Prejudice involves forming opinions based on unfounded biases or stereotypes, often leading to unfair treatment of pets. Judgment, however, is grounded in objective observation and experience, allowing pet owners to make informed decisions about their animals' behavior and needs. Distinguishing between the two helps promote compassionate care and understanding in pet ownership.
Table of Comparison
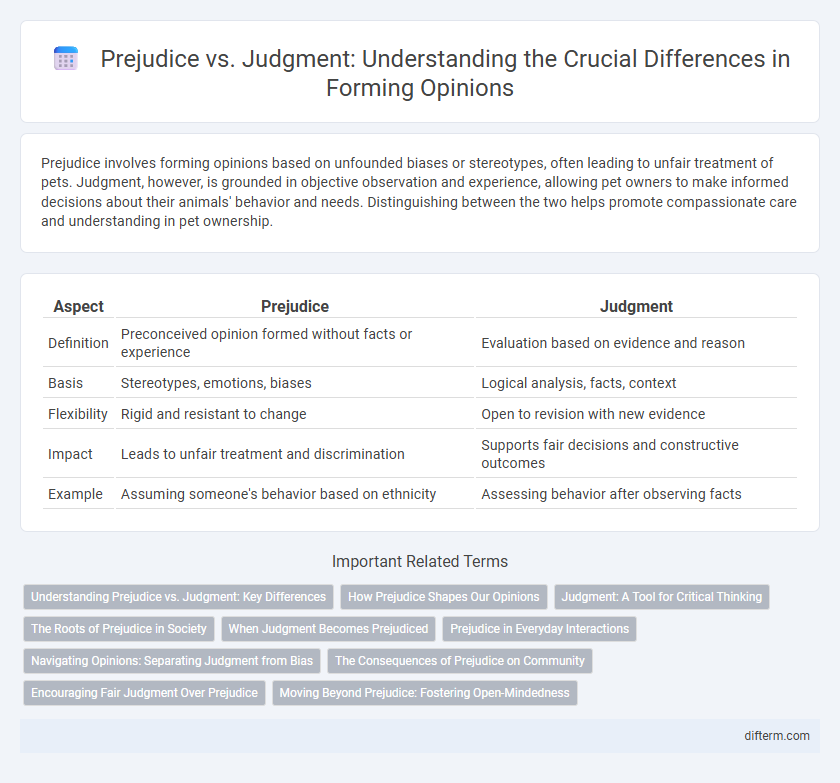
| Aspect | Prejudice | Judgment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Preconceived opinion formed without facts or experience | Evaluation based on evidence and reason |
| Basis | Stereotypes, emotions, biases | Logical analysis, facts, context |
| Flexibility | Rigid and resistant to change | Open to revision with new evidence |
| Impact | Leads to unfair treatment and discrimination | Supports fair decisions and constructive outcomes |
| Example | Assuming someone's behavior based on ethnicity | Assessing behavior after observing facts |
Understanding Prejudice vs. Judgment: Key Differences
Prejudice involves preconceived opinions formed without sufficient knowledge, often based on stereotypes or biases, while judgment is a reasoned evaluation grounded in evidence and critical thinking. Understanding prejudice requires recognizing its emotional and irrational roots, contrasting with judgment's reliance on objective assessment and fairness. Distinguishing between these concepts is essential for fostering empathy and promoting informed decision-making.
How Prejudice Shapes Our Opinions
Prejudice distorts our opinions by embedding biased assumptions before we even assess facts, leading to unfair stereotypes and misunderstandings. Unlike judgment, which relies on evidence and critical thinking, prejudice filters perceptions through emotional and cultural biases, shaping attitudes unconsciously. This skewed lens can hinder objective decision-making and perpetuate social divisions.
Judgment: A Tool for Critical Thinking
Judgment serves as a vital tool for critical thinking, allowing individuals to assess situations and information based on evidence and reason rather than bias. Unlike prejudice, which relies on preconceived notions without sufficient analysis, judgment encourages an open-minded evaluation of facts. Developing sound judgment enhances decision-making skills and promotes fairness in complex social and intellectual contexts.
The Roots of Prejudice in Society
Prejudice in society often stems from deep-seated stereotypes and inherited biases that shape individual and collective perceptions from an early age. These prejudices are reinforced by social norms, media portrayal, and limited exposure to diverse groups, leading to generalized assumptions rather than informed judgments. Understanding the roots of prejudice highlights the importance of education, empathy, and direct interaction in overcoming unfounded biases and fostering more nuanced evaluation.
When Judgment Becomes Prejudiced
Judgment becomes prejudiced when it is based on unfounded stereotypes or biased assumptions rather than objective evidence and individualized evaluation. This shift transforms a reasoned opinion into a harmful generalization that unfairly categorizes people or groups, leading to discrimination and social division. Recognizing and challenging these biases is essential to promote fairness and open-mindedness in decision-making.
Prejudice in Everyday Interactions
Prejudice in everyday interactions often leads to unfair assumptions about individuals based on race, gender, or socioeconomic status, which can perpetuate social inequalities. These biased perceptions hinder genuine communication and create barriers to understanding diverse perspectives. Challenging personal prejudices requires conscious effort to recognize and question ingrained stereotypes during daily social encounters.
Navigating Opinions: Separating Judgment from Bias
Navigating opinions requires a clear distinction between judgment, which is based on reasoned evaluation, and prejudice, rooted in unfounded bias. Understanding the cognitive processes behind each allows individuals to assess situations objectively without allowing ingrained stereotypes to cloud their perspective. This separation is crucial for fostering fair decision-making and promoting empathy in social interactions.
The Consequences of Prejudice on Community
Prejudice fosters division and mistrust within communities, leading to social fragmentation and reduced cohesion. It often results in discrimination and unequal opportunities, which undermine collective progress and economic growth. The persistence of biased attitudes can escalate conflicts, perpetuating cycles of injustice and social instability.
Encouraging Fair Judgment Over Prejudice
Encouraging fair judgment over prejudice fosters unbiased decision-making rooted in facts rather than assumptions. Developing critical thinking skills and empathy helps individuals recognize and challenge their unconscious biases. Promoting diverse perspectives within communities nurtures understanding and reduces the harmful impact of stereotypes.
Moving Beyond Prejudice: Fostering Open-Mindedness
Moving beyond prejudice requires cultivating open-mindedness through active listening and empathy, allowing individuals to challenge their implicit biases and embrace diverse perspectives. Engaging with unfamiliar cultures and ideas promotes critical thinking, reducing snap judgments rooted in stereotypes. This shift fosters inclusive environments where fair and informed evaluations replace unfounded assumptions.
Prejudice vs Judgment Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com