Mobility for pets through Transportation Network Companies (TNCs) offers greater flexibility and on-demand service compared to traditional fleet options, which often operate on fixed schedules and routes. TNCs use advanced technology to connect pet owners with drivers specifically trained to handle animal transport, ensuring safety and comfort. This dynamic approach enhances convenience and accessibility, making pet transportation more efficient and tailored to individual needs.
Table of Comparison
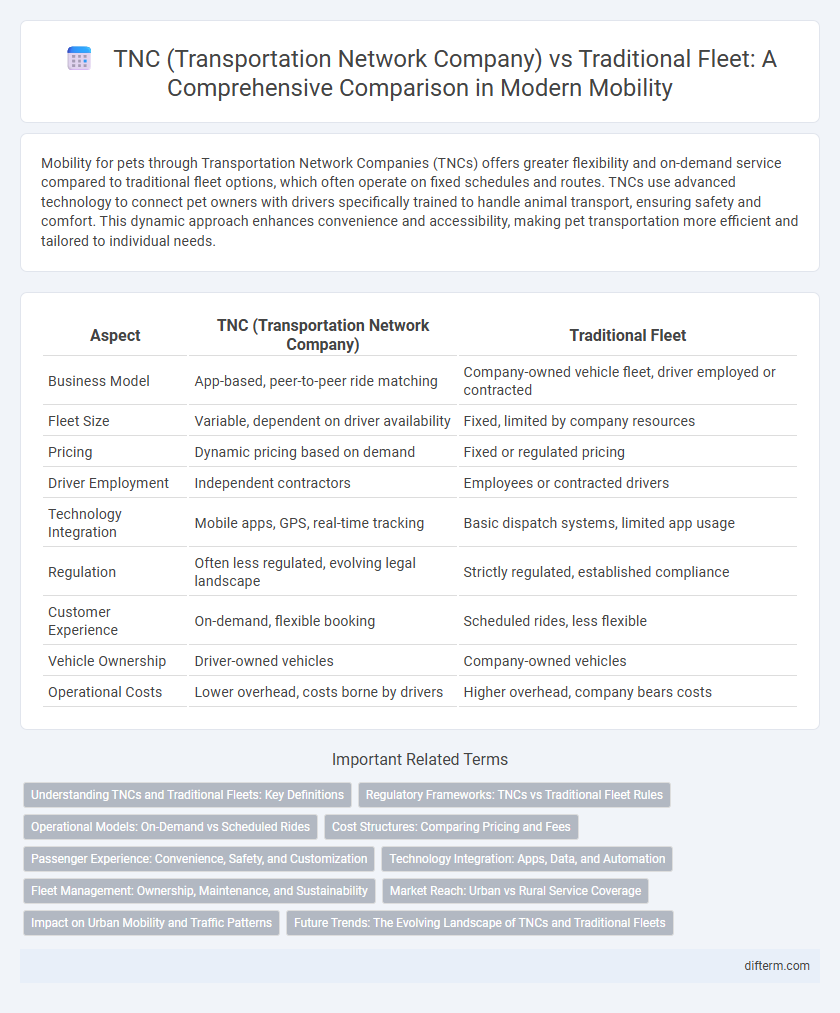
| Aspect | TNC (Transportation Network Company) | Traditional Fleet |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model | App-based, peer-to-peer ride matching | Company-owned vehicle fleet, driver employed or contracted |
| Fleet Size | Variable, dependent on driver availability | Fixed, limited by company resources |
| Pricing | Dynamic pricing based on demand | Fixed or regulated pricing |
| Driver Employment | Independent contractors | Employees or contracted drivers |
| Technology Integration | Mobile apps, GPS, real-time tracking | Basic dispatch systems, limited app usage |
| Regulation | Often less regulated, evolving legal landscape | Strictly regulated, established compliance |
| Customer Experience | On-demand, flexible booking | Scheduled rides, less flexible |
| Vehicle Ownership | Driver-owned vehicles | Company-owned vehicles |
| Operational Costs | Lower overhead, costs borne by drivers | Higher overhead, company bears costs |
Understanding TNCs and Traditional Fleets: Key Definitions
Transportation Network Companies (TNCs) operate digital platforms connecting passengers with independent drivers using personal vehicles, while traditional fleets consist of company-owned or leased vehicles managed by centralized dispatch operations. TNCs leverage app-based ride-hailing services to provide flexible, on-demand transportation, contrasting with the scheduled or pre-arranged services typical of traditional fleets. Understanding these distinctions highlights the impact of technology on modern urban mobility and fleet management strategies.
Regulatory Frameworks: TNCs vs Traditional Fleet Rules
Transportation Network Companies (TNCs) operate under distinct regulatory frameworks compared to traditional fleets, often facing more flexible licensing and insurance requirements that vary by jurisdiction. Traditional fleet vehicles are subject to stringent safety inspections, fixed-route mandates, and comprehensive commercial vehicle regulations enforced by local or national authorities. Regulatory disparities influence operational costs, liability standards, and market entry barriers, shaping competitive dynamics between TNCs and traditional fleet services.
Operational Models: On-Demand vs Scheduled Rides
Transportation Network Companies (TNCs) operate primarily on an on-demand ride model, leveraging real-time data and mobile apps to match riders with nearby drivers instantly, enhancing flexibility and reducing wait times. In contrast, traditional fleets predominantly follow a scheduled rides model, relying on pre-booked trips that optimize routes and vehicle allocation for predictable demand. The operational efficiency of TNCs stems from dynamic dispatch algorithms that adapt to fluctuating demand patterns, while traditional fleets benefit from route planning and fixed schedules that cater to consistent passenger flows.
Cost Structures: Comparing Pricing and Fees
Transportation Network Companies (TNCs) often operate with lower fixed costs compared to traditional fleets due to their asset-light business model relying on independent drivers. Traditional fleets incur higher expenses from vehicle ownership, maintenance, and insurance, which are typically reflected in higher base fares and fixed fees. Variable pricing models used by TNCs, including surge pricing and dynamic fee adjustments, enable more flexible cost structures that can offer competitive pricing relative to the more rigid, standardized fee schedules of traditional fleets.
Passenger Experience: Convenience, Safety, and Customization
Transportation Network Companies (TNCs) offer enhanced passenger convenience through on-demand ride requests, real-time tracking, and cashless payments, significantly reducing wait times compared to traditional fleet services. Safety features in TNCs include driver background checks, in-app emergency buttons, and GPS monitoring, providing a higher sense of security for passengers. Customization options such as ride preferences, vehicle choice, and rating systems enable a more personalized travel experience that traditional fleets often cannot match.
Technology Integration: Apps, Data, and Automation
Transportation Network Companies (TNCs) leverage advanced technology integration through user-friendly apps, real-time data analytics, and automation, significantly enhancing ride efficiency and customer experience compared to traditional fleets. Traditional fleets often rely on legacy dispatch systems with limited data utilization, resulting in less dynamic routing and slower response times. TNC platforms continuously optimize operations using machine learning algorithms and GPS tracking to reduce wait times and improve fleet management.
Fleet Management: Ownership, Maintenance, and Sustainability
Transportation Network Companies (TNCs) operate decentralized fleets by leveraging driver-owned vehicles, reducing direct ownership costs and shifting maintenance responsibilities to individual drivers, contrasting traditional fleet management where companies maintain centralized vehicle ownership and rigorous maintenance schedules. Traditional fleets enable tighter control over vehicle conditions and sustainability initiatives, often incorporating electric or hybrid vehicles to minimize environmental impact, whereas TNCs face challenges in enforcing consistent sustainability practices across diverse, independently maintained vehicles. Fleet management in traditional models emphasizes long-term asset utilization and lifecycle cost optimization, while TNCs prioritize flexible scalability and reduced capital expenditure, impacting overall sustainability and operational efficiency.
Market Reach: Urban vs Rural Service Coverage
Transportation Network Companies (TNCs) excel in urban market reach by leveraging digital platforms and flexible driver networks, enabling rapid response and extensive service coverage in densely populated areas. Traditional fleets typically maintain stronger presence in rural regions due to established infrastructure and local familiarity, but often face challenges scaling in cities. The contrasting market reach highlights TNCs' dominance in urban mobility and traditional fleets' resilience in rural transport service coverage.
Impact on Urban Mobility and Traffic Patterns
Transportation Network Companies (TNCs) like Uber and Lyft reshape urban mobility by offering flexible, on-demand rides that reduce personal car ownership but may increase empty vehicle miles traveled, contributing to traffic congestion. Traditional fleet services operate on predetermined routes and schedules, which can optimize traffic patterns through predictable demand, yet lack the customization and real-time responsiveness of TNCs. The dynamic nature of TNCs introduces complex traffic impacts, including higher curbside demand and potential displacement of public transit ridership, challenging urban planners to balance efficiency and sustainability.
Future Trends: The Evolving Landscape of TNCs and Traditional Fleets
The future of mobility sees Transportation Network Companies (TNCs) integrating autonomous vehicles and electric fleets, enhancing efficiency and sustainability compared to traditional fleets reliant on human drivers and fossil fuels. Data-driven ride-hailing algorithms in TNCs optimize route planning and dynamic pricing, outpacing the static scheduling systems of traditional fleets. Emerging trends emphasize multimodal connectivity, with TNC platforms partnering with public transit to offer seamless, integrated mobility solutions.
TNC (Transportation Network Company) vs traditional fleet Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com