Progressivism in politics emphasizes social reform, equality, and environmental sustainability, advocating policies that prioritize human rights and social justice. Developmentalism focuses on economic growth and infrastructure development, promoting state intervention to accelerate industrialization and modernization. Both approaches aim to improve society but differ in their priorities and methods of achieving progress.
Table of Comparison
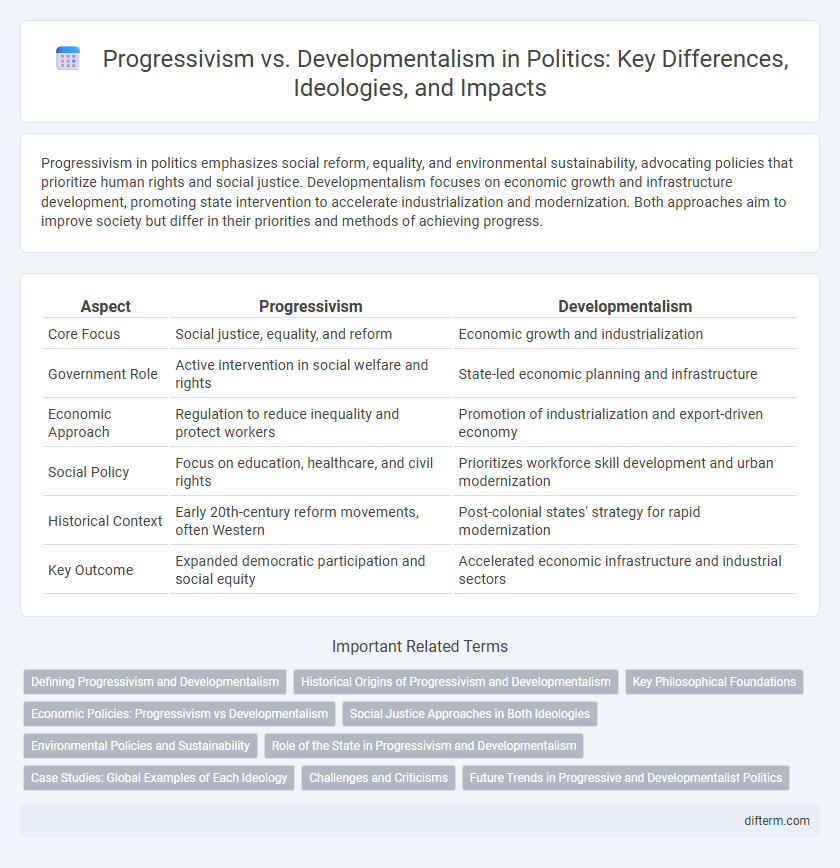
| Aspect | Progressivism | Developmentalism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Focus | Social justice, equality, and reform | Economic growth and industrialization |
| Government Role | Active intervention in social welfare and rights | State-led economic planning and infrastructure |
| Economic Approach | Regulation to reduce inequality and protect workers | Promotion of industrialization and export-driven economy |
| Social Policy | Focus on education, healthcare, and civil rights | Prioritizes workforce skill development and urban modernization |
| Historical Context | Early 20th-century reform movements, often Western | Post-colonial states' strategy for rapid modernization |
| Key Outcome | Expanded democratic participation and social equity | Accelerated economic infrastructure and industrial sectors |
Defining Progressivism and Developmentalism
Progressivism is a political ideology that prioritizes social reform, advocating for equality, government intervention, and the protection of individual rights to address societal injustices. Developmentalism emphasizes economic growth through state-led industrialization, infrastructure development, and modernization to enhance national productivity and self-sufficiency. While progressivism focuses on social justice and equitable policies, developmentalism centers on economic strategies to drive structural transformation and national progress.
Historical Origins of Progressivism and Developmentalism
Progressivism emerged in the late 19th and early 20th centuries as a response to industrialization's social inequalities, emphasizing reforms such as labor rights, government regulation, and social justice. Developmentalism originated in the mid-20th century, primarily in Latin America and Asia, advocating for state-led economic growth through industrialization, infrastructure investment, and protectionist policies. Both ideologies shaped political agendas by prioritizing social welfare and economic development, but progressivism centers on democratic reforms while developmentalism focuses on economic modernization.
Key Philosophical Foundations
Progressivism is grounded in principles of social justice, emphasizing equality, individual rights, and government intervention to address societal inequities. Developmentalism prioritizes economic growth and state-led industrialization, advocating for strategic planning and infrastructure investment as key drivers of national progress. Both philosophies diverge in their foundational goals, with progressivism focusing on expanding democratic participation and welfare, while developmentalism emphasizes modernization through economic development.
Economic Policies: Progressivism vs Developmentalism
Progressivism in economic policies emphasizes reducing inequality through social welfare programs, progressive taxation, and strong labor rights to ensure inclusive growth. Developmentalism prioritizes state-led industrialization, investment in infrastructure, and export-oriented growth to drive rapid economic expansion. Both approaches address economic development but differ in their reliance on market regulation versus state intervention.
Social Justice Approaches in Both Ideologies
Progressivism emphasizes social justice through policies that address systemic inequalities, advocating for robust welfare programs, equal rights, and inclusive governance to promote equity. Developmentalism prioritizes economic growth and modernization but incorporates social justice by aiming to improve living standards and reduce poverty through state-led industrialization and infrastructural development. Both ideologies intersect on enhancing social welfare, yet progressivism foregrounds redistribution and rights, while developmentalism stresses economic foundations for long-term social improvements.
Environmental Policies and Sustainability
Progressivism champions aggressive environmental regulations and sustainability initiatives aimed at reducing carbon emissions and promoting renewable energy sources. Developmentalism prioritizes economic growth and infrastructure expansion, often balancing environmental concerns with industrial and agricultural productivity. The tension between these approaches influences policy decisions on climate change mitigation and resource management at national and global levels.
Role of the State in Progressivism and Developmentalism
The role of the state in progressivism emphasizes regulatory intervention to promote social justice, economic equality, and protect individual rights through welfare programs and progressive taxation. In developmentalism, the state acts as a central planner and catalyst for economic growth, driving industrialization and infrastructure development while coordinating investments and resources to accelerate national development. Both frameworks assign significant power to the state but differ in prioritizing social equity versus economic expansion as primary objectives.
Case Studies: Global Examples of Each Ideology
Progressivism in politics emphasizes social reforms and equity, illustrated by Scandinavian countries like Sweden, which prioritize welfare systems and environmental sustainability. Developmentalism focuses on economic growth through state-led industrialization, exemplified by South Korea's rapid transformation under Park Chung-hee's regime in the late 20th century. Contrasting these, Brazil's recent policies reflect a blend of progressive social programs alongside developmentalist infrastructure projects, showcasing hybrid approaches in emerging economies.
Challenges and Criticisms
Progressivism faces criticism for prioritizing social reforms that critics argue may hinder economic growth and strain public resources. Developmentalism is challenged for its emphasis on rapid industrialization, which often leads to environmental degradation and socioeconomic inequalities. Both approaches struggle with balancing equitable growth and sustainable development amid complex political dynamics.
Future Trends in Progressive and Developmentalist Politics
Future trends in progressive politics emphasize inclusive social policies, climate justice, and digital democracy to address systemic inequalities and enhance civic participation. Developmentalism is projected to prioritize infrastructure modernization, technological innovation, and sustainable economic growth, particularly in emerging markets aiming to boost industrial capacity and reduce poverty. Converging these approaches could reshape governance frameworks by integrating social equity with economic development, fostering resilient and adaptive political systems.
progressivism vs developmentalism Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com