Dead stock in retail pet refers to products that have never sold and remain in inventory, tying up capital and storage space without generating revenue. Obsolete stock includes items that are no longer sellable due to expiration dates, changes in pet care trends, or updated formulations, making them a liability. Efficient inventory management and regular stock reviews help minimize both dead and obsolete stock, improving cash flow and customer satisfaction.
Table of Comparison
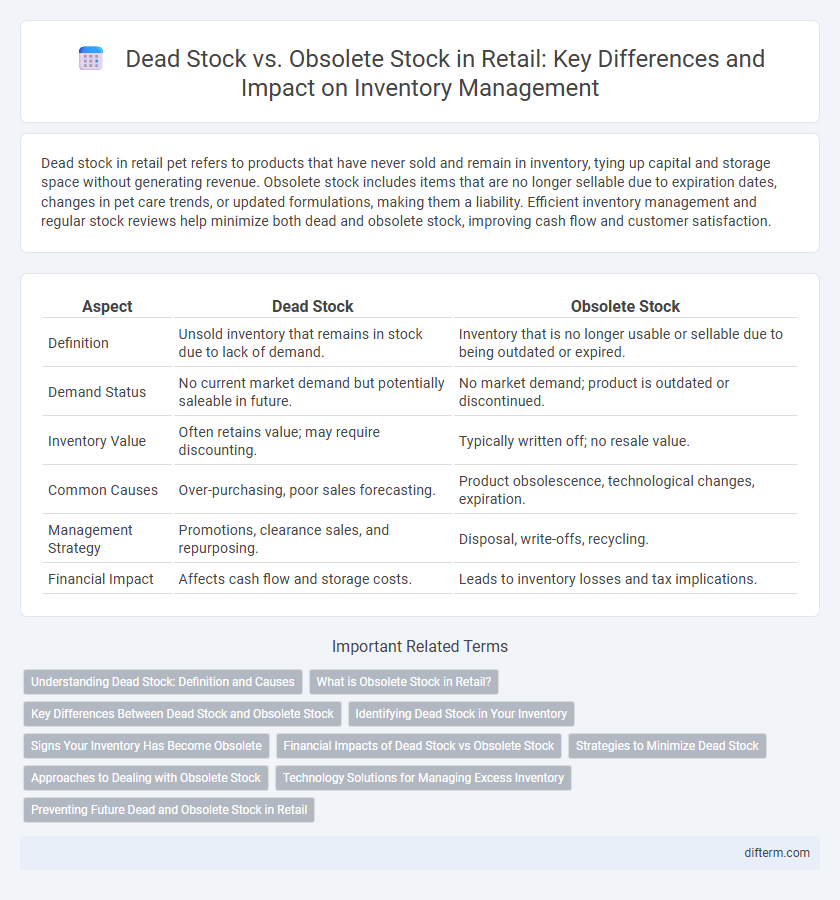
| Aspect | Dead Stock | Obsolete Stock |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unsold inventory that remains in stock due to lack of demand. | Inventory that is no longer usable or sellable due to being outdated or expired. |
| Demand Status | No current market demand but potentially saleable in future. | No market demand; product is outdated or discontinued. |
| Inventory Value | Often retains value; may require discounting. | Typically written off; no resale value. |
| Common Causes | Over-purchasing, poor sales forecasting. | Product obsolescence, technological changes, expiration. |
| Management Strategy | Promotions, clearance sales, and repurposing. | Disposal, write-offs, recycling. |
| Financial Impact | Affects cash flow and storage costs. | Leads to inventory losses and tax implications. |
Understanding Dead Stock: Definition and Causes
Dead stock refers to retail inventory that remains unsold and stagnant over an extended period, often due to changes in consumer preferences, seasonal fluctuations, or inaccurate demand forecasting. Causes of dead stock include over-purchasing, poor inventory management, and market saturation, leading to increased holding costs and reduced cash flow. Identifying dead stock early helps retailers optimize inventory turnover and minimize losses associated with obsolete or excess merchandise.
What is Obsolete Stock in Retail?
Obsolete stock in retail refers to inventory that is no longer sellable due to factors like changing consumer preferences, expired shelf life, or outdated product models. This type of stock ties up capital and occupies valuable storage space without generating revenue. Effective inventory management strategies are essential to minimize obsolete stock and reduce financial losses.
Key Differences Between Dead Stock and Obsolete Stock
Dead stock refers to inventory that has never been sold or used, often due to overproduction or lack of demand, while obsolete stock includes items that were once sellable but have become outdated or expired. Dead stock remains new but unsold, whereas obsolete stock loses value due to changes in market trends, technology, or product lifecycle. Efficient inventory management differentiates these types to optimize stock clearance strategies and minimize financial loss.
Identifying Dead Stock in Your Inventory
Identifying dead stock in your retail inventory involves analyzing sales data to pinpoint items with no movement over an extended period, typically six months or more. Utilize inventory management systems to track product turnover rates and flag slow-moving goods that occupy valuable shelf space and capital. Regular audits and categorizing by product demand help differentiate dead stock from potentially obsolete stock, enabling strategic clearance or reallocation efforts.
Signs Your Inventory Has Become Obsolete
Dead stock in retail refers to inventory that has never sold or moved for an extended period, typically over 12 months, while obsolete stock includes items that no longer meet current market demand or trends, often due to seasonality, product updates, or changes in consumer preferences. Signs your inventory has become obsolete include consistent lack of sales despite price reductions, accumulation of excess stock taking up valuable storage space, and frequent appearance of outdated models or styles that fail to attract customers. Monitoring turnover rates and comparing current demand against inventory age helps retailers identify and manage obsolete stock effectively.
Financial Impacts of Dead Stock vs Obsolete Stock
Dead stock ties up capital and storage resources without generating revenue, negatively affecting cash flow and increasing holding costs. Obsolete stock often incurs write-downs or disposal expenses, leading to direct financial losses and reduced profitability. Effective inventory management minimizes both dead and obsolete stock to improve financial performance and operational efficiency.
Strategies to Minimize Dead Stock
Implementing advanced inventory management systems and demand forecasting tools reduces dead stock by aligning stock levels with real-time consumer trends. Regularly reviewing product life cycles and conducting promotions or bundling slow-moving items help convert dead inventory into sales. Collaborating closely with suppliers enables flexible order sizes and return agreements, minimizing excess stock and obsolescence risks.
Approaches to Dealing with Obsolete Stock
Effective approaches to dealing with obsolete stock in retail include implementing discount strategies to accelerate clearance, donating products to charitable organizations to reduce holding costs, and recycling or repurposing materials to minimize environmental impact. Leveraging data analytics helps identify slow-moving items early, enabling proactive clearance before stock becomes fully obsolete. Collaborative supplier agreements can also facilitate returns or exchanges, mitigating the financial burden of unsellable inventory.
Technology Solutions for Managing Excess Inventory
Technology solutions for managing excess inventory differentiate between dead stock and obsolete stock by using advanced data analytics and AI-driven forecasting to identify slow-moving and unsellable items. Inventory management software platforms integrate real-time sales data and historical trends to optimize stock liquidation strategies, minimizing holding costs and improving cash flow. Automated alerts and predictive modeling enable retailers to proactively address excess inventory and implement timely promotions or discounts to reduce dead stock and obsolete stock effectively.
Preventing Future Dead and Obsolete Stock in Retail
Implementing advanced inventory management systems and demand forecasting tools significantly reduces dead stock and obsolete stock in retail by aligning stock levels with real-time consumer trends. Regularly analyzing sales data and product lifecycle stages enables retailers to identify slow-moving items early and adjust procurement strategies accordingly. Collaboration with suppliers for flexible ordering and integrating automated replenishment further prevents excess inventory and financial losses.
Dead Stock vs Obsolete Stock Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com