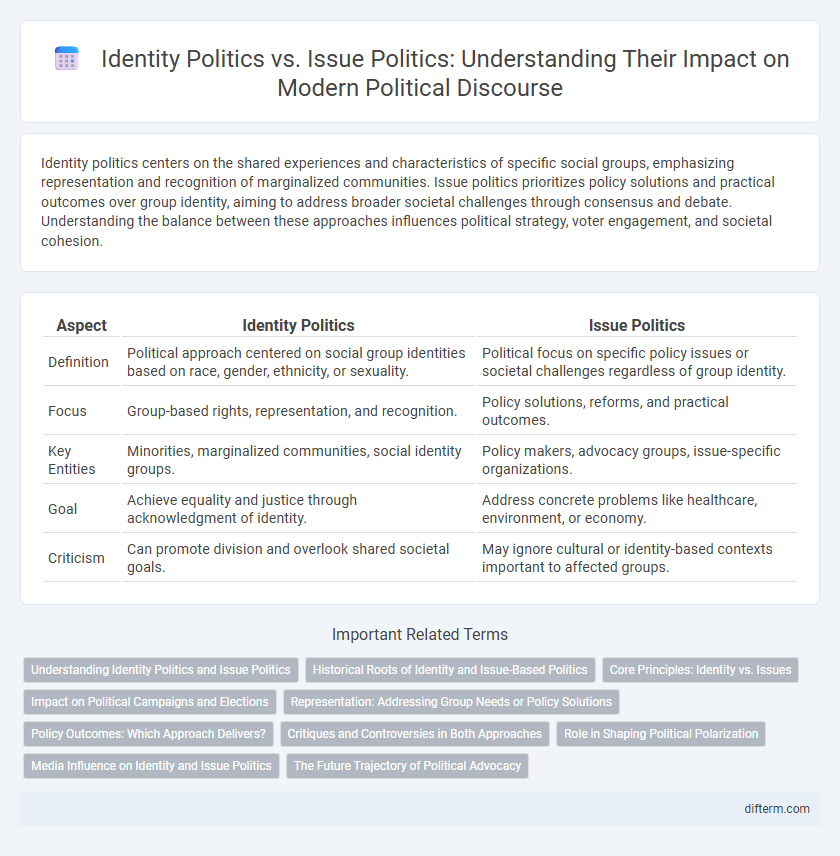
Identity politics centers on the shared experiences and characteristics of specific social groups, emphasizing representation and recognition of marginalized communities. Issue politics prioritizes policy solutions and practical outcomes over group identity, aiming to address broader societal challenges through consensus and debate. Understanding the balance between these approaches influences political strategy, voter engagement, and societal cohesion.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Identity Politics | Issue Politics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political approach centered on social group identities based on race, gender, ethnicity, or sexuality. | Political focus on specific policy issues or societal challenges regardless of group identity. |
| Focus | Group-based rights, representation, and recognition. | Policy solutions, reforms, and practical outcomes. |
| Key Entities | Minorities, marginalized communities, social identity groups. | Policy makers, advocacy groups, issue-specific organizations. |
| Goal | Achieve equality and justice through acknowledgment of identity. | Address concrete problems like healthcare, environment, or economy. |
| Criticism | Can promote division and overlook shared societal goals. | May ignore cultural or identity-based contexts important to affected groups. |
Understanding Identity Politics and Issue Politics
Identity politics centers on advocating for the interests and rights of specific social groups based on race, gender, ethnicity, or sexual orientation, emphasizing lived experiences and collective identity. Issue politics, in contrast, prioritizes policy debates and solutions addressing broad societal problems such as healthcare, education, and economic inequality, focusing on shared challenges rather than group affiliation. Understanding the distinction between these approaches aids in analyzing political behavior, voter alignment, and policy formulation in diverse democratic societies.
Historical Roots of Identity and Issue-Based Politics
Identity politics emerged prominently during the Civil Rights Movement of the 1960s, emphasizing the experiences and rights of marginalized groups such as African Americans, women, and LGBTQ+ communities. Issue-based politics has deeper roots in Enlightenment ideals, focusing on policy debates around universal concerns like economic reform, healthcare, and governance. The divergence reflects historical shifts where identity politics challenges systemic exclusion, while issue politics aims for broad consensus on policy solutions.
Core Principles: Identity vs. Issues
Identity politics centers on representing the experiences and rights of specific social groups, emphasizing shared characteristics such as race, gender, or ethnicity to advocate for equality and justice. Issue politics prioritizes broad policy concerns like healthcare, economic reform, and education, aiming to address systemic problems that affect diverse populations. The core divergence lies in identity politics using group-based solidarity for empowerment, while issue politics seeks solutions through policy-driven, inclusive approaches.
Impact on Political Campaigns and Elections
Identity politics shapes voter behavior by emphasizing group affiliations such as race, gender, and ethnicity, often leading to mobilization based on shared experiences and collective identity. Issue politics directs attention to specific policy concerns like healthcare, economy, and climate change, influencing campaigns to prioritize substantive solutions and legislative agendas. The interplay between identity and issue politics significantly affects candidate strategies, voter turnout, and election outcomes by balancing emotional resonance with practical policy appeals.
Representation: Addressing Group Needs or Policy Solutions
Identity politics prioritizes representation by emphasizing the unique experiences and needs of specific social groups, advocating for policies that directly address historical injustices and systemic inequalities faced by these communities. Issue politics focuses on broad policy solutions that transcend group boundaries, aiming to implement effective legislation based on shared societal challenges like healthcare, economic reform, or environmental protection. The debate centers on whether political representation should primarily reflect group identities to empower marginalized populations or concentrate on universal policy outcomes to achieve collective progress.
Policy Outcomes: Which Approach Delivers?
Issue politics tends to deliver more measurable policy outcomes by focusing on specific problems such as healthcare reform, economic inequality, or climate change. Identity politics often centers around representation and social recognition, which can influence policy indirectly but may struggle to translate into concrete legislative changes. Empirical studies suggest that coalitions built around shared policy goals typically achieve more substantial legislative success than those primarily organized by identity groups.
Critiques and Controversies in Both Approaches
Identity politics faces critiques for fostering division by emphasizing group differences over common goals, potentially undermining social cohesion. Issue politics is criticized for overlooking systemic inequalities by focusing narrowly on specific policies without addressing underlying power dynamics. Both approaches encounter controversies related to inclusivity, representation, and the balance between individual and collective concerns in shaping political agendas.
Role in Shaping Political Polarization
Identity politics concentrates on group affiliations such as race, ethnicity, and religion, often intensifying political polarization by highlighting perceived in-group versus out-group distinctions. Issue politics emphasizes policy-specific concerns like healthcare, climate change, and economic reform, which can foster more issue-driven debate but may also become divisive when aligned with partisan identities. The interplay between identity and issue politics is a key driver in contemporary political polarization, influencing voter behavior and legislative gridlock.
Media Influence on Identity and Issue Politics
Media significantly shapes identity politics by amplifying group-based narratives and framing social issues in ways that reinforce collective identities. This focus often leads to heightened emphasis on symbolic representation and cultural values over policy specifics, influencing public discourse and political mobilization. In contrast, issue politics coverage tends to prioritize policy analysis and pragmatic solutions, although media bias and sensationalism can distort the complexity of these topics.
The Future Trajectory of Political Advocacy
The future trajectory of political advocacy is increasingly shaped by the tension between identity politics and issue politics, where identity-based movements mobilize communities around shared cultural and social identities, while issue politics centers on specific policy concerns with broader consensus. Emerging trends suggest that successful advocacy will require integrating identity narratives with actionable policy solutions to build inclusive coalitions and achieve legislative impact. Data from recent elections reveal that candidates and parties embracing this hybrid approach tend to secure stronger grassroots support and sustained voter engagement.
identity politics vs issue politics Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com