Normative statements express subjective judgments about what ought to be, often reflecting personal values or ethical beliefs regarding pet ownership and care. Analytic statements are objective and verifiable, focusing on factual information such as the biological needs or behaviors of pets. Understanding the distinction between normative and analytic perspectives clarifies debates about pet welfare, grounding opinions either in ethical considerations or empirical evidence.
Table of Comparison
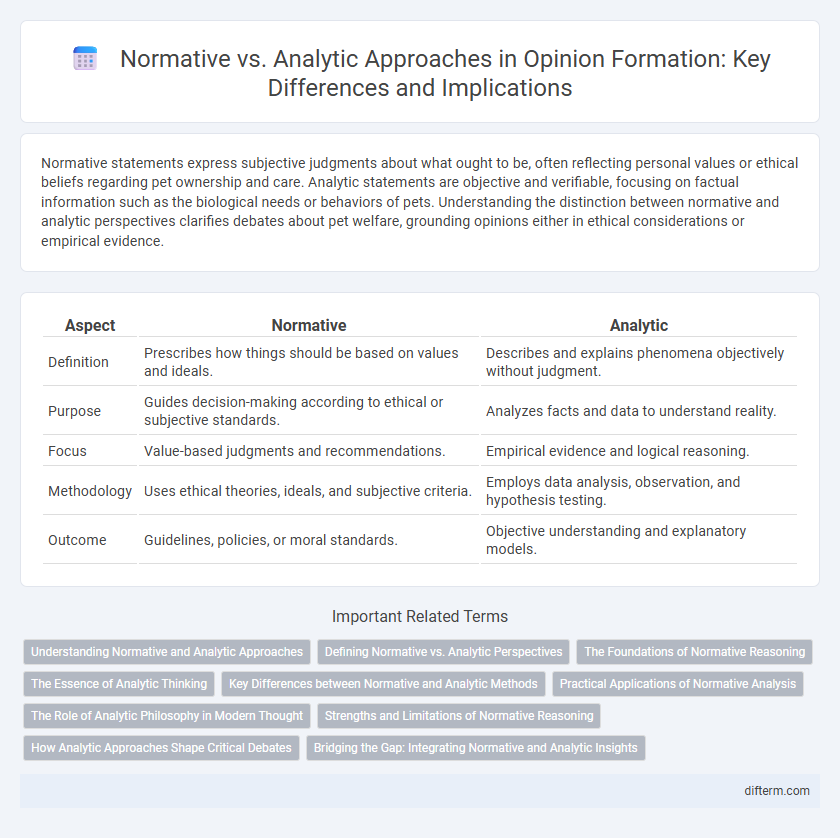
| Aspect | Normative | Analytic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Prescribes how things should be based on values and ideals. | Describes and explains phenomena objectively without judgment. |
| Purpose | Guides decision-making according to ethical or subjective standards. | Analyzes facts and data to understand reality. |
| Focus | Value-based judgments and recommendations. | Empirical evidence and logical reasoning. |
| Methodology | Uses ethical theories, ideals, and subjective criteria. | Employs data analysis, observation, and hypothesis testing. |
| Outcome | Guidelines, policies, or moral standards. | Objective understanding and explanatory models. |
Understanding Normative and Analytic Approaches
Normative approaches prioritize ethical principles and value judgments to guide decision-making and assess what ought to be done, often rooted in philosophical theories like deontology or utilitarianism. Analytic methods emphasize logical evaluation, empirical data, and conceptual clarity to describe and explain phenomena without prescribing specific values. Understanding both approaches is essential for a comprehensive analysis, as normative perspectives address the moral dimensions while analytic approaches provide rigorous, evidence-based assessment.
Defining Normative vs. Analytic Perspectives
Normative perspectives prescribe how things ought to be, emphasizing values, ethics, and ideals to guide decision-making and behavior. Analytic perspectives focus on objective examination and description of how things actually are, relying on empirical evidence and logical reasoning. Distinguishing between these approaches clarifies debates by separating value judgments from factual analysis.
The Foundations of Normative Reasoning
Normative reasoning establishes standards for evaluating actions and beliefs based on ethical principles, contrasting with analytic reasoning, which focuses on logical clarity and conceptual analysis. The Foundations of Normative Reasoning emphasize moral values, duties, and obligations as essential criteria for judgment, grounding ethical decision-making in reasoned justification rather than empirical observation. Understanding these foundations clarifies how normative frameworks guide practical choices by setting criteria beyond mere factual correctness.
The Essence of Analytic Thinking
Analytic thinking epitomizes the essence of breaking down complex information into fundamental principles and evidence-based reasoning, facilitating clear and objective evaluation of ideas. Unlike normative approaches that emphasize how things ought to be, analytic thinking prioritizes empirical data and logical consistency to understand reality. This method enhances problem-solving effectiveness by systematically dissecting components and uncovering underlying structures.
Key Differences between Normative and Analytic Methods
Normative methods focus on prescribing how things ought to be based on values and ethical considerations, emphasizing subjective judgments and goals. Analytic methods prioritize objective analysis of facts and data, seeking descriptive, evidence-based conclusions without value-laden recommendations. Key differences include the normative method's emphasis on ideals and prescriptions versus the analytic method's emphasis on explanation and prediction through empirical observation.
Practical Applications of Normative Analysis
Normative analysis informs decision-making in economics, ethics, and public policy by establishing value-based criteria for evaluating choices and outcomes. Its practical applications include designing equitable tax systems, setting environmental regulations, and guiding healthcare priorities to promote social welfare. By integrating moral principles with empirical data, normative analysis facilitates informed judgments that shape effective and just policies.
The Role of Analytic Philosophy in Modern Thought
Analytic philosophy's rigorous focus on clarity, logic, and language analysis plays a crucial role in shaping contemporary intellectual discourse by providing precise tools for dissecting complex concepts. Its emphasis on argument structure and linguistic clarity advances critical thinking across disciplines like science, ethics, and epistemology. This methodological approach fosters intellectual transparency, enabling more robust debates and the progressive refinement of ideas in modern thought.
Strengths and Limitations of Normative Reasoning
Normative reasoning excels in guiding decision-making by establishing principles based on values and ideals, offering clear standards for evaluating choices and actions. Its strength lies in providing ethical frameworks and goals that shape behavior, but it can be limited by subjective interpretations and cultural variability, which may hinder consensus. The lack of empirical verification and reliance on prescriptive judgments present challenges in applying normative reasoning universally across diverse contexts.
How Analytic Approaches Shape Critical Debates
Analytic approaches prioritize clarity, precision, and logical coherence, which shape critical debates by enabling systematic evaluation of arguments and identification of implicit assumptions. This rigorous methodology fosters deeper understanding and challenges normative claims by grounding discussions in empirical evidence and logical consistency. The emphasis on analytic reasoning transforms normative debates into structured inquiries, enhancing the quality and impact of critical discourse.
Bridging the Gap: Integrating Normative and Analytic Insights
Bridging the gap between normative and analytic approaches enhances decision-making by combining ethical principles with empirical data. Integrating normative theories with analytic methods fosters comprehensive solutions that respect moral values while ensuring practical feasibility. This synthesis promotes balanced outcomes, aligning ideal standards with real-world constraints.
normative vs analytic Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com