Sell-through rate measures the percentage of inventory sold within a specific period, reflecting how quickly products move off shelves in retail pet stores. Turnover ratio indicates the number of times inventory is sold and replaced over a given timeframe, providing insight into overall inventory efficiency. Comparing these metrics helps pet retailers optimize stock levels, improve cash flow, and meet customer demand more effectively.
Table of Comparison
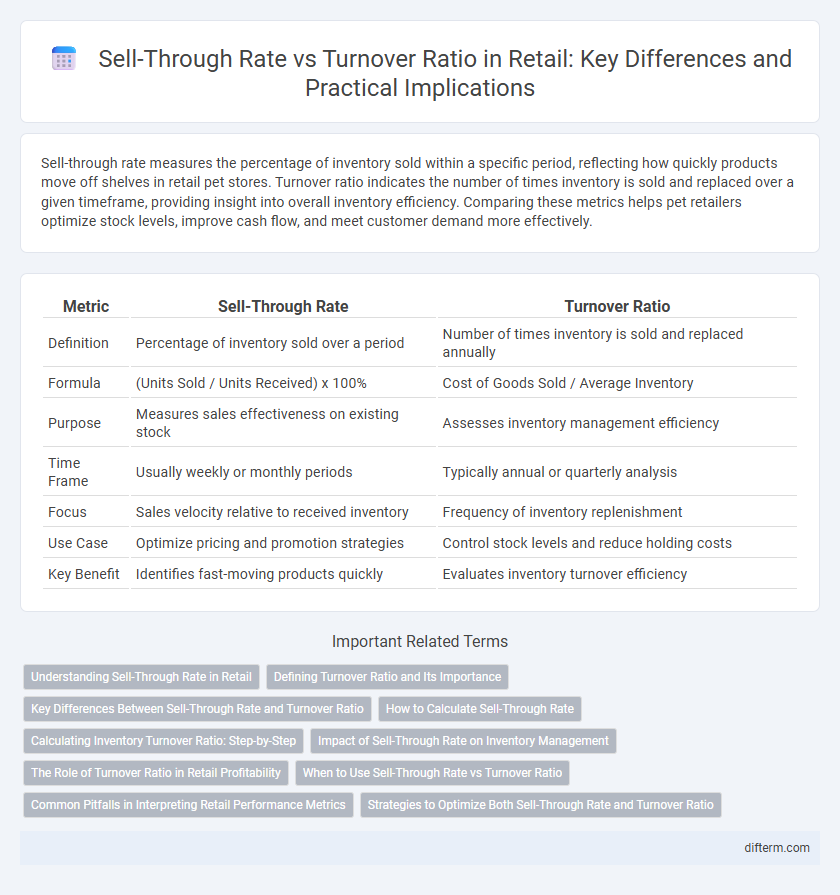
| Metric | Sell-Through Rate | Turnover Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Percentage of inventory sold over a period | Number of times inventory is sold and replaced annually |
| Formula | (Units Sold / Units Received) x 100% | Cost of Goods Sold / Average Inventory |
| Purpose | Measures sales effectiveness on existing stock | Assesses inventory management efficiency |
| Time Frame | Usually weekly or monthly periods | Typically annual or quarterly analysis |
| Focus | Sales velocity relative to received inventory | Frequency of inventory replenishment |
| Use Case | Optimize pricing and promotion strategies | Control stock levels and reduce holding costs |
| Key Benefit | Identifies fast-moving products quickly | Evaluates inventory turnover efficiency |
Understanding Sell-Through Rate in Retail
Sell-through rate in retail measures the percentage of inventory sold within a specific period, reflecting product demand and inventory efficiency. Unlike turnover ratio, which indicates how many times inventory is sold and replaced annually, sell-through rate provides immediate insights into product performance and sales velocity. Monitoring sell-through rates helps retailers optimize stock levels, reduce overstock, and improve cash flow management.
Defining Turnover Ratio and Its Importance
Turnover ratio in retail measures the frequency at which inventory is sold and replaced over a specific period, reflecting operational efficiency and inventory management effectiveness. A high turnover ratio indicates strong sales performance and optimized stock levels, reducing holding costs and minimizing obsolescence risks. Retailers use turnover ratio to gauge product demand, adjust purchasing strategies, and improve cash flow by ensuring stock aligns with consumer buying patterns.
Key Differences Between Sell-Through Rate and Turnover Ratio
Sell-through rate measures the percentage of inventory sold within a specific period, providing insight into product demand and sales effectiveness. Turnover ratio, or inventory turnover, calculates how many times inventory is sold and replaced over a period, indicating overall inventory management efficiency. The key difference lies in sell-through rate focusing on sales performance per product, while turnover ratio assesses the broader inventory cycle and stock replenishment speed.
How to Calculate Sell-Through Rate
Sell-through rate is calculated by dividing the quantity of units sold by the inventory received during a specific period, then multiplying the result by 100 to get a percentage. This metric helps retailers measure the effectiveness of their inventory management and product demand. Unlike turnover ratio, which assesses how often inventory is sold and replaced over a period, sell-through rate provides insight into product-specific sales performance.
Calculating Inventory Turnover Ratio: Step-by-Step
Calculating inventory turnover ratio involves dividing the cost of goods sold (COGS) by the average inventory value during a specific period, providing insight into how efficiently inventory is being managed. This metric helps retailers determine how many times inventory is sold and replaced over a timeframe, directly impacting cash flow and storage costs. Accurate calculation requires precise COGS data and consistent inventory valuation methods to optimize stock levels and improve sell-through rates.
Impact of Sell-Through Rate on Inventory Management
Sell-through rate directly impacts inventory management by indicating the percentage of stock sold within a specific period, allowing retailers to optimize reorder levels and reduce excess inventory. A high sell-through rate helps identify fast-moving products, minimizing holding costs and improving cash flow. Efficient management of sell-through rates prevents stockouts and overstock situations, enhancing overall retail profitability.
The Role of Turnover Ratio in Retail Profitability
The turnover ratio in retail measures how efficiently inventory is sold and replaced over a specific period, directly impacting profitability by reducing holding costs and minimizing stock obsolescence. A higher turnover ratio indicates strong product demand and effective inventory management, leading to increased cash flow and improved profit margins. Retailers with optimized turnover ratios can better align stock levels with consumer demand, enhancing overall operational efficiency and financial performance.
When to Use Sell-Through Rate vs Turnover Ratio
Sell-through rate is most effective for assessing product performance within a specific timeframe, helping retailers identify fast-moving items and optimize inventory levels. Turnover ratio provides insight into how efficiently overall inventory is cycled through a store or product category, aiding long-term inventory replenishment strategies. Use sell-through rate for short-term sales velocity analysis and turnover ratio for evaluating inventory management over extended periods.
Common Pitfalls in Interpreting Retail Performance Metrics
Misinterpreting sell-through rate and turnover ratio often leads to flawed retail performance insights due to their distinct measurement scopes; sell-through rate tracks the percentage of inventory sold over a specific period, while turnover ratio reflects the frequency of inventory replacement annually. Retailers frequently confuse high turnover with strong sales performance, ignoring factors such as stockouts or markdowns that can inflate these metrics. Accurate analysis requires contextualizing both metrics with inventory levels, sales velocity, and replenishment cycles to avoid misleading conclusions about product demand and operational efficiency.
Strategies to Optimize Both Sell-Through Rate and Turnover Ratio
Implement dynamic pricing strategies and targeted promotions to enhance the sell-through rate while maintaining optimal inventory levels to improve turnover ratio. Employ advanced demand forecasting tools and data analytics to align stock replenishment with consumer purchasing patterns, minimizing overstock and stockouts. Optimize product assortment and shelf placement to drive faster inventory turnover and higher sales efficiency in retail operations.
Sell-through rate vs Turnover ratio Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com