Bias often stems from unconscious preferences or stereotypes that influence perceptions and actions, whereas prejudice involves preconceived opinions typically rooted in negative attitudes and a lack of factual knowledge. Both bias and prejudice can distort judgment and lead to unfair treatment of others, but bias may sometimes be unintentional while prejudice is more deliberate and resistant to change. Recognizing these distinctions is crucial for fostering open-mindedness and promoting equality in society.
Table of Comparison
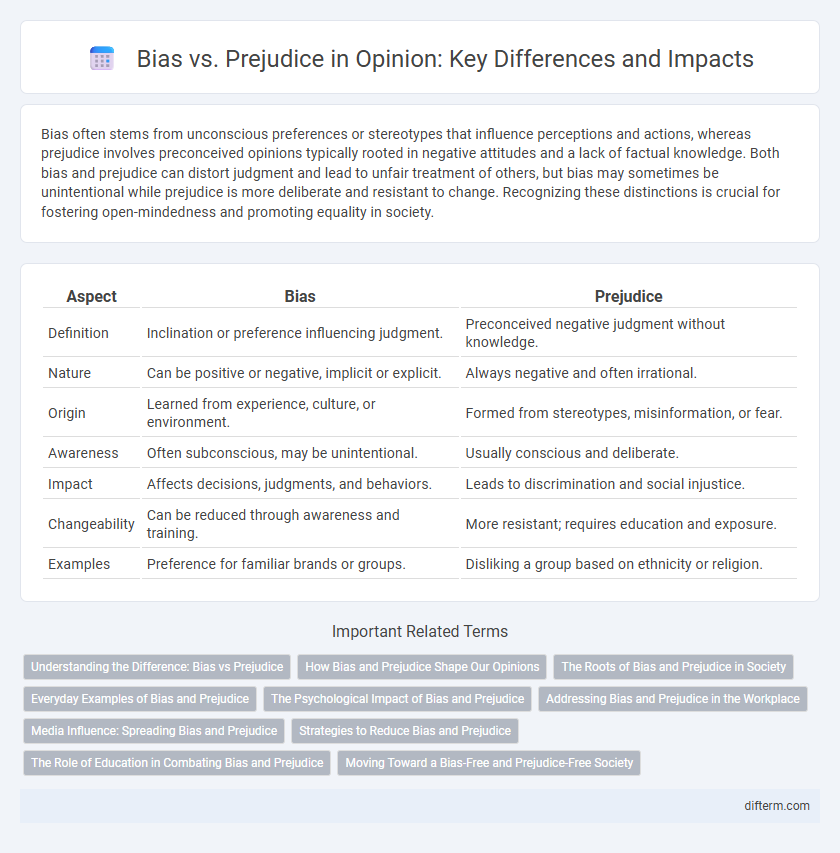
| Aspect | Bias | Prejudice |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inclination or preference influencing judgment. | Preconceived negative judgment without knowledge. |
| Nature | Can be positive or negative, implicit or explicit. | Always negative and often irrational. |
| Origin | Learned from experience, culture, or environment. | Formed from stereotypes, misinformation, or fear. |
| Awareness | Often subconscious, may be unintentional. | Usually conscious and deliberate. |
| Impact | Affects decisions, judgments, and behaviors. | Leads to discrimination and social injustice. |
| Changeability | Can be reduced through awareness and training. | More resistant; requires education and exposure. |
| Examples | Preference for familiar brands or groups. | Disliking a group based on ethnicity or religion. |
Understanding the Difference: Bias vs Prejudice
Bias involves an unconscious inclination or preference towards a person, group, or idea, often shaped by personal experiences and societal influences. Prejudice is a preconceived judgment or opinion, frequently negative, formed without factual evidence or direct experience. Distinguishing bias from prejudice requires recognizing bias as an implicit tendency, while prejudice reflects explicit, often hostile attitudes.
How Bias and Prejudice Shape Our Opinions
Bias and prejudice significantly influence the formation of our opinions by filtering information through preconceived notions. These cognitive shortcuts often lead to unfair judgments and reinforce stereotypes, limiting open-minded analysis. Understanding the distinction--bias as a tendency and prejudice as an entrenched negative attitude--helps mitigate their impact on our decision-making processes.
The Roots of Bias and Prejudice in Society
Bias and prejudice often stem from deeply ingrained social and cultural influences that shape individual perceptions and group stereotypes. Historical power dynamics, economic inequalities, and limited exposure to diverse perspectives contribute to the persistence of unconscious biases and prejudiced attitudes. Understanding these roots is crucial for developing strategies to foster inclusivity and challenge systemic discrimination in society.
Everyday Examples of Bias and Prejudice
Bias appears in everyday situations such as favoring a colleague based on friendship rather than merit, while prejudice often manifests in negative assumptions about individuals from different ethnicities or social groups. For example, a hiring manager might unknowingly favor applicants with similar backgrounds, reflecting implicit bias, whereas denying service to someone due to their race exemplifies explicit prejudice. Recognizing these distinctions helps address discriminatory behaviors that persist in daily interactions.
The Psychological Impact of Bias and Prejudice
Bias and prejudice both distort perception, but prejudice often leads to deeper psychological harm by fostering negative stereotypes and hostility. Exposure to biased attitudes can increase anxiety, reduce self-esteem, and contribute to social exclusion, whereas prejudice intensifies feelings of marginalization and identity threat. The sustained psychological impact of these attitudes undermines mental health and impairs social cohesion.
Addressing Bias and Prejudice in the Workplace
Addressing bias and prejudice in the workplace requires implementing comprehensive diversity training programs that emphasize unconscious bias recognition and inclusive behaviors. Establishing clear anti-discrimination policies and promoting open dialogue cultivates a culture of respect and equity among employees. Regular assessment through employee feedback and performance metrics helps identify ongoing issues and measure progress toward a bias-free environment.
Media Influence: Spreading Bias and Prejudice
Media influence significantly shapes public perception by reinforcing bias and prejudice through selective reporting and sensationalism. Algorithms on social media platforms often amplify echo chambers, intensifying discriminatory views and limiting exposure to diverse perspectives. This persistent exposure perpetuates stereotypes, fostering division and misunderstanding within society.
Strategies to Reduce Bias and Prejudice
Effective strategies to reduce bias and prejudice include promoting intergroup contact, which fosters empathy and understanding through meaningful interactions. Implementing diversity training programs that focus on implicit bias awareness helps individuals recognize and modify unconscious stereotypes. Encouraging inclusive policies and environments supports equitable treatment and diminishes systemic discrimination.
The Role of Education in Combating Bias and Prejudice
Education plays a crucial role in combating bias and prejudice by promoting critical thinking and empathy through inclusive curricula that reflect diverse perspectives. Structured programs that challenge stereotypes and encourage open dialogue help individuals recognize and overcome unconscious biases. Equipping students with cultural competence and social awareness fosters more equitable attitudes and reduces discriminatory behaviors in society.
Moving Toward a Bias-Free and Prejudice-Free Society
Moving toward a bias-free and prejudice-free society requires intentional efforts to recognize and dismantle unconscious stereotypes embedded in cultural norms and institutions. Education systems and media platforms play critical roles in promoting critical thinking and empathy to challenge ingrained misconceptions about race, gender, and other identities. Sustainable change depends on collective accountability and inclusive policies that foster equitable treatment and authentic understanding across diverse communities.
bias vs prejudice Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com