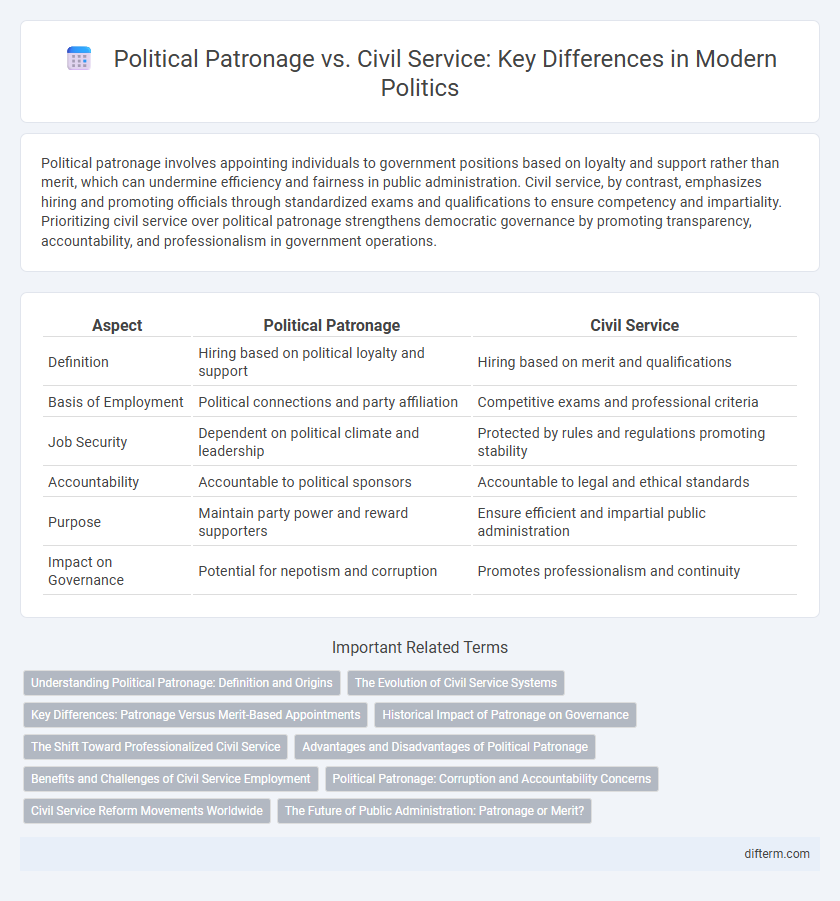
Political patronage involves appointing individuals to government positions based on loyalty and support rather than merit, which can undermine efficiency and fairness in public administration. Civil service, by contrast, emphasizes hiring and promoting officials through standardized exams and qualifications to ensure competency and impartiality. Prioritizing civil service over political patronage strengthens democratic governance by promoting transparency, accountability, and professionalism in government operations.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Political Patronage | Civil Service |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hiring based on political loyalty and support | Hiring based on merit and qualifications |
| Basis of Employment | Political connections and party affiliation | Competitive exams and professional criteria |
| Job Security | Dependent on political climate and leadership | Protected by rules and regulations promoting stability |
| Accountability | Accountable to political sponsors | Accountable to legal and ethical standards |
| Purpose | Maintain party power and reward supporters | Ensure efficient and impartial public administration |
| Impact on Governance | Potential for nepotism and corruption | Promotes professionalism and continuity |
Understanding Political Patronage: Definition and Origins
Political patronage refers to the practice of appointing government jobs and favors to loyal supporters, often as a reward for political support, rather than based on merit or qualifications. Originating in ancient civilizations such as Rome and Greece, patronage evolved as a system to consolidate power and maintain political alliances. Unlike the professional civil service, which emphasizes competence and fairness, political patronage prioritizes loyalty and political advantage, impacting governance and administrative efficiency.
The Evolution of Civil Service Systems
The evolution of civil service systems emphasizes merit-based recruitment and promotion, contrasting sharply with political patronage, where appointments often depend on loyalty or political connections. Institutional reforms across various democracies have established standardized exams and transparent criteria to curb nepotism and enhance administrative efficiency. These changes have strengthened governance by fostering professionalism, accountability, and stability within the public sector.
Key Differences: Patronage Versus Merit-Based Appointments
Political patronage involves appointing individuals to government positions based on loyalty, connections, or political support rather than qualifications, often leading to favoritism and inefficiency. In contrast, civil service appointments emphasize merit-based selection through competitive exams and standardized evaluations, promoting professionalism and competence in public administration. This key difference impacts government accountability, with patronage systems potentially fostering corruption while merit-based civil service supports transparency and career stability.
Historical Impact of Patronage on Governance
Political patronage historically shaped governance by embedding loyalty-based appointments that often compromised administrative efficiency and accountability. Patronage systems, prevalent in 19th-century democracies, fueled corruption and hindered meritocratic development, contrasting sharply with civil service reforms that introduced standardized, competence-based hiring. These reforms gradually professionalized public administration, promoting stability and impartiality in governmental operations.
The Shift Toward Professionalized Civil Service
The shift toward a professionalized civil service marks a significant move away from traditional political patronage systems, emphasizing merit-based recruitment and impartiality. This transformation enhances administrative efficiency and reduces corruption by ensuring that government positions are filled by qualified individuals rather than political allies. As a result, the civil service becomes more stable and capable of implementing long-term policy goals without partisan interference.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Political Patronage
Political patronage enables rapid appointment of loyal personnel aligned with the governing party, enhancing policy implementation efficiency but often undermines meritocracy and creates risks of corruption and incompetence. This system strengthens political loyalty and aids in mobilizing electoral support, yet it frequently results in biased resource distribution and diminished public trust in government institutions. The trade-off between political responsiveness and administrative professionalism shapes debates on governance quality and public sector performance.
Benefits and Challenges of Civil Service Employment
Civil service employment offers benefits such as job stability, merit-based advancement, and a focus on public interest, reducing corruption risks associated with political patronage. It fosters professionalism and continuity in government operations, ensuring policy implementation transcends political cycles. Challenges include potential bureaucratic rigidity and slower decision-making due to strict rules and procedures.
Political Patronage: Corruption and Accountability Concerns
Political patronage often fosters corruption by enabling the appointment of officials based on loyalty rather than merit, undermining the principles of fair governance. This system compromises accountability, as patronage hires may prioritize political interests over public service responsibilities, leading to inefficiency and abuse of power. Empirical studies link patronage-heavy administrations with increased corruption indices and weakened institutional checks, highlighting a persistent challenge in democratic governance.
Civil Service Reform Movements Worldwide
Civil service reform movements worldwide have targeted the eradication of political patronage to establish merit-based public administration systems. These reforms emphasize competitive examinations, transparent hiring processes, and protection from political interference to enhance efficiency and accountability in government. Countries like the United Kingdom, India, and the United States exemplify successful civil service reforms that prioritize competence over partisan loyalty.
The Future of Public Administration: Patronage or Merit?
The future of public administration hinges on balancing political patronage with merit-based civil service to ensure efficient governance and public trust. Merit systems promote transparency and competence by prioritizing qualifications and performance, while patronage risks favoritism and inefficiency. Reform efforts increasingly advocate for meritocratic frameworks to enhance accountability and professionalization in government institutions.
political patronage vs civil service Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com