Populist rhetoric often appeals to emotions and simple solutions, positioning itself against the perceived elite and bureaucratic technocracy. Technocratic discourse emphasizes data-driven policies and expert knowledge to address complex societal issues. The tension between these approaches shapes political debates, influencing voter trust and policy effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
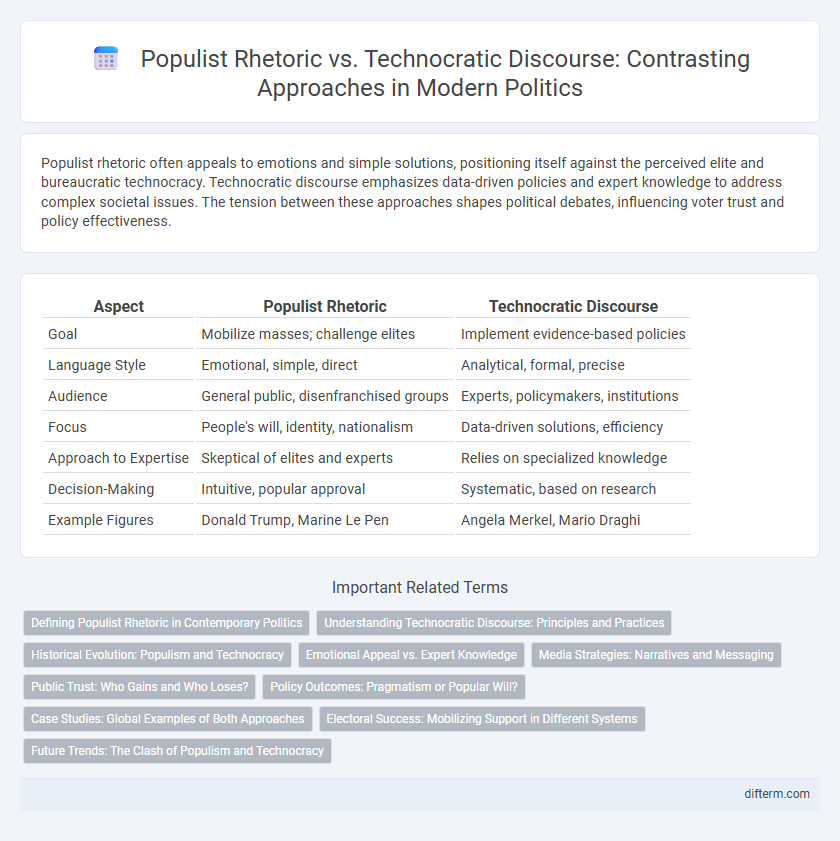
| Aspect | Populist Rhetoric | Technocratic Discourse |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Mobilize masses; challenge elites | Implement evidence-based policies |
| Language Style | Emotional, simple, direct | Analytical, formal, precise |
| Audience | General public, disenfranchised groups | Experts, policymakers, institutions |
| Focus | People's will, identity, nationalism | Data-driven solutions, efficiency |
| Approach to Expertise | Skeptical of elites and experts | Relies on specialized knowledge |
| Decision-Making | Intuitive, popular approval | Systematic, based on research |
| Example Figures | Donald Trump, Marine Le Pen | Angela Merkel, Mario Draghi |
Defining Populist Rhetoric in Contemporary Politics
Populist rhetoric in contemporary politics centers on a dichotomy between "the pure people" and "the corrupt elite," using emotionally charged language to mobilize popular support by appealing to national identity and perceived grievances. This communication style often simplifies complex policy issues, prioritizing direct connection with the public over expert analysis or institutional processes characteristic of technocratic discourse. By emphasizing anti-establishment sentiments and personalizing political conflicts, populist rhetoric challenges the legitimacy of technocratic governance and reshapes democratic debate.
Understanding Technocratic Discourse: Principles and Practices
Technocratic discourse centers on expert knowledge, data-driven policy-making, and evidence-based solutions, emphasizing rationality and scientific methods in governance. It contrasts sharply with populist rhetoric, which often appeals to emotions and popular sentiments over empirical facts. Understanding technocratic principles involves recognizing the value of specialized expertise and institutional frameworks designed to implement efficient, pragmatic public policies.
Historical Evolution: Populism and Technocracy
Populist rhetoric has evolved from early 20th-century agrarian movements emphasizing direct appeals to the "common people" against elite establishments, while technocratic discourse emerged mid-century, rooted in expertise and rational governance often promoted by institutions like the UN and IMF. The historical trajectory reveals populism's cyclical resurgence during periods of economic or social crisis, contrasting with technocracy's steady rise amid post-war modernization and globalization. This dynamic tension reflects broader political shifts where emotional appeals and expert-driven policies contend for legitimacy in democratic systems.
Emotional Appeal vs. Expert Knowledge
Populist rhetoric leverages emotional appeal to resonate with public frustrations, often simplifying complex issues into relatable narratives that mobilize mass support. Technocratic discourse emphasizes expert knowledge and data-driven solutions, prioritizing rationality and specialized understanding over mass persuasion. The tension between these approaches shapes political communication strategies, influencing policy acceptance and public trust.
Media Strategies: Narratives and Messaging
Populist rhetoric in media strategies often relies on emotionally charged narratives that emphasize a direct connection with "the people," using simplified language and polarizing themes to mobilize support. In contrast, technocratic discourse prioritizes expert-driven messaging, highlighting data, evidence-based solutions, and complex policy analysis to appeal to rational decision-making audiences. Media outlets shape the impact of these approaches by selectively framing issues to either amplify emotional resonance or underscore technical competence.
Public Trust: Who Gains and Who Loses?
Populist rhetoric often gains public trust by appealing to widespread frustrations and promising simple solutions, resonating with voters who feel marginalized by elite institutions. Technocratic discourse, grounded in expertise and data-driven decision-making, tends to lose trust among those who perceive it as disconnected or elitist. Public trust fluctuates between these narratives, with populists capitalizing on emotional engagement while technocrats appeal to rational governance.
Policy Outcomes: Pragmatism or Popular Will?
Populist rhetoric often emphasizes the popular will by appealing to broad public sentiments and promising immediate, tangible benefits, which can lead to swift but sometimes unsustainable policy outcomes. In contrast, technocratic discourse prioritizes pragmatic, evidence-based decision-making, fostering long-term solutions guided by expert knowledge and data analysis. The tension between these approaches influences governance effectiveness, with populist policies risking volatility and technocratic ones potentially facing public resistance due to perceived elitism.
Case Studies: Global Examples of Both Approaches
Populist rhetoric often emphasizes direct appeals to the "common people" and national sovereignty, exemplified by leaders like Donald Trump in the United States and Jair Bolsonaro in Brazil, who utilize simplified narratives and emotional language to mobilize support. In contrast, technocratic discourse prioritizes expert-driven policy-making and data-based decisions, as seen in Germany under Angela Merkel and Singapore's government, which rely on specialized knowledge and pragmatic solutions. These case studies illustrate the stark contrast between emotionally charged populism and rational, evidence-based governance models observed worldwide.
Electoral Success: Mobilizing Support in Different Systems
Populist rhetoric often mobilizes electoral support by appealing directly to popular grievances and emphasizing a clear divide between "the people" and the elite, resonating strongly in systems with lower political trust and fragmented party structures. Technocratic discourse, emphasizing expertise and evidence-based policy, tends to gain traction in systems with higher political stability and institutional trust, attracting voters who prioritize competence over ideological appeal. The effectiveness of each approach is contingent on the political environment, with populism thriving in volatile contexts and technocracy succeeding where governance complexity demands informed decision-making.
Future Trends: The Clash of Populism and Technocracy
Emerging political landscapes reveal a growing tension between populist rhetoric, which prioritizes emotional appeal and mass mobilization, and technocratic discourse centered on expertise and data-driven policy-making. Future trends indicate this clash will intensify as global challenges demand both inclusive political participation and specialized knowledge for sustainable solutions. Political analysts forecast increased polarization, with policymakers balancing populist pressures against technocratic imperatives to maintain governance efficacy.
populist rhetoric vs technocratic discourse Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com