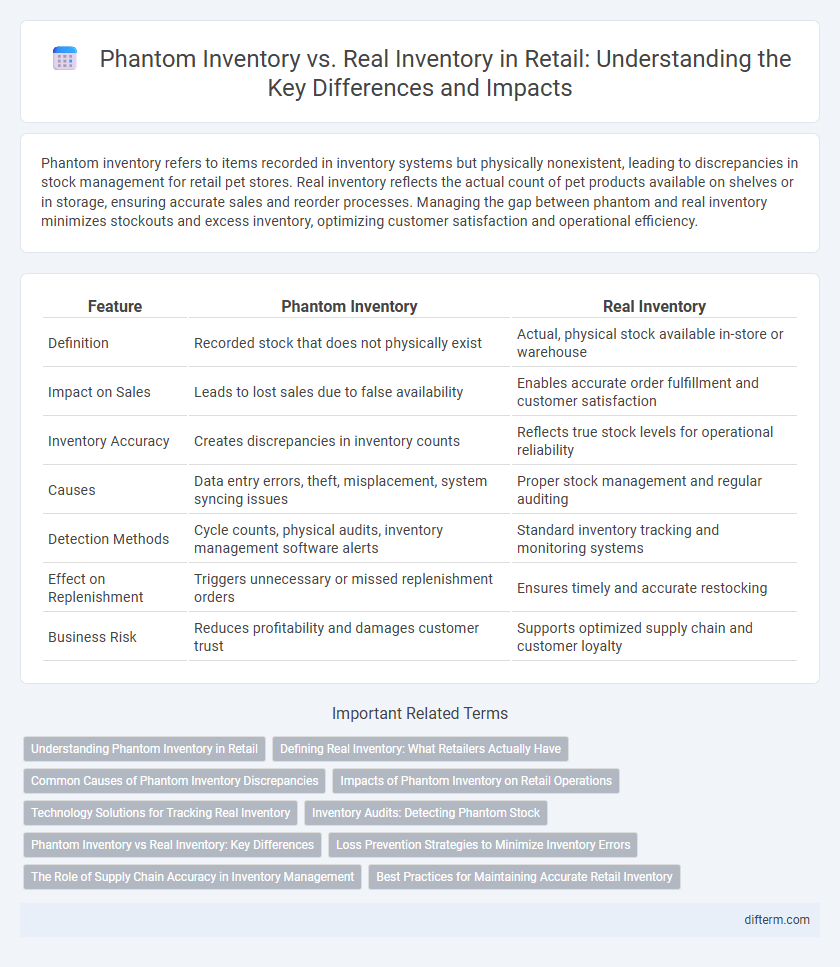
Phantom inventory refers to items recorded in inventory systems but physically nonexistent, leading to discrepancies in stock management for retail pet stores. Real inventory reflects the actual count of pet products available on shelves or in storage, ensuring accurate sales and reorder processes. Managing the gap between phantom and real inventory minimizes stockouts and excess inventory, optimizing customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Phantom Inventory | Real Inventory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recorded stock that does not physically exist | Actual, physical stock available in-store or warehouse |
| Impact on Sales | Leads to lost sales due to false availability | Enables accurate order fulfillment and customer satisfaction |
| Inventory Accuracy | Creates discrepancies in inventory counts | Reflects true stock levels for operational reliability |
| Causes | Data entry errors, theft, misplacement, system syncing issues | Proper stock management and regular auditing |
| Detection Methods | Cycle counts, physical audits, inventory management software alerts | Standard inventory tracking and monitoring systems |
| Effect on Replenishment | Triggers unnecessary or missed replenishment orders | Ensures timely and accurate restocking |
| Business Risk | Reduces profitability and damages customer trust | Supports optimized supply chain and customer loyalty |
Understanding Phantom Inventory in Retail
Phantom inventory refers to stock that appears in a retail system but is physically missing from the store, leading to discrepancies between recorded and actual inventory levels. This issue arises due to theft, misplacement, data entry errors, or unrecorded sales, and it significantly impacts inventory accuracy and sales forecasting. Understanding phantom inventory enables retailers to implement effective loss prevention strategies, improve inventory management, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Defining Real Inventory: What Retailers Actually Have
Real inventory refers to the accurate physical stock of products available on retail shelves or in storage, verified through periodic cycle counts or audits. Unlike phantom inventory, which is the discrepancy caused by errors in tracking systems or theft, real inventory represents what is genuinely accessible for sale. Retailers rely on real inventory data to optimize stock levels, reduce stockouts, and improve supply chain efficiency.
Common Causes of Phantom Inventory Discrepancies
Phantom inventory discrepancies in retail often arise from data entry errors, theft, and misplacement of products, leading to inaccurate stock levels. Supply chain disruptions and unrecorded sales transactions also contribute substantially to the gap between phantom inventory and real inventory. Regular physical audits and integration of advanced inventory management systems help minimize these issues by ensuring better data accuracy and visibility.
Impacts of Phantom Inventory on Retail Operations
Phantom inventory, representing stock that appears in system records but is physically absent, leads to inaccurate stock levels, causing overstocking or stockouts in retail operations. These discrepancies disrupt sales forecasts, customer service, and replenishment processes, resulting in lost revenue and diminished customer satisfaction. Retailers face increased operational costs and inefficient labor allocation while struggling to maintain inventory accuracy and supply chain reliability.
Technology Solutions for Tracking Real Inventory
Advanced technology solutions like RFID and IoT sensors significantly enhance tracking accuracy by providing real-time visibility into actual stock levels, reducing discrepancies caused by phantom inventory. Inventory management software integrated with machine learning algorithms can predict and identify inventory anomalies, facilitating timely corrections and improving supply chain efficiency. These technologies not only optimize stock accuracy but also minimize lost sales and overstocking risks in retail operations.
Inventory Audits: Detecting Phantom Stock
Inventory audits play a critical role in detecting phantom inventory, which refers to stock that appears in records but is physically absent. By comparing real inventory counts with system data, retailers identify discrepancies that expose hidden losses and inaccurate stock levels. Effective audit processes enhance inventory accuracy, reduce shrinkage, and improve demand forecasting.
Phantom Inventory vs Real Inventory: Key Differences
Phantom inventory refers to stock recorded in the system but physically absent, causing discrepancies between actual and reported assets. Real inventory represents the tangible products available for sale, accurately reflected in inventory management systems. Understanding the key differences between phantom and real inventory helps retailers minimize losses, optimize stock levels, and improve customer satisfaction.
Loss Prevention Strategies to Minimize Inventory Errors
Phantom inventory, which refers to stock recorded in the system but physically absent, poses significant challenges in retail loss prevention by leading to inaccurate stock counts and unnoticed shrinkage. Employing advanced inventory management software with real-time tracking, frequent cycle counts, and integrating RFID technology enhances visibility to detect discrepancies promptly. Training staff on precise data entry and implementing robust audit protocols further minimizes inventory errors, optimizing stock accuracy and reducing financial losses.
The Role of Supply Chain Accuracy in Inventory Management
Accurate supply chain data is critical in differentiating phantom inventory from real inventory, ensuring precise stock visibility and reducing costly stockouts or overstocks. Phantom inventory occurs when inventory records show stock that is physically unavailable, often due to errors in receiving, shipping, or inventory counts. Implementing advanced inventory tracking systems and real-time data synchronization improves supply chain accuracy, enabling retailers to optimize inventory management and enhance customer satisfaction.
Best Practices for Maintaining Accurate Retail Inventory
Regular cycle counting and integrating advanced RFID technology are essential best practices for maintaining accurate retail inventory, minimizing discrepancies between phantom inventory and real inventory. Implementing real-time inventory management systems ensures immediate updates on stock movement, reducing errors caused by theft, misplacement, or data entry mistakes. Consistent staff training on inventory handling and thorough reconciliation processes further enhance accuracy and prevent phantom stock from distorting financial and operational decisions.
Phantom Inventory vs Real Inventory Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com