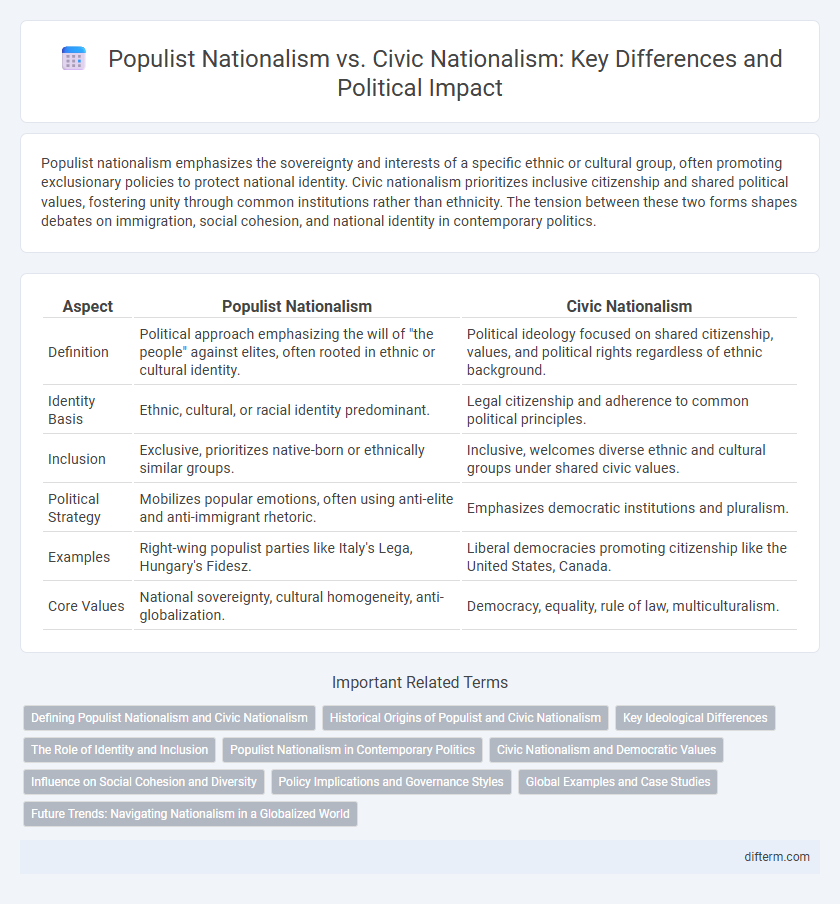
Populist nationalism emphasizes the sovereignty and interests of a specific ethnic or cultural group, often promoting exclusionary policies to protect national identity. Civic nationalism prioritizes inclusive citizenship and shared political values, fostering unity through common institutions rather than ethnicity. The tension between these two forms shapes debates on immigration, social cohesion, and national identity in contemporary politics.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Populist Nationalism | Civic Nationalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political approach emphasizing the will of "the people" against elites, often rooted in ethnic or cultural identity. | Political ideology focused on shared citizenship, values, and political rights regardless of ethnic background. |
| Identity Basis | Ethnic, cultural, or racial identity predominant. | Legal citizenship and adherence to common political principles. |
| Inclusion | Exclusive, prioritizes native-born or ethnically similar groups. | Inclusive, welcomes diverse ethnic and cultural groups under shared civic values. |
| Political Strategy | Mobilizes popular emotions, often using anti-elite and anti-immigrant rhetoric. | Emphasizes democratic institutions and pluralism. |
| Examples | Right-wing populist parties like Italy's Lega, Hungary's Fidesz. | Liberal democracies promoting citizenship like the United States, Canada. |
| Core Values | National sovereignty, cultural homogeneity, anti-globalization. | Democracy, equality, rule of law, multiculturalism. |
Defining Populist Nationalism and Civic Nationalism
Populist nationalism emphasizes a unified popular identity often defined against perceived elites or outsiders, prioritizing the interests of a specific national group and appealing to widespread public sentiments. Civic nationalism centers on shared political values, citizenship, and inclusive participation, promoting national unity through common rights and democratic principles rather than ethnic or cultural homogeneity. The distinction lies in populist nationalism's focus on exclusionary identity versus civic nationalism's emphasis on inclusive national belonging.
Historical Origins of Populist and Civic Nationalism
Populist nationalism traces its historical origins to the 19th-century movements that emphasized the sovereignty of the "common people" against elite dominance, often rooted in agrarian and working-class grievances. Civic nationalism emerged during the Enlightenment, grounded in the principles of citizenship, legal equality, and shared political values rather than ethnic or cultural identity. The contrasting origins highlight populist nationalism's focus on emotional collective identity and exclusion, while civic nationalism prioritizes inclusive political participation and universal rights.
Key Ideological Differences
Populist nationalism centers on a homogeneous national identity often defined by ethnicity or culture, prioritizing the interests of 'the people' against perceived elites or outsiders. Civic nationalism promotes inclusive citizenship based on shared values, legal equality, and participation, regardless of ethnic or cultural background. While populist nationalism emphasizes exclusion and protectionism, civic nationalism advocates pluralism and democratic institutions.
The Role of Identity and Inclusion
Populist nationalism emphasizes exclusionary identity politics, often defining national belonging through ethnicity, culture, or heritage, which can marginalize minority groups. Civic nationalism promotes political inclusion by fostering a shared commitment to democratic values and citizenship regardless of ethnic or cultural background. This inclusive identity framework supports social cohesion and equal participation in the political process.
Populist Nationalism in Contemporary Politics
Populist nationalism in contemporary politics emphasizes a strong national identity often defined by exclusionary rhetoric and opposition to perceived elites or foreign influences. It leverages emotional appeals to mobilize support through themes of sovereignty, cultural purity, and anti-globalization. Key examples include movements in countries such as Hungary under Viktor Orban, Brazil with Jair Bolsonaro, and the United States during Donald Trump's presidency.
Civic Nationalism and Democratic Values
Civic nationalism emphasizes inclusive citizenship based on shared political values, democratic institutions, and the rule of law, fostering social cohesion and political participation regardless of ethnic or cultural background. It champions democratic values such as equality, individual rights, and pluralism, which underpin stable governance and protect minority interests within diverse societies. This form of nationalism contrasts with populist nationalism by promoting unity through common civic responsibilities rather than ethnic or cultural homogeneity.
Influence on Social Cohesion and Diversity
Populist nationalism often emphasizes exclusionary identity politics that can deepen social divisions and undermine diversity by promoting an "us versus them" mentality. Civic nationalism, by contrast, fosters social cohesion through shared political values and inclusive citizenship that embraces cultural pluralism. The influence of civic nationalism typically results in stronger societal integration and support for diverse communities within democratic frameworks.
Policy Implications and Governance Styles
Populist nationalism often drives policy toward exclusionary immigration laws, protectionist trade measures, and prioritization of the majority ethnic group, resulting in governance that emphasizes strong, centralized leadership and direct appeals to popular sentiment. Civic nationalism promotes inclusive policies that uphold minority rights, encourage multicultural participation, and foster allegiance to shared political values, supporting democratic institutions and collaborative decision-making processes. These contrasting approaches influence legislative priorities, social cohesion, and the balance between majority rule and minority protections in governance.
Global Examples and Case Studies
Populist nationalism emphasizes exclusive national identity and often exploits socio-economic grievances, as seen in Hungary under Viktor Orban and Brazil with Jair Bolsonaro's rhetoric. Civic nationalism, exemplified by Canada and post-apartheid South Africa, promotes inclusive citizenship based on shared values and legal recognition rather than ethnicity. Comparative case studies highlight how populist nationalism tends to polarize societies, while civic nationalism fosters social cohesion and democratic resilience.
Future Trends: Navigating Nationalism in a Globalized World
Populist nationalism emphasizes exclusive identity politics, often promoting protectionism and skepticism toward global institutions, while civic nationalism advocates inclusive citizenship and cooperative internationalism. Future trends suggest rising tensions as globalization challenges state sovereignty, urging a recalibration toward hybrid models blending national pride with global engagement. Digital communication and transnational issues like climate change and migration will increasingly shape nationalist discourses and policy responses.
populist nationalism vs civic nationalism Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com