Active wheelchairs offer enhanced maneuverability and lightweight design, ideal for users seeking greater independence and agility in daily activities. Passive wheelchairs prioritize comfort and stability, often featuring robust frames suited for users who require minimal physical effort to navigate. Choosing between active and passive wheelchairs depends on individual mobility needs, lifestyle, and the level of physical activity desired.
Table of Comparison
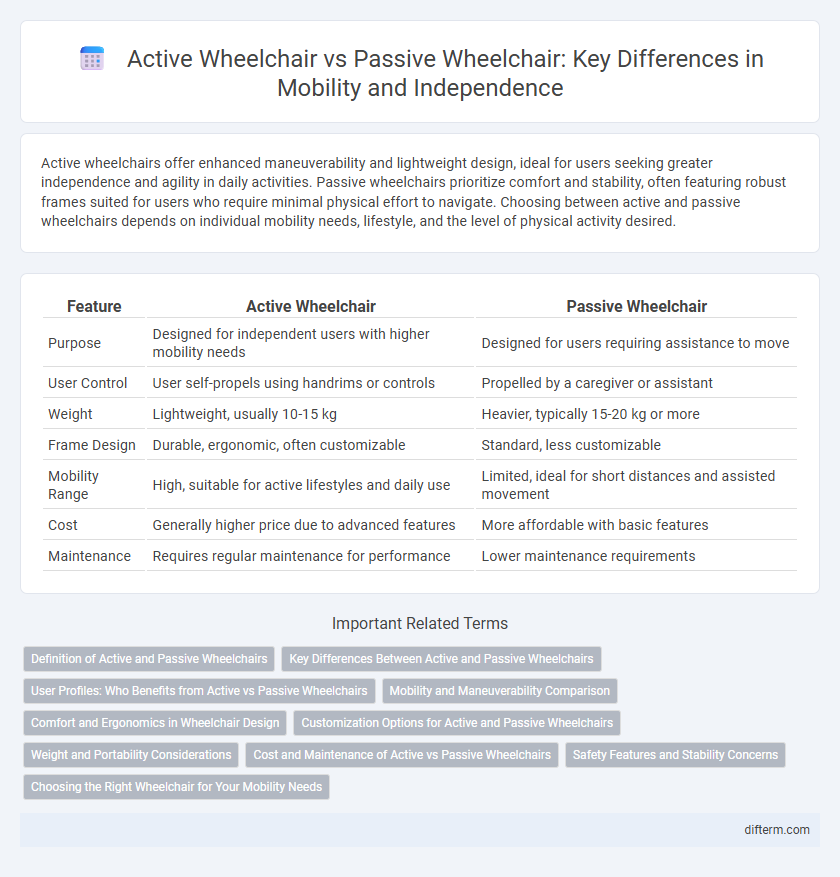
| Feature | Active Wheelchair | Passive Wheelchair |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Designed for independent users with higher mobility needs | Designed for users requiring assistance to move |
| User Control | User self-propels using handrims or controls | Propelled by a caregiver or assistant |
| Weight | Lightweight, usually 10-15 kg | Heavier, typically 15-20 kg or more |
| Frame Design | Durable, ergonomic, often customizable | Standard, less customizable |
| Mobility Range | High, suitable for active lifestyles and daily use | Limited, ideal for short distances and assisted movement |
| Cost | Generally higher price due to advanced features | More affordable with basic features |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance for performance | Lower maintenance requirements |
Definition of Active and Passive Wheelchairs
Active wheelchairs are designed for users who independently propel themselves, featuring lightweight frames and enhanced maneuverability tailored for everyday mobility and sports activities. Passive wheelchairs require an attendant or caregiver to push and support the user, emphasizing comfort and stability with heavier, more robust frames suited for limited self-mobility. Both types cater to different levels of physical ability and lifestyle needs, optimizing mobility solutions accordingly.
Key Differences Between Active and Passive Wheelchairs
Active wheelchairs are designed for users seeking greater independence and mobility, featuring lightweight frames and enhanced maneuverability, while passive wheelchairs prioritize comfort and support with heavier, more stable constructions ideal for transportation by a caregiver. Key differences include control mechanisms, with active wheelchairs allowing self-propulsion through large rear wheels, whereas passive wheelchairs often require assistance due to smaller wheels and less ergonomic design. Battery-powered options are uncommon in traditional active models but may be integrated into passive wheelchairs for easier transport in some cases.
User Profiles: Who Benefits from Active vs Passive Wheelchairs
Active wheelchairs are designed for users with higher upper body strength and mobility, such as athletes or individuals seeking independence and enhanced maneuverability in daily activities. Passive wheelchairs better serve users with limited strength or endurance, including elderly individuals or those with severe disabilities who rely on caregivers for mobility support. Choosing between active and passive wheelchairs depends on the user's physical capabilities, lifestyle needs, and level of required assistance.
Mobility and Maneuverability Comparison
Active wheelchairs offer superior mobility and maneuverability due to their lightweight design and user-powered controls, allowing for greater speed and agility in various environments. Passive wheelchairs, typically heavier and designed for assistance by a caregiver, provide limited maneuverability and are less suited for independent navigation. Users seeking enhanced autonomy and responsiveness often prefer active wheelchairs for improved mobility performance.
Comfort and Ergonomics in Wheelchair Design
Active wheelchairs prioritize lightweight materials and adjustable components to enhance mobility and user control, significantly improving comfort during prolonged use. Ergonomic features such as contoured seating, customizable backrests, and pressure-relief cushions reduce the risk of pressure sores and musculoskeletal strain. Passive wheelchairs often lack these advanced ergonomic adjustments, focusing instead on basic support and stability, which may compromise comfort during extended periods of use.
Customization Options for Active and Passive Wheelchairs
Active wheelchairs offer extensive customization options including adjustable seat height, lightweight frames, and specialized wheel configurations designed for enhanced maneuverability and user independence. Passive wheelchairs typically feature more standardized components with limited customization, focusing on comfort and ease of use for caregivers, often including adjustable armrests and footrests. Customization in active models prioritizes performance and adaptability for various activities, while passive models emphasize stability and support.
Weight and Portability Considerations
Active wheelchairs are designed with lightweight materials such as aluminum or carbon fiber, enhancing portability and ease of maneuverability for users who require frequent movement or travel. Passive wheelchairs tend to be heavier due to sturdier frames and additional features aimed at comfort rather than mobility, which can limit ease of transport and user handling. Weight and portability are key factors influencing the choice between active and passive wheelchairs, impacting user independence and convenience in different environments.
Cost and Maintenance of Active vs Passive Wheelchairs
Active wheelchairs generally incur higher initial costs due to advanced features such as lightweight frames and customizable components, while passive wheelchairs are more affordable with basic designs. Maintenance expenses for active wheelchairs tend to be greater because of intricate parts and frequent adjustments, whereas passive wheelchairs require minimal upkeep owing to their simpler construction. Users prioritizing cost efficiency and low maintenance typically prefer passive wheelchairs over active models.
Safety Features and Stability Concerns
Active wheelchairs typically offer advanced safety features such as enhanced braking systems and reinforced frames to support dynamic movement and reduce the risk of tipping during active use. Passive wheelchairs prioritize stability through wider wheelbases and lower centers of gravity, providing a secure platform for users with limited mobility. Both types address safety differently, with active models balancing agility with protection and passive models emphasizing stability over maneuverability.
Choosing the Right Wheelchair for Your Mobility Needs
Active wheelchairs are designed for individuals seeking greater independence and mobility, featuring lightweight frames and enhanced maneuverability for daily use and outdoor activities. Passive wheelchairs offer more support and stability, ideal for users requiring assistance with movement or longer periods of sitting. Selecting the right wheelchair depends on your lifestyle, physical strength, and specific mobility challenges to ensure comfort and functionality.
Active wheelchair vs Passive wheelchair Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com