Last mile delivery in retail pet focuses on delivering products directly to customers' doors, ensuring fast and convenient access to pet supplies. Middle mile delivery involves transporting goods from warehouses to local distribution centers, optimizing inventory flow and reducing overall delivery times. Efficient coordination between middle and last mile delivery enhances customer satisfaction by balancing speed, cost, and reliability in pet product distribution.
Table of Comparison
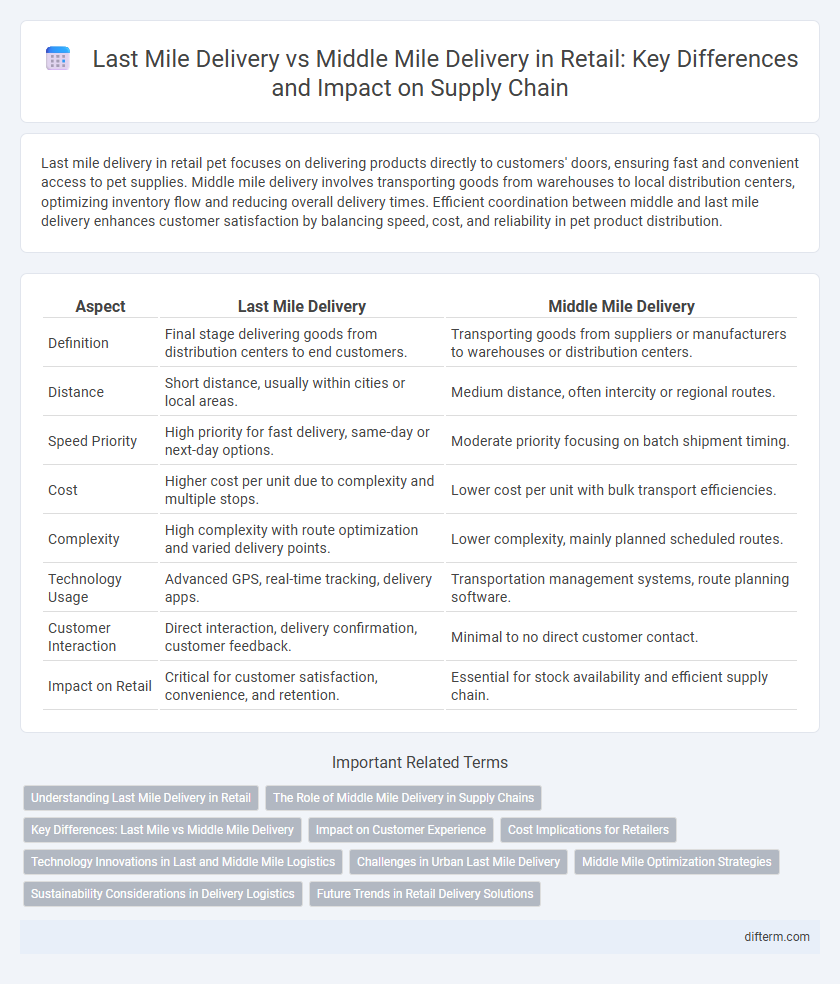
| Aspect | Last Mile Delivery | Middle Mile Delivery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Final stage delivering goods from distribution centers to end customers. | Transporting goods from suppliers or manufacturers to warehouses or distribution centers. |
| Distance | Short distance, usually within cities or local areas. | Medium distance, often intercity or regional routes. |
| Speed Priority | High priority for fast delivery, same-day or next-day options. | Moderate priority focusing on batch shipment timing. |
| Cost | Higher cost per unit due to complexity and multiple stops. | Lower cost per unit with bulk transport efficiencies. |
| Complexity | High complexity with route optimization and varied delivery points. | Lower complexity, mainly planned scheduled routes. |
| Technology Usage | Advanced GPS, real-time tracking, delivery apps. | Transportation management systems, route planning software. |
| Customer Interaction | Direct interaction, delivery confirmation, customer feedback. | Minimal to no direct customer contact. |
| Impact on Retail | Critical for customer satisfaction, convenience, and retention. | Essential for stock availability and efficient supply chain. |
Understanding Last Mile Delivery in Retail
Last mile delivery in retail refers to the final step of the shipping process, where products are transported from a local distribution center directly to the customer's doorstep, impacting customer satisfaction and brand loyalty. It typically involves smaller delivery vehicles, real-time tracking technologies, and efficient route planning to reduce delivery times and costs. Unlike middle mile delivery, which focuses on bulk shipment between warehouses or distribution hubs, last mile delivery emphasizes speed, flexibility, and personalized service to meet consumer expectations in an increasingly competitive retail environment.
The Role of Middle Mile Delivery in Supply Chains
Middle mile delivery plays a crucial role in retail supply chains by transporting goods from distribution centers to local hubs or fulfillment centers, optimizing inventory management and reducing lead times. Efficient middle mile operations enable retailers to maintain product availability and ensure faster last mile delivery to customers. Investing in middle mile infrastructure, such as regional warehouses and transportation networks, enhances overall supply chain resilience and cost-effectiveness.
Key Differences: Last Mile vs Middle Mile Delivery
Last mile delivery involves transporting goods from a distribution center directly to the customer's doorstep, emphasizing speed, accuracy, and customer satisfaction. Middle mile delivery covers the movement of products from manufacturers or warehouses to regional distribution hubs, focusing on efficiency and cost-effectiveness in bulk transportation. Key differences include distance covered, delivery speed priorities, and logistical challenges, with last mile being the most complex and expensive segment in the supply chain.
Impact on Customer Experience
Last mile delivery directly influences customer satisfaction by ensuring timely and accurate order fulfillment, often determining repeat business and brand loyalty. Middle mile delivery impacts the efficiency and reliability of last mile operations by optimizing inventory movement between warehouses and distribution centers. Streamlined middle mile processes reduce delays and stockouts, enhancing the overall customer experience through faster last mile delivery.
Cost Implications for Retailers
Last mile delivery incurs higher costs for retailers due to increased labor, fuel, and infrastructure expenses compared to middle mile delivery, which involves bulk transportation to regional distribution centers. Middle mile logistics benefit from economies of scale and optimized routing, reducing per-unit transportation costs and improving overall supply chain efficiency. Retailers must balance these cost implications by strategically investing in automation and location planning to minimize expensive last mile delivery expenses while maintaining service speed.
Technology Innovations in Last and Middle Mile Logistics
Technology innovations in last mile delivery focus on real-time GPS tracking, autonomous delivery vehicles, and drone integrations to enhance speed and customer experience. Middle mile logistics leverage AI-driven route optimization, IoT-enabled warehouse automation, and blockchain for transparent supply chain management. Both segments utilize advanced data analytics and machine learning to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure seamless inventory flow from distribution centers to end consumers.
Challenges in Urban Last Mile Delivery
Urban last mile delivery faces significant challenges including congested traffic, limited parking availability, and stringent delivery time windows, which increase operational complexity for retailers. The high density of recipients demands efficient route optimization and real-time tracking to minimize delays and reduce costs. These urban constraints contrast with middle mile delivery, where logistics primarily involve longer distances and bulk transportation between warehouses and distribution centers.
Middle Mile Optimization Strategies
Middle mile optimization strategies in retail focus on streamlining the transit of goods from distribution centers to local hubs, reducing transportation costs and improving delivery speed. Implementing advanced route planning software and leveraging real-time inventory data enhances load consolidation and minimizes empty miles, boosting operational efficiency. Employing cross-docking techniques and strategic warehouse placement further accelerates product flow, ensuring faster fulfillment in the last mile.
Sustainability Considerations in Delivery Logistics
Last mile delivery significantly impacts carbon emissions due to dense urban routes and frequent stops, making it a primary focus for sustainability improvements in retail logistics. Middle mile delivery, often characterized by longer distances and bulk transport between warehouses, benefits from route optimization and use of energy-efficient vehicles to reduce environmental footprint. Integrating electric or alternative fuel vehicles in both last and middle mile transportation supports retailers' goals to minimize greenhouse gas emissions and promote eco-friendly supply chains.
Future Trends in Retail Delivery Solutions
Last mile delivery is evolving with advancements in autonomous vehicles, drones, and smart lockers to enhance speed and customer experience, while middle mile delivery focuses on optimizing route efficiency and sustainability through electric trucks and data-driven logistics platforms. Integration of AI and IoT technologies is driving predictive analytics and real-time tracking, enabling seamless coordination between warehouses and final delivery points. Retailers are increasingly adopting hybrid delivery models combining centralized distribution centers with local micro-fulfillment hubs to reduce costs and meet rising consumer demands for faster, flexible delivery options.
last mile delivery vs middle mile delivery Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com