Demand-responsive transport offers flexible routing and timing, adapting to individual passenger needs for greater convenience and efficiency, especially in areas with low or variable demand. Scheduled transport operates on fixed routes and timetables, providing predictability and simplicity but often lacking the adaptability required for dynamic travel patterns. For mobility, demand-responsive services enhance accessibility by tailoring trips on demand, while scheduled transport remains valuable for high-density corridors with consistent passenger volumes.
Table of Comparison
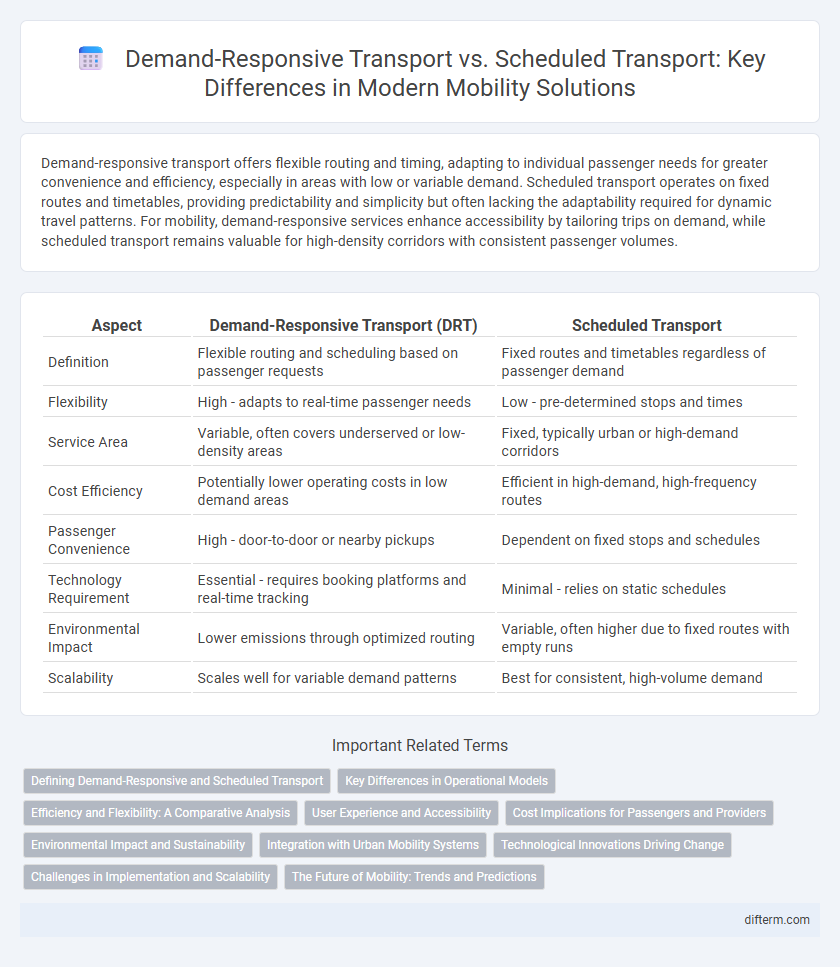
| Aspect | Demand-Responsive Transport (DRT) | Scheduled Transport |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Flexible routing and scheduling based on passenger requests | Fixed routes and timetables regardless of passenger demand |
| Flexibility | High - adapts to real-time passenger needs | Low - pre-determined stops and times |
| Service Area | Variable, often covers underserved or low-density areas | Fixed, typically urban or high-demand corridors |
| Cost Efficiency | Potentially lower operating costs in low demand areas | Efficient in high-demand, high-frequency routes |
| Passenger Convenience | High - door-to-door or nearby pickups | Dependent on fixed stops and schedules |
| Technology Requirement | Essential - requires booking platforms and real-time tracking | Minimal - relies on static schedules |
| Environmental Impact | Lower emissions through optimized routing | Variable, often higher due to fixed routes with empty runs |
| Scalability | Scales well for variable demand patterns | Best for consistent, high-volume demand |
Defining Demand-Responsive and Scheduled Transport
Demand-responsive transport (DRT) adapts routes and schedules dynamically based on real-time passenger requests, optimizing flexibility and efficiency in service provision. Scheduled transport operates on fixed routes and timetables, offering consistent and predictable service useful for mass transit systems. Differentiating these modes highlights the contrast between user-driven demand and pre-planned service patterns in urban mobility frameworks.
Key Differences in Operational Models
Demand-responsive transport operates on flexible routes and schedules, adjusting in real-time to passenger requests, enhancing convenience and reducing wait times. Scheduled transport follows fixed routes and timetables, optimizing resource allocation and providing predictable service for regular commuters. The operational model of demand-responsive transport leverages advanced algorithms and dynamic routing, while scheduled transport relies on established infrastructure and consistent scheduling frameworks.
Efficiency and Flexibility: A Comparative Analysis
Demand-responsive transport (DRT) optimizes efficiency by dynamically adjusting routes and schedules based on real-time passenger demand, reducing idle times and operational costs compared to fixed-route scheduled transport. Scheduled transport offers predictable timetables and fixed routes, ensuring reliability but often resulting in underutilized capacity during off-peak hours. The flexibility of DRT enhances service coverage in low-density areas, while scheduled transport provides higher frequency and capacity on busy corridors, highlighting a trade-off between tailored service and operational consistency.
User Experience and Accessibility
Demand-responsive transport enhances user experience by offering flexible routes and on-demand pick-ups, significantly improving accessibility for passengers with mobility challenges and those in underserved areas. Scheduled transport, while reliable with fixed routes and timetables, often limits accessibility due to its rigid structure, making it less convenient for users requiring personalized travel options. Integrating demand-responsive services into existing transport networks can bridge gaps in accessibility and elevate overall passenger satisfaction.
Cost Implications for Passengers and Providers
Demand-responsive transport reduces operational costs for providers by optimizing routes based on real-time demand, leading to lower fuel consumption and decreased vehicle wear. Passengers often face variable pricing tied to distance and demand, which can result in cost savings during off-peak hours but higher fares during peak times. Scheduled transport offers predictable fares and fixed routes, providing cost stability for passengers but potentially higher operational expenses for providers due to underutilized capacity and rigid scheduling.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Demand-responsive transport (DRT) significantly reduces environmental impact by optimizing routes and maximizing vehicle occupancy, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to scheduled transport with fixed routes and low passenger loads. DRT enhances sustainability by minimizing fuel consumption and traffic congestion, thus supporting urban air quality improvements and reducing carbon footprints. In contrast, scheduled transport often results in underutilized capacity and higher per-passenger emissions, making DRT a more eco-friendly alternative for flexible, efficient mobility solutions.
Integration with Urban Mobility Systems
Demand-responsive transport enhances urban mobility integration by offering flexible routing and real-time responsiveness, seamlessly connecting with public transit hubs and adapting to fluctuating passenger demand. Scheduled transport operates on fixed routes and timetables, providing reliability but limited adaptability within dynamic urban environments. Integration of demand-responsive solutions with existing scheduled services optimizes coverage, reduces transit gaps, and improves overall efficiency in urban transportation networks.
Technological Innovations Driving Change
Demand-responsive transport leverages advanced algorithms, real-time data analytics, and mobile applications to dynamically adjust routes and pick-up times, enhancing efficiency and reducing wait times. Scheduled transport relies on fixed routes and timetables, limiting flexibility but benefiting from established infrastructure and predictability. Emerging technologies such as AI-driven route optimization and IoT sensors are propelling demand-responsive systems to become more adaptive and user-centric, reshaping urban mobility landscapes.
Challenges in Implementation and Scalability
Demand-responsive transport faces challenges in implementation due to fluctuating demand patterns, requiring sophisticated real-time data integration and dynamic routing algorithms to maintain efficiency. Scalability is limited by the need for substantial investments in technology infrastructure and continuous operational adjustments to accommodate varying user densities. Scheduled transport, while easier to scale owing to fixed routes and timings, struggles with inefficiencies when demand is unpredictable, leading to underutilized vehicles and increased operational costs.
The Future of Mobility: Trends and Predictions
Demand-responsive transport (DRT) is poised to revolutionize the future of mobility by offering flexible, on-demand routing that adapts to real-time passenger needs, reducing wait times and optimizing fleet efficiency. Scheduled transport maintains reliability for high-capacity routes, but the integration of DRT with traditional systems predicts a shift toward hybrid models, enhancing urban connectivity and decreasing congestion. Advances in AI and data analytics will further refine demand forecasting, enabling seamless multimodal transport ecosystems that prioritize sustainability and user convenience.
Demand-responsive transport vs Scheduled transport Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com