Progressivism advocates for social reform, equality, and government intervention to address injustices, emphasizing change and innovation in political policies. Conservatism prioritizes tradition, limited government, and individual responsibility, seeking to preserve established institutions and values. The ongoing debate highlights differing visions for society's evolution and the role of government in shaping public life.
Table of Comparison
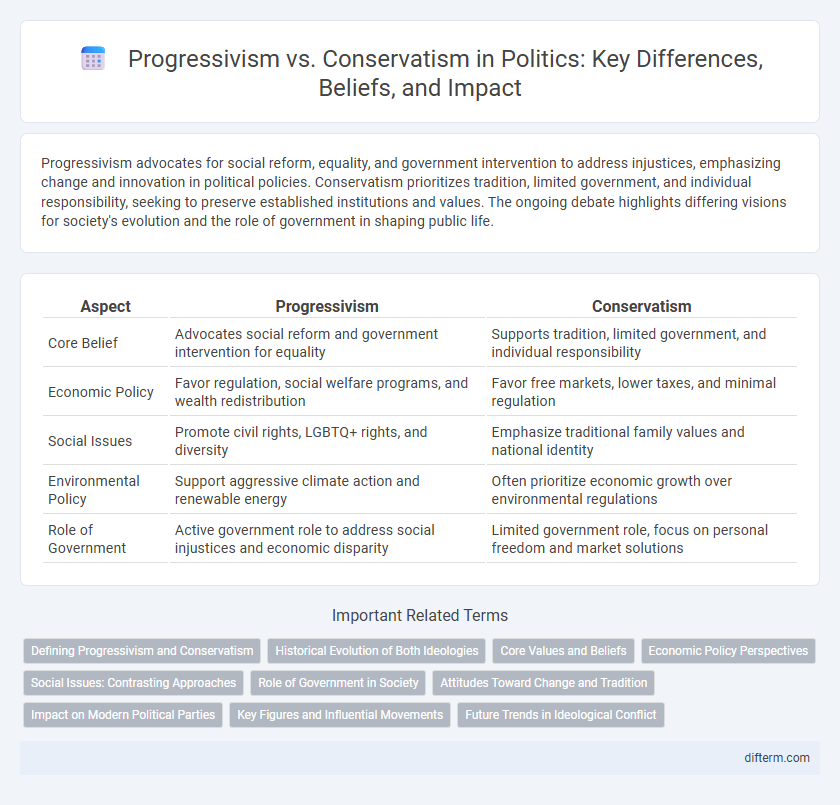
| Aspect | Progressivism | Conservatism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Belief | Advocates social reform and government intervention for equality | Supports tradition, limited government, and individual responsibility |
| Economic Policy | Favor regulation, social welfare programs, and wealth redistribution | Favor free markets, lower taxes, and minimal regulation |
| Social Issues | Promote civil rights, LGBTQ+ rights, and diversity | Emphasize traditional family values and national identity |
| Environmental Policy | Support aggressive climate action and renewable energy | Often prioritize economic growth over environmental regulations |
| Role of Government | Active government role to address social injustices and economic disparity | Limited government role, focus on personal freedom and market solutions |
Defining Progressivism and Conservatism
Progressivism advocates for social reform, economic equality, and government intervention to address systemic injustices, emphasizing change and innovation in policies. Conservatism prioritizes tradition, limited government, and individual responsibility, seeking to preserve established social structures and cultural norms. These ideologies fundamentally differ in approaches to governance, societal change, and the role of state in citizens' lives.
Historical Evolution of Both Ideologies
Progressivism emerged in the late 19th and early 20th centuries as a response to industrialization and social inequality, advocating for reforms such as labor rights, women's suffrage, and antitrust regulations. Conservatism has roots in the 18th century, emphasizing tradition, social stability, and limited government intervention, often resisting rapid change to preserve established institutions. Over time, both ideologies have evolved, with progressivism expanding to include civil rights and environmental issues, while conservatism increasingly focuses on free-market policies and cultural values.
Core Values and Beliefs
Progressivism emphasizes social equality, government intervention for economic justice, and the protection of civil rights, advocating for reforms to address systemic inequalities. Conservatism prioritizes tradition, limited government, individual responsibility, and the preservation of established social orders to maintain stability and continuity. Core beliefs in progressivism center on change and innovation for societal improvement, while conservatism values enduring customs and cautious adaptation.
Economic Policy Perspectives
Progressivism advocates for government intervention in the economy to promote social equity, including support for higher minimum wages, progressive taxation, and expanded social welfare programs. Conservatism emphasizes free-market principles, limited government regulation, and fiscal restraint to stimulate economic growth and maintain individual liberties. Debates often center on balancing wealth redistribution with market efficiency to achieve sustainable economic development.
Social Issues: Contrasting Approaches
Progressivism advocates for social reforms that promote equality, individual rights, and inclusivity, often supporting policies like LGBTQ+ rights, racial justice, and gender equality. Conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional values, institutions, and social norms, prioritizing family structure, religious beliefs, and law and order. These contrasting approaches shape debates on healthcare, education, and civil liberties, influencing legislative agendas and public policy outcomes.
Role of Government in Society
Progressivism advocates for an expanded government role to address social inequalities, regulate the economy, and provide public services, emphasizing collective responsibility for welfare. Conservatism supports limited government intervention, prioritizing individual freedoms, free-market principles, and traditional values to maintain social order. The debate centers on balancing government authority with personal liberty and economic efficiency in shaping societal outcomes.
Attitudes Toward Change and Tradition
Progressivism advocates for embracing change through social reforms and innovation to address inequalities, emphasizing forward-thinking policies that challenge established norms. Conservatism prioritizes preserving tradition and maintaining social stability, valuing historical continuity and skepticism toward rapid transformation. These contrasting attitudes shape political debates on governance, cultural values, and policy development in democratic societies.
Impact on Modern Political Parties
Progressivism shapes modern political parties by advocating for social justice, environmental reform, and expanded civil rights, influencing platforms that emphasize equality and government intervention. Conservatism impacts these parties through its promotion of tradition, limited government, and free-market principles, appealing to constituents valuing stability and personal responsibility. The dynamic tension between these ideologies drives policy debates, election strategies, and party realignments in contemporary politics.
Key Figures and Influential Movements
Progressivism, championed by figures like Theodore Roosevelt and Franklin D. Roosevelt, emphasizes social reform, government intervention, and expanding civil rights through movements such as the New Deal and the Civil Rights Movement. Conservatism, represented by leaders like Ronald Reagan and Barry Goldwater, prioritizes limited government, free-market principles, and traditional values, with influential movements including the Reagan Revolution and the Tea Party. Both ideologies have shaped political discourse by mobilizing distinct voter bases and influencing policy directions in American politics.
Future Trends in Ideological Conflict
Future trends in ideological conflict reveal an intensification between progressivism, which advocates for systemic reform addressing social justice and climate change, and conservatism, emphasizing tradition, economic stability, and limited government intervention. Demographic shifts, digital media influence, and economic uncertainty are amplifying polarization, with younger generations largely aligning with progressive values while older voters tend to uphold conservative principles. Emerging policy debates on technology regulation, environmental action, and equity are expected to deepen ideological divisions shaping global political landscapes.
progressivism vs conservatism Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com