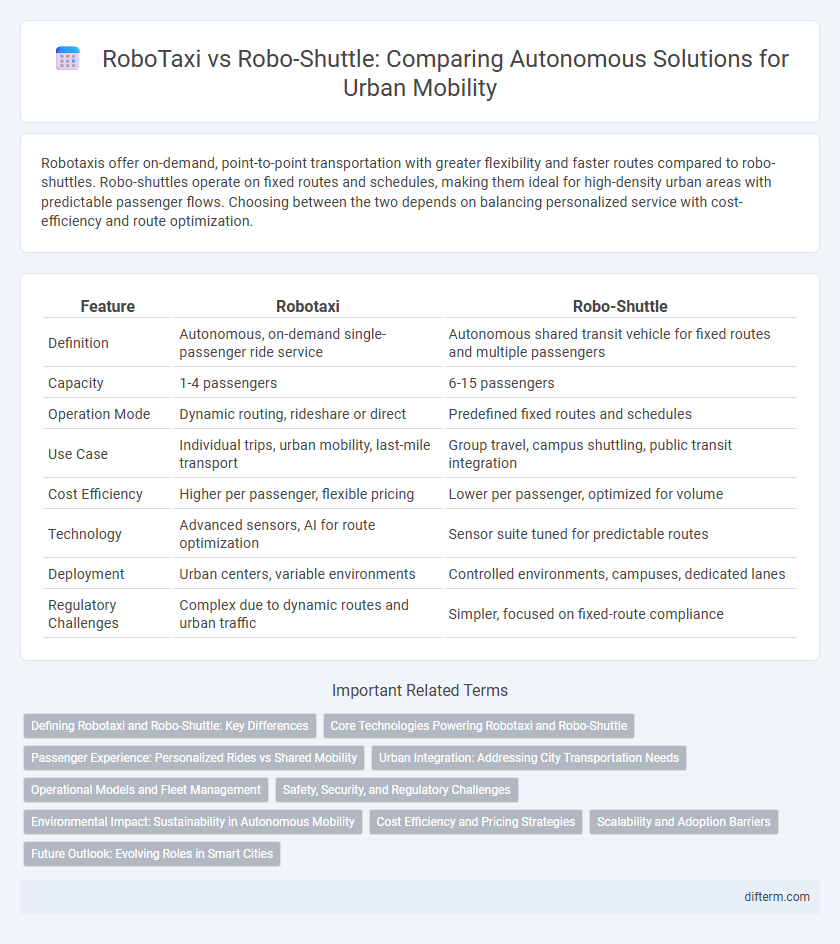
Robotaxis offer on-demand, point-to-point transportation with greater flexibility and faster routes compared to robo-shuttles. Robo-shuttles operate on fixed routes and schedules, making them ideal for high-density urban areas with predictable passenger flows. Choosing between the two depends on balancing personalized service with cost-efficiency and route optimization.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Robotaxi | Robo-Shuttle |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Autonomous, on-demand single-passenger ride service | Autonomous shared transit vehicle for fixed routes and multiple passengers |
| Capacity | 1-4 passengers | 6-15 passengers |
| Operation Mode | Dynamic routing, rideshare or direct | Predefined fixed routes and schedules |
| Use Case | Individual trips, urban mobility, last-mile transport | Group travel, campus shuttling, public transit integration |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher per passenger, flexible pricing | Lower per passenger, optimized for volume |
| Technology | Advanced sensors, AI for route optimization | Sensor suite tuned for predictable routes |
| Deployment | Urban centers, variable environments | Controlled environments, campuses, dedicated lanes |
| Regulatory Challenges | Complex due to dynamic routes and urban traffic | Simpler, focused on fixed-route compliance |
Defining Robotaxi and Robo-Shuttle: Key Differences
Robotaxis are autonomous, driverless vehicles designed primarily for individual or small group transportation, operating on-demand like traditional taxis but without human drivers. Robo-shuttles are larger, shared autonomous vehicles intended for fixed-route or flexible-route transit, accommodating multiple passengers simultaneously to optimize urban mobility. The key difference lies in capacity and operation mode: robotaxis emphasize personalized, door-to-door service, while robo-shuttles focus on cost-effective mass transit solutions in urban and suburban environments.
Core Technologies Powering Robotaxi and Robo-Shuttle
Robotaxi systems leverage advanced AI-driven perception, precise LiDAR mapping, and high-performance computing for dynamic urban navigation, enabling individualized point-to-point travel. Robo-shuttles rely on robust sensor fusion, geofencing technology, and optimized route algorithms designed to manage fixed or semi-flexible paths within controlled environments. Both platforms integrate V2X communication and real-time data processing to ensure safe, efficient autonomous mobility in complex traffic scenarios.
Passenger Experience: Personalized Rides vs Shared Mobility
Robotaxis offer personalized rides tailored to individual passenger preferences, enhancing comfort and convenience through customizable in-vehicle settings and direct point-to-point travel. Robo-shuttles prioritize shared mobility by optimizing routes for multiple passengers, promoting social interaction and reducing costs per ride. Passenger experience contrasts as robotaxis provide exclusive, flexible journeys, while robo-shuttles focus on efficient, community-oriented transportation solutions.
Urban Integration: Addressing City Transportation Needs
Robotaxis offer flexible, on-demand point-to-point transport ideal for diverse urban routes and individual passengers, enhancing last-mile connectivity. Robo-shuttles serve fixed routes with higher passenger capacity, efficiently managing peak-time commuter flows and reducing traffic congestion on busy corridors. Both solutions integrate with public transit systems, facilitating seamless multimodal trips and optimizing urban mobility networks.
Operational Models and Fleet Management
Robotaxis operate on-demand, providing individual rides with dynamic routing, which requires sophisticated real-time fleet management systems to optimize vehicle availability and reduce wait times. Robo-shuttles typically follow fixed or semi-fixed routes with scheduled stops, enabling predictable fleet deployment and simpler operational models focused on high passenger volumes in specific corridors. Efficient fleet management for robotaxis emphasizes flexibility and adaptive dispatch algorithms, while robo-shuttle systems prioritize route optimization and capacity planning to maximize service frequency and coverage.
Safety, Security, and Regulatory Challenges
Robotaxis and robo-shuttles face significant safety challenges, including reliable obstacle detection and passenger protection in diverse urban environments. Security concerns encompass safeguarding against cyber-attacks and ensuring data privacy for passengers, crucial for maintaining user trust. Regulatory hurdles involve navigating complex local and national laws while achieving certifications that validate safety and operational standards for autonomous public transportation.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability in Autonomous Mobility
Robotaxis offer flexible, on-demand transportation that can reduce private car ownership and lower emissions by optimizing ride-sharing and route efficiency. Robo-shuttles, typically operating on fixed routes, contribute to sustainability by replacing high-occupancy transit trips with electric or zero-emission vehicles, decreasing urban congestion and pollution. Both solutions leverage autonomous technology to promote cleaner, energy-efficient mobility, supporting broader goals of reducing carbon footprints in urban environments.
Cost Efficiency and Pricing Strategies
Robotaxis generally offer higher cost efficiency due to their on-demand, point-to-point service model, which maximizes vehicle utilization and minimizes idle time. Robo-shuttles, with fixed routes and shared rides, reduce operational costs by serving multiple passengers simultaneously but may face pricing challenges from lower flexibility. Dynamic pricing strategies in robotaxis optimize revenue through demand-responsive fares, while robo-shuttles often rely on flat or subscription-based pricing to attract consistent ridership.
Scalability and Adoption Barriers
Robotaxis offer greater scalability due to their flexible routing capabilities and lower infrastructure requirements compared to robo-shuttles, which often operate on fixed routes and need dedicated lanes or stops. Adoption barriers for robotaxis include regulatory approval and public trust in fully autonomous vehicles, while robo-shuttles face challenges related to limited service areas and integration with existing transit systems. Both modes require advancements in technology and policy frameworks to achieve widespread deployment.
Future Outlook: Evolving Roles in Smart Cities
Robotaxis are expected to dominate long-distance urban travel with their flexibility and on-demand service, while robo-shuttles will transform short-distance commutes through fixed-route, high-frequency networks. Integration of advanced AI and V2X communication technologies will enable both to operate seamlessly within smart city ecosystems, enhancing traffic flow and reducing emissions. City planners are prioritizing multimodal connectivity, where robotaxis and robo-shuttles collaboratively complement public transit to optimize urban mobility efficiency.
robotaxi vs robo-shuttle Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com