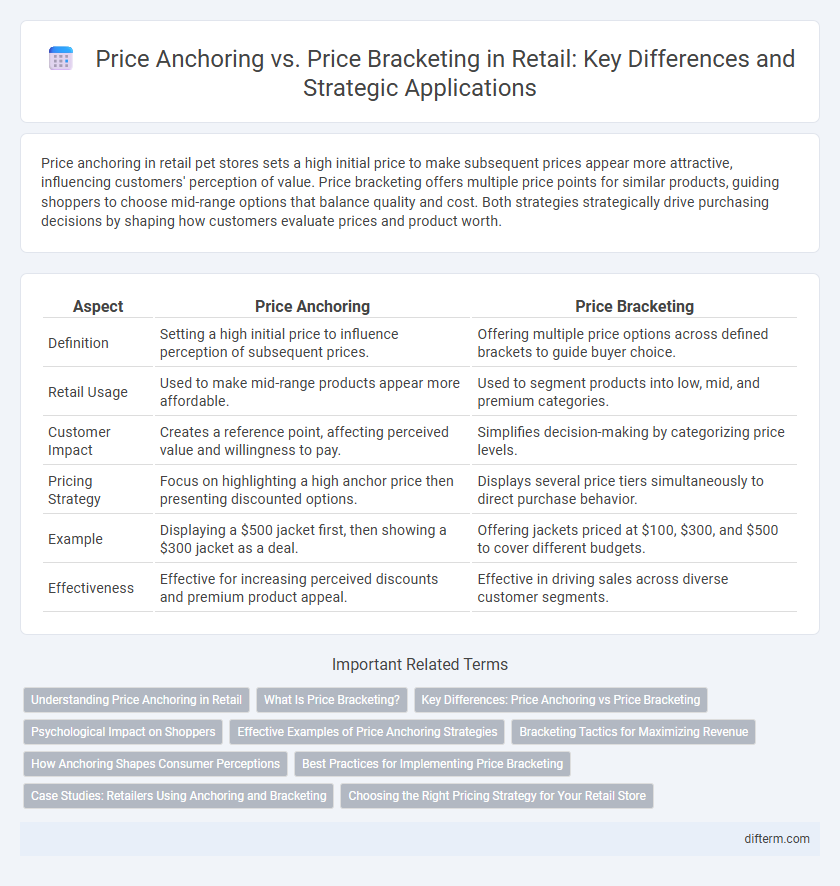
Price anchoring in retail pet stores sets a high initial price to make subsequent prices appear more attractive, influencing customers' perception of value. Price bracketing offers multiple price points for similar products, guiding shoppers to choose mid-range options that balance quality and cost. Both strategies strategically drive purchasing decisions by shaping how customers evaluate prices and product worth.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Price Anchoring | Price Bracketing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Setting a high initial price to influence perception of subsequent prices. | Offering multiple price options across defined brackets to guide buyer choice. |
| Retail Usage | Used to make mid-range products appear more affordable. | Used to segment products into low, mid, and premium categories. |
| Customer Impact | Creates a reference point, affecting perceived value and willingness to pay. | Simplifies decision-making by categorizing price levels. |
| Pricing Strategy | Focus on highlighting a high anchor price then presenting discounted options. | Displays several price tiers simultaneously to direct purchase behavior. |
| Example | Displaying a $500 jacket first, then showing a $300 jacket as a deal. | Offering jackets priced at $100, $300, and $500 to cover different budgets. |
| Effectiveness | Effective for increasing perceived discounts and premium product appeal. | Effective in driving sales across diverse customer segments. |
Understanding Price Anchoring in Retail
Price anchoring in retail involves setting a reference price to influence consumer perception of value, often by displaying a higher original price alongside a discounted offer. This psychological pricing strategy leverages customers' tendency to rely heavily on the first price they see, making the discounted price appear more attractive. Retailers use price anchoring to boost sales conversion rates and enhance perceived savings without lowering the actual product value.
What Is Price Bracketing?
Price bracketing is a retail pricing strategy that involves setting multiple price points within a product category to guide customer perception and encourage purchases. Unlike price anchoring, which highlights a single high-price option to make other prices appear more attractive, price bracketing offers a range of choices, helping shoppers compare and choose based on different value levels. This approach improves sales by catering to diverse budgets and enhancing the perceived value of mid-tier products.
Key Differences: Price Anchoring vs Price Bracketing
Price anchoring in retail involves establishing a reference price to influence customers' perception of value, often by displaying a higher original price next to the discounted price. Price bracketing presents multiple price points, guiding customers to choose from a range of options within defined spending limits, enhancing perceived control over purchase decisions. The key difference lies in anchoring relying on a singular comparative benchmark, while bracketing offers a spectrum of prices to frame buying choices.
Psychological Impact on Shoppers
Price anchoring influences shoppers by establishing a reference point that makes a product's price appear more reasonable when compared against higher-priced options. Price bracketing, on the other hand, leverages a range of prices to segment products into different value categories, guiding consumers to choose mid-tier options perceived as optimal compromises. Both strategies exploit cognitive biases to shape purchasing decisions, enhancing perceived value and increasing the likelihood of conversion.
Effective Examples of Price Anchoring Strategies
Price anchoring strategies in retail effectively influence consumer perception by presenting a high initial price, making subsequent offers appear more attractive and affordable. Examples include displaying a premium product alongside mid-tier options or showing the original price with a discounted tag, which anchors the consumer's expectation around the higher value. This technique contrasts with price bracketing, which narrows choices within set price ranges, whereas price anchoring leverages psychological reference points to drive purchasing decisions.
Bracketing Tactics for Maximizing Revenue
Price bracketing tactics in retail strategically present multiple product options at varied price points to guide customers toward higher-value purchases, effectively leveraging consumer psychology to maximize revenue. By framing prices within distinct brackets, retailers capitalize on perceived value differences, encouraging upselling and reducing price sensitivity. Implementing dynamic price brackets based on demand and customer segmentation further optimizes conversion rates and profitability.
How Anchoring Shapes Consumer Perceptions
Price anchoring sets a reference point that significantly influences consumer perception by making subsequent prices appear more or less reasonable based on the initial anchor. This cognitive bias directs shoppers to evaluate prices relative to the first figure they encounter, often leading to increased willingness to pay when the anchor is high. In contrast to price bracketing, which presents multiple price options to guide choice through comparison, anchoring powerfully shapes perceived value even before consumers consider alternative products.
Best Practices for Implementing Price Bracketing
Price bracketing enhances consumer decision-making by presenting products within strategically defined price ranges, encouraging higher-value purchases while reducing cognitive overload. Best practices for implementing price bracketing include segmenting products into clear, distinct price tiers, using visual cues to highlight value differences, and aligning brackets with customer willingness to pay based on behavioral data. Retailers should continuously analyze sales patterns and adjust brackets dynamically to optimize conversion rates and profit margins.
Case Studies: Retailers Using Anchoring and Bracketing
Retailers like Amazon effectively use price anchoring by displaying a higher original price alongside a discounted price, increasing perceived value and driving purchases. Target employs price bracketing by offering products in tiered price ranges, helping customers quickly identify options within their budget while encouraging upselling. Case studies reveal that combining anchoring and bracketing strategies enhances consumer decision-making and boosts overall sales performance.
Choosing the Right Pricing Strategy for Your Retail Store
Price anchoring leverages a high reference price to influence customer perception of value, making the actual selling price appear more attractive, while price bracketing presents multiple product options at different price points to segment customers and maximize sales. Choosing the right pricing strategy for your retail store involves analyzing customer demographics, competitor pricing, and product value to determine whether anchoring with premium items or bracketed pricing tiers better aligns with your sales goals. Both strategies can enhance perceived value and increase conversion rates when implemented based on thorough market insights.
price anchoring vs price bracketing Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com