Ride-sharing offers a convenient way for individuals to share trips with others going in the same direction, reducing travel costs and minimizing environmental impact. Car-sharing provides users with greater flexibility by allowing access to vehicles on demand without ownership responsibilities, ideal for short-term or spontaneous use. Comparing these options highlights ride-sharing as a social and cost-effective solution, while car-sharing excels in offering independence and availability for diverse mobility needs.
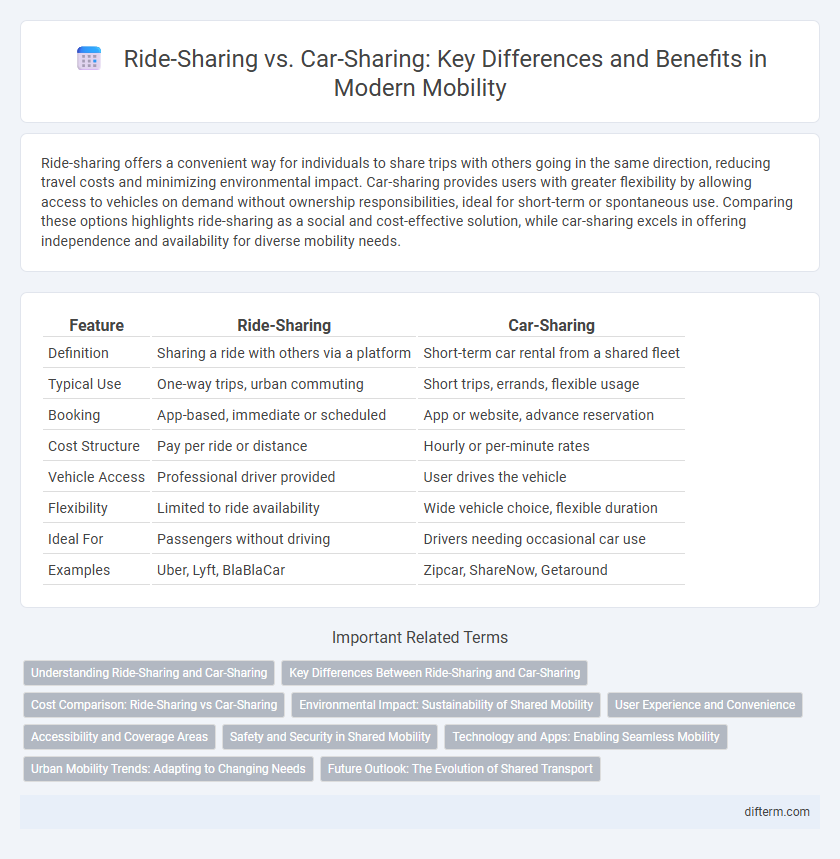
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ride-Sharing | Car-Sharing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sharing a ride with others via a platform | Short-term car rental from a shared fleet |
| Typical Use | One-way trips, urban commuting | Short trips, errands, flexible usage |
| Booking | App-based, immediate or scheduled | App or website, advance reservation |
| Cost Structure | Pay per ride or distance | Hourly or per-minute rates |
| Vehicle Access | Professional driver provided | User drives the vehicle |
| Flexibility | Limited to ride availability | Wide vehicle choice, flexible duration |
| Ideal For | Passengers without driving | Drivers needing occasional car use |
| Examples | Uber, Lyft, BlaBlaCar | Zipcar, ShareNow, Getaround |
Understanding Ride-Sharing and Car-Sharing
Ride-sharing involves multiple passengers sharing a single vehicle for a common route, reducing costs and traffic congestion through platforms like Uber and Lyft. Car-sharing offers users short-term access to vehicles on-demand, typically through services such as Zipcar or Car2Go, promoting flexibility without ownership. Both models support sustainable urban mobility by optimizing vehicle usage and lowering individual carbon footprints.
Key Differences Between Ride-Sharing and Car-Sharing
Ride-sharing involves multiple passengers sharing a single vehicle with a driver, optimizing route efficiency and reducing individual travel costs, whereas car-sharing provides users with access to a vehicle for personal use without a driver, offering greater flexibility and autonomy. Ride-sharing services typically operate on demand for specific trips, while car-sharing platforms allow hourly or daily rentals, catering to varied mobility needs. The environmental impact of ride-sharing tends to be lower due to increased vehicle occupancy, while car-sharing reduces the necessity of private car ownership, contributing to decreased urban congestion.
Cost Comparison: Ride-Sharing vs Car-Sharing
Ride-sharing services typically incur costs based on distance and time, often resulting in variable pricing influenced by demand and surge rates, making short or infrequent trips more economical. Car-sharing offers a flat hourly or daily rate with fuel and insurance included, providing cost efficiency for longer usage or frequent trips. Evaluating total expenses reveals ride-sharing suits those seeking occasional mobility without ownership, while car-sharing benefits users requiring extended vehicle access without long-term commitment.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability of Shared Mobility
Ride-sharing platforms reduce carbon emissions by maximizing vehicle occupancy, decreasing the number of individual trips and lowering overall fuel consumption. Car-sharing services promote sustainable urban mobility through reduced private car ownership, leading to less parking demand and fewer vehicles on roads. Both models contribute to environmental benefits by encouraging efficient resource use and supporting the transition to greener transportation systems.
User Experience and Convenience
Ride-sharing offers users real-time matching with nearby drivers, enhancing flexibility and reducing waiting times, while car-sharing provides autonomous access to vehicles without the need for a driver, promoting independence and control. User experience in ride-sharing is often defined by app interface efficiency and seamless payment integration, whereas car-sharing emphasizes vehicle availability, ease of pickup/drop-off, and minimal fuel or charging concerns. Convenience in ride-sharing largely depends on dynamic routing and pooled rides, while car-sharing excels in offering spontaneous car access for extended periods, catering to diverse mobility needs.
Accessibility and Coverage Areas
Ride-sharing services offer flexible pick-up and drop-off points, enhancing accessibility in densely populated urban areas and providing door-to-door convenience for users. Car-sharing programs typically feature designated parking spots and fixed service zones, which can limit coverage areas but ensure vehicle availability within specific neighborhoods. Both models contribute to reducing private car ownership, yet ride-sharing generally boasts broader geographic reach while car-sharing emphasizes localized control and reliability.
Safety and Security in Shared Mobility
Ride-sharing platforms implement rigorous driver background checks and real-time GPS tracking to enhance passenger safety, reducing risks associated with unknown drivers. Car-sharing services prioritize vehicle maintenance, keyless entry systems, and secure app-based access to protect users and prevent theft or unauthorized use. Both models continuously invest in trust-building features such as user reviews, emergency assistance, and insurance coverage to bolster overall security in shared mobility ecosystems.
Technology and Apps: Enabling Seamless Mobility
Ride-sharing platforms leverage advanced GPS technology and real-time data analytics to match riders with drivers efficiently, optimizing routes and reducing wait times. Car-sharing apps utilize IoT connectivity and mobile integration to grant users instant access to vehicles, allowing for flexible, on-demand usage without traditional rental procedures. These technologies enhance seamless mobility by providing user-friendly, scalable solutions tailored to urban transportation needs.
Urban Mobility Trends: Adapting to Changing Needs
Ride-sharing platforms optimize urban mobility by reducing private vehicle usage and lowering emissions through shared rides, fostering efficient congestion management. Car-sharing services provide flexible vehicle access without ownership, addressing short-term transportation needs and decreasing parking demand in dense city environments. Both models complement public transit by enhancing first- and last-mile connectivity, driving sustainable urban mobility trends.
Future Outlook: The Evolution of Shared Transport
Ride-sharing and car-sharing continue to transform urban mobility by reducing reliance on private vehicle ownership and decreasing traffic congestion. Advances in AI-driven routing algorithms and electric vehicle integration are set to enhance efficiency and environmental benefits in both models. Emerging trends suggest a convergence towards multimodal platforms that seamlessly blend ride-sharing, car-sharing, and public transit for optimized user experience.
ride-sharing vs car-sharing Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com