemployment benefits, and disability allowances. Both systems collaborate to reduce poverty and improve quality of life, but social welfare emphasizes broad community support while social security targets individual economic stability.
Major Components and Programs
Social welfare encompasses a broad range of government programs aimed at improving quality of life, including cash assistance, healthcare services, and housing support. Social security specifically refers to federal programs like retirement benefits, disability insurance, and survivors' benefits administered by the Social Security Administration. Major components of social welfare include public assistance programs such as Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF) and the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), while social security programs primarily provide financial protection against risks related to aging, disability, and death.
Funding Mechanisms and Resource Allocation
Social welfare programs primarily rely on general taxation revenues and targeted governmental budgets, ensuring resources are allocated to vulnerable populations for basic needs and services. Social security systems are typically funded through payroll taxes or mandatory contributions from employers and employees, creating dedicated funds for retirement, disability, and unemployment benefits. Efficient resource allocation in social security aims to provide sustainable, long-term economic support, while social welfare focuses on immediate relief and community well-being.
Eligibility Criteria and Accessibility
Social welfare programs typically have broader eligibility criteria aimed at assisting low-income individuals and families, often based on income levels, family size, and specific social vulnerabilities. Social security benefits generally require insured status through prior employment contributions, with accessibility contingent on meeting age, disability, or survivor criteria. Accessibility to social welfare is usually more inclusive and immediate, while social security benefits depend on formal employment history and established legal qualifications.
Impact on Poverty and Vulnerable Populations
Social welfare programs provide direct assistance such as food aid, housing support, and healthcare services, significantly reducing poverty and enhancing the quality of life for vulnerable populations. Social security systems primarily offer financial stability through pensions and unemployment benefits, helping to prevent economic hardship among elderly, disabled, and unemployed individuals. Together, these mechanisms create a safety net that mitigates the risk of falling into poverty and supports social inclusion for marginalized groups.
Challenges and Criticisms
Social welfare programs often face challenges related to funding sustainability and effective targeting, leading to concerns about dependency and inefficiency. Social security systems encounter criticisms over demographic shifts, such as aging populations, which strain financial resources and question long-term viability. Both frameworks struggle with balancing immediate assistance needs and fostering economic self-sufficiency among beneficiaries.
Global Perspectives: Comparing Systems Worldwide
Social welfare and social security systems vary widely across countries, reflecting different economic structures and cultural values. Social welfare often encompasses broad support services like education, housing, and healthcare, while social security primarily provides income protection through pensions, unemployment benefits, and disability payments. Nordic countries such as Sweden and Denmark exemplify comprehensive social welfare models with robust social security nets, contrasting with the more targeted social security systems seen in countries like the United States and India.
Future Trends and Policy Recommendations
Emerging trends in social welfare emphasize integrating technology to enhance accessibility and personalized support, while social security systems increasingly focus on sustainability amid aging populations and economic uncertainties. Policy recommendations include adopting flexible benefit structures and expanding coverage to informal sectors to ensure inclusivity and resilience. Strengthening data-driven decision-making and fostering public-private partnerships will be critical for adapting social protection frameworks to future demographic and economic challenges.
social welfare vs social security Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com