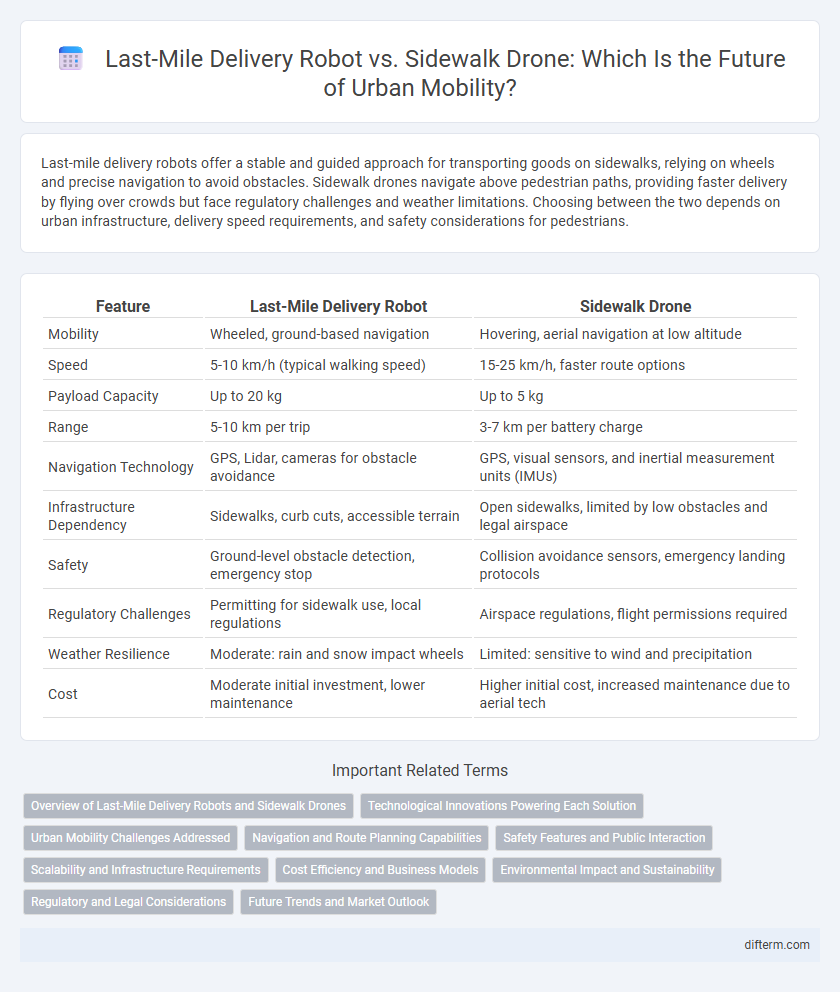
Last-mile delivery robots offer a stable and guided approach for transporting goods on sidewalks, relying on wheels and precise navigation to avoid obstacles. Sidewalk drones navigate above pedestrian paths, providing faster delivery by flying over crowds but face regulatory challenges and weather limitations. Choosing between the two depends on urban infrastructure, delivery speed requirements, and safety considerations for pedestrians.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Last-Mile Delivery Robot | Sidewalk Drone |
|---|---|---|
| Mobility | Wheeled, ground-based navigation | Hovering, aerial navigation at low altitude |
| Speed | 5-10 km/h (typical walking speed) | 15-25 km/h, faster route options |
| Payload Capacity | Up to 20 kg | Up to 5 kg |
| Range | 5-10 km per trip | 3-7 km per battery charge |
| Navigation Technology | GPS, Lidar, cameras for obstacle avoidance | GPS, visual sensors, and inertial measurement units (IMUs) |
| Infrastructure Dependency | Sidewalks, curb cuts, accessible terrain | Open sidewalks, limited by low obstacles and legal airspace |
| Safety | Ground-level obstacle detection, emergency stop | Collision avoidance sensors, emergency landing protocols |
| Regulatory Challenges | Permitting for sidewalk use, local regulations | Airspace regulations, flight permissions required |
| Weather Resilience | Moderate: rain and snow impact wheels | Limited: sensitive to wind and precipitation |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment, lower maintenance | Higher initial cost, increased maintenance due to aerial tech |
Overview of Last-Mile Delivery Robots and Sidewalk Drones
Last-mile delivery robots navigate sidewalks and urban pathways using advanced sensors and AI to transport goods directly to consumers, offering a scalable solution for dense metropolitan areas. Sidewalk drones, equipped with compact rotor systems and lightweight frames, provide aerial delivery primarily in congested environments where ground traffic delays are significant. Both technologies aim to reduce delivery times and lower operational costs while enhancing urban mobility efficiency.
Technological Innovations Powering Each Solution
Last-mile delivery robots leverage advanced sensor fusion, AI-powered navigation, and real-time mapping to autonomously maneuver urban environments with high precision. Sidewalk drones integrate cutting-edge lightweight materials, multi-rotor propulsion systems, and automated obstacle avoidance algorithms to achieve efficient aerial mobility in dense pedestrian areas. Both solutions utilize machine learning models and IoT connectivity to optimize route planning, enhance delivery speed, and ensure safety compliance in dynamic urban settings.
Urban Mobility Challenges Addressed
Last-mile delivery robots and sidewalk drones address urban mobility challenges by reducing congestion and lowering carbon emissions in densely populated areas. Delivery robots navigate sidewalks with precise obstacle avoidance, enhancing pedestrian safety, while sidewalk drones utilize compact aerial routes to bypass ground traffic entirely. Both technologies improve delivery efficiency and reliability, tackling urban logistics bottlenecks and promoting sustainable city transportation systems.
Navigation and Route Planning Capabilities
Last-mile delivery robots leverage advanced LiDAR sensors and AI-based route planning algorithms to navigate complex urban sidewalks with precision and obstacle avoidance. Sidewalk drones utilize real-time GPS data combined with computer vision to dynamically adjust flight paths, ensuring efficient navigation over pedestrian areas. Both systems incorporate machine learning models to optimize routes for speed, safety, and energy efficiency in dense, variable environments.
Safety Features and Public Interaction
Last-mile delivery robots incorporate enclosed designs with sensors and cameras to detect obstacles and ensure pedestrian safety, while sidewalk drones utilize low-altitude flight controls and obstacle avoidance technology to minimize accidents. Both technologies integrate real-time communication systems to interact with the public, including audio alerts and visual signals that inform pedestrians of their presence and movement intentions. Enhanced safety protocols, such as emergency stop functions and speed regulation, are critical in maintaining trust and preventing incidents in busy urban environments.
Scalability and Infrastructure Requirements
Last-mile delivery robots require well-maintained sidewalks and curb ramps to navigate urban environments efficiently, limiting their scalability in areas with uneven or obstructed pedestrian paths. Sidewalk drones, capable of aerial movement, bypass ground-level obstacles but demand robust 5G connectivity and dedicated airspace regulations to scale effectively. Infrastructure investments for sidewalk drones focus on communication networks and air traffic management, while robots rely on physical sidewalk quality and pedestrian infrastructure enhancements.
Cost Efficiency and Business Models
Last-mile delivery robots demonstrate higher cost efficiency than sidewalk drones by minimizing maintenance expenses and energy consumption while leveraging existing sidewalk infrastructure, which reduces deployment complexity. Business models for delivery robots often emphasize subscription services and partnerships with retailers to ensure predictable revenue streams and scalability. Sidewalk drones, while innovative, face increased operational costs and regulatory challenges, prompting models centered on niche deliveries and premium pricing strategies.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Last-mile delivery robots and sidewalk drones both offer sustainable alternatives to traditional delivery vehicles, significantly reducing carbon emissions by utilizing electric power and minimizing reliance on fossil fuels. Delivery robots, designed for ground navigation, typically consume less energy per trip due to efficient route planning and physical contact with sidewalks, whereas sidewalk drones, which fly short distances, have higher energy demands but reduce road congestion and noise pollution. Integrating these technologies into urban logistics supports environmental goals by lowering greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable, low-impact delivery solutions.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations
Last-mile delivery robots face stringent regulatory frameworks governing sidewalk usage, speed limits, and pedestrian safety, which vary significantly across cities and countries. Sidewalk drones encounter additional legal challenges related to airspace regulations, privacy concerns, and potential interference with manned aircraft. Compliance with data protection laws and securing operational permits are critical for both technologies to achieve scalable urban deployment.
Future Trends and Market Outlook
Last-mile delivery robots and sidewalk drones are poised to transform urban logistics by enhancing efficiency and reducing delivery times. Market forecasts indicate a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 20% for autonomous delivery systems through 2030, driven by rising e-commerce demand and advancements in AI navigation. Future trends emphasize integration with smart city infrastructure, improved battery technology, and regulatory frameworks fostering widespread adoption in congested metropolitan areas.
last-mile delivery robot vs sidewalk drone Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com