Dynamic pricing allows retailers to adjust pet product prices in real-time based on demand, inventory, and competitor pricing, maximizing profitability and minimizing stockouts. Markdowns are predetermined price reductions used to clear out excess or slow-moving inventory quickly, helping to free up shelf space and reduce holding costs. Both strategies improve financial performance but serve different purposes: dynamic pricing optimizes revenue continuously, whereas markdowns focus on liquidation.
Table of Comparison
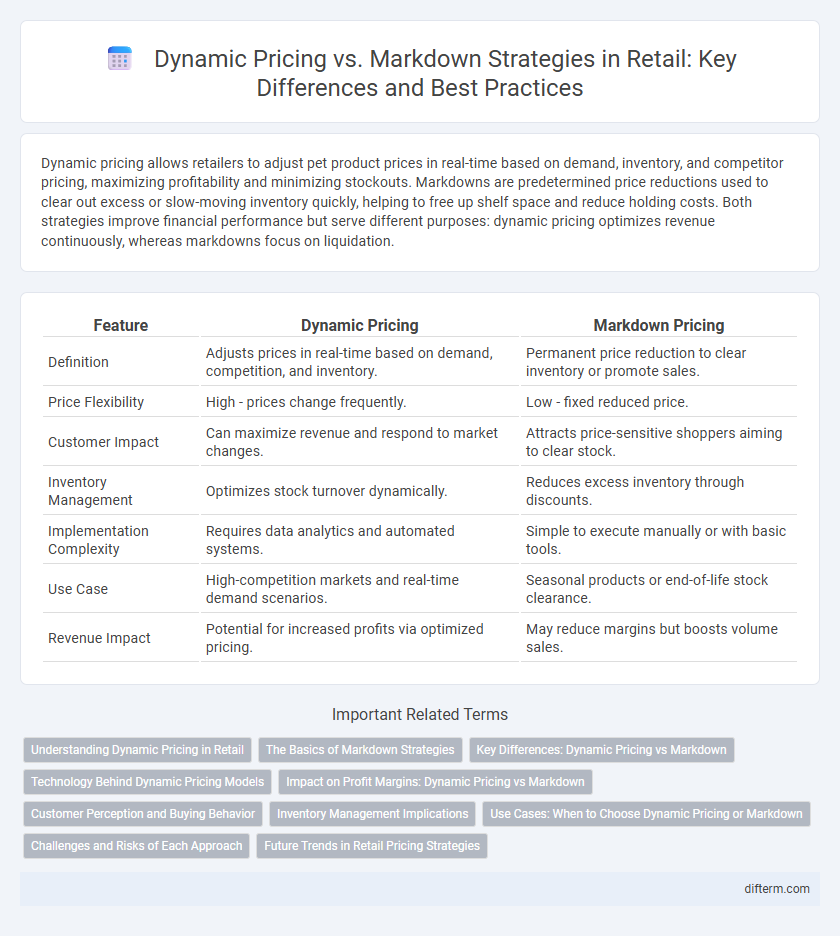
| Feature | Dynamic Pricing | Markdown Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adjusts prices in real-time based on demand, competition, and inventory. | Permanent price reduction to clear inventory or promote sales. |
| Price Flexibility | High - prices change frequently. | Low - fixed reduced price. |
| Customer Impact | Can maximize revenue and respond to market changes. | Attracts price-sensitive shoppers aiming to clear stock. |
| Inventory Management | Optimizes stock turnover dynamically. | Reduces excess inventory through discounts. |
| Implementation Complexity | Requires data analytics and automated systems. | Simple to execute manually or with basic tools. |
| Use Case | High-competition markets and real-time demand scenarios. | Seasonal products or end-of-life stock clearance. |
| Revenue Impact | Potential for increased profits via optimized pricing. | May reduce margins but boosts volume sales. |
Understanding Dynamic Pricing in Retail
Dynamic pricing in retail involves adjusting product prices in real-time based on market demand, competitor pricing, and inventory levels, enabling retailers to maximize revenue and respond swiftly to consumer behavior. Unlike traditional markdown strategies, which apply fixed discounts after demand wanes, dynamic pricing leverages algorithms and data analytics to optimize prices continuously throughout the sales cycle. This approach enhances profit margins and inventory turnover by aligning prices with consumer willingness to pay and competitive market conditions.
The Basics of Markdown Strategies
Markdown strategies in retail involve systematically reducing prices on products to stimulate sales and clear inventory, often based on product lifecycle, seasonality, and demand fluctuations. Dynamic pricing adjusts prices in real-time using algorithms that consider competitor pricing, market trends, and consumer behavior, while markdown strategies typically follow predetermined schedules or thresholds. Effective markdown planning minimizes margin erosion and inventory holding costs, enhancing overall profitability.
Key Differences: Dynamic Pricing vs Markdown
Dynamic pricing adjusts product prices in real-time based on market demand, competitor pricing, and inventory levels, optimizing revenue continuously. Markdowns are predetermined price reductions applied to clear excess inventory or slow-moving items, aiming to boost sales and manage stock efficiently. While dynamic pricing enhances responsiveness to market conditions, markdowns are typically static and used for inventory clearance strategies.
Technology Behind Dynamic Pricing Models
Dynamic pricing models leverage advanced algorithms and real-time data analysis to adjust retail prices based on factors such as demand fluctuations, competitor pricing, and inventory levels. Machine learning techniques enable these systems to predict customer behavior and optimize price points dynamically, maximizing revenue and minimizing stockouts. In contrast, markdown strategies rely on preset rules and historical sales data, lacking the adaptive responsiveness and granular precision offered by technology-driven dynamic pricing solutions.
Impact on Profit Margins: Dynamic Pricing vs Markdown
Dynamic pricing leverages real-time data and demand fluctuations to optimize prices, often leading to higher profit margins by capturing maximum willingness to pay. Markdown strategies reduce prices to clear inventory but typically compress profit margins due to discounted sales. Retailers employing dynamic pricing often experience improved profitability compared to relying solely on traditional markdowns.
Customer Perception and Buying Behavior
Dynamic pricing adapts in real-time to market demand, often enhancing customer perception of fairness when prices reflect current trends, encouraging quicker purchase decisions. Markdown strategies signal clear discounts, appealing to bargain hunters by creating a sense of urgency and value, which can drive immediate sales but may risk conditioning customers to wait for lower prices. Balancing dynamic pricing with strategic markdowns leverages both urgency and perceived fairness, ultimately shaping positive buying behavior and customer loyalty in retail environments.
Inventory Management Implications
Dynamic pricing enhances inventory management by adjusting prices in real-time based on demand fluctuations, minimizing overstock and stockouts. Markdown strategies help clear excess inventory but often signal slower sales and can erode profit margins. Integrating dynamic pricing with markdowns optimizes stock turnover, balances inventory levels, and maximizes overall profitability.
Use Cases: When to Choose Dynamic Pricing or Markdown
Dynamic pricing is ideal for high-demand, time-sensitive products like electronics or seasonal items, enabling retailers to adjust prices based on real-time market conditions and consumer behavior. Markdown strategies work best for clearing out excess inventory or end-of-season merchandise, helping to boost sales and reduce holding costs without the need for constant price fluctuations. Retailers should choose dynamic pricing for maximizing revenue in competitive markets and markdowns for managing stock levels and minimizing losses.
Challenges and Risks of Each Approach
Dynamic pricing in retail faces challenges such as fluctuating customer perceptions of fairness and the complexity of real-time data analytics, risking alienation of loyal shoppers. Markdowns carry risks of eroding brand value and profit margins, as frequent discounting can condition consumers to wait for sales, reducing full-price purchases. Both approaches require careful balance between maximizing revenue and maintaining customer trust and brand integrity.
Future Trends in Retail Pricing Strategies
Dynamic pricing leverages real-time data analytics and AI algorithms to adjust prices based on demand, competition, and inventory levels, offering a more responsive and personalized pricing strategy than traditional markdowns. Future trends indicate increased integration of machine learning and customer behavior insights, enabling retailers to optimize profit margins while enhancing customer experience through predictive pricing models. The shift towards omnichannel retailing further necessitates seamless dynamic pricing strategies across online and physical stores to maintain competitive advantage.
dynamic pricing vs markdown Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com