Public transit offers an eco-friendly and cost-effective alternative to private vehicles, reducing traffic congestion and lowering carbon emissions. Private vehicles provide greater flexibility and convenience, especially in areas with limited public transport options or for individuals with specific mobility needs. Choosing between public transit and private vehicles depends on factors such as accessibility, cost, environmental impact, and personal lifestyle preferences.
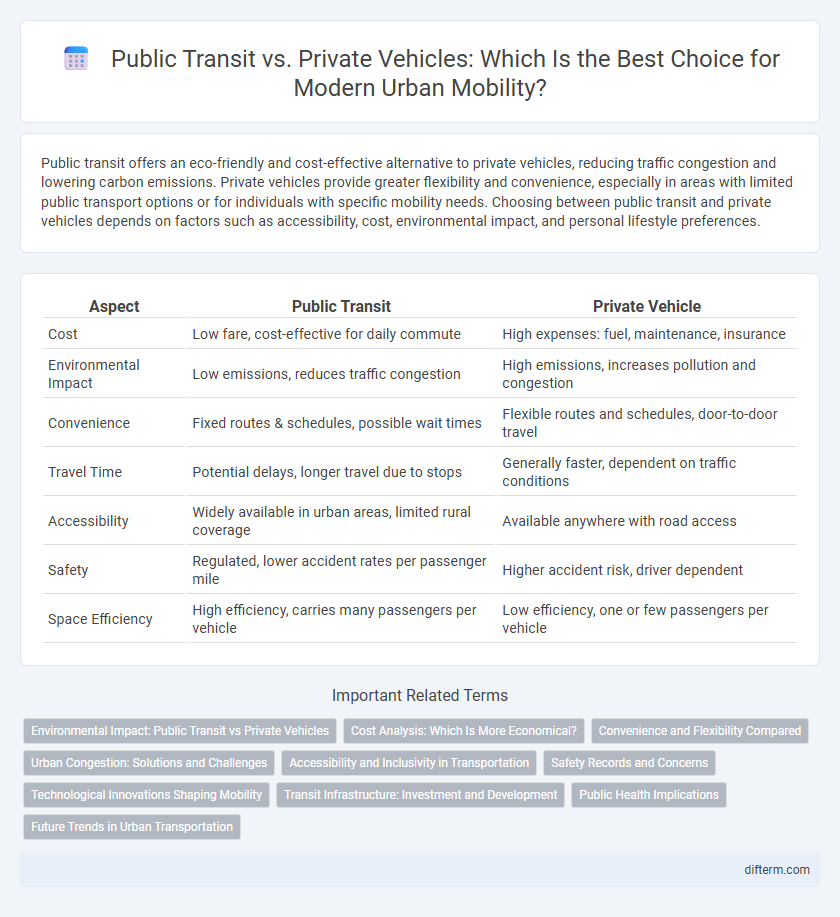
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Public Transit | Private Vehicle |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Low fare, cost-effective for daily commute | High expenses: fuel, maintenance, insurance |
| Environmental Impact | Low emissions, reduces traffic congestion | High emissions, increases pollution and congestion |
| Convenience | Fixed routes & schedules, possible wait times | Flexible routes and schedules, door-to-door travel |
| Travel Time | Potential delays, longer travel due to stops | Generally faster, dependent on traffic conditions |
| Accessibility | Widely available in urban areas, limited rural coverage | Available anywhere with road access |
| Safety | Regulated, lower accident rates per passenger mile | Higher accident risk, driver dependent |
| Space Efficiency | High efficiency, carries many passengers per vehicle | Low efficiency, one or few passengers per vehicle |
Environmental Impact: Public Transit vs Private Vehicles
Public transit systems significantly reduce per capita greenhouse gas emissions by transporting multiple passengers simultaneously, lowering overall fuel consumption and air pollution. In contrast, private vehicles contribute substantially to carbon emissions due to single-occupancy trips and inefficient fuel use, exacerbating urban congestion and environmental degradation. Shifting to widespread public transit adoption supports sustainable mobility by minimizing fossil fuel dependence and promoting cleaner air quality.
Cost Analysis: Which Is More Economical?
Public transit often proves more economical than private vehicles due to lower per-trip costs, reduced fuel expenses, and decreased maintenance fees. While private vehicles require substantial initial investment, insurance, parking, and depreciation, public transit users benefit from fare structures that spread costs over numerous passengers. Urban areas with efficient transit systems maximize cost savings by minimizing congestion and lowering overall transportation expenses for commuters.
Convenience and Flexibility Compared
Public transit offers cost-effective, environmentally friendly transportation but follows fixed schedules and routes, limiting convenience and flexibility for spontaneous trips. Private vehicles provide unmatched flexibility and door-to-door convenience, enabling users to travel on their own time and directly to diverse destinations without relying on transit timetables. The choice between public transit and private vehicles often depends on individual priorities for convenience, travel flexibility, and cost efficiency.
Urban Congestion: Solutions and Challenges
Urban congestion intensifies as private vehicle use surpasses public transit capacity, causing increased travel time and pollution. Expanding efficient public transit systems, such as bus rapid transit (BRT) and light rail networks, reduces road congestion and lowers carbon emissions. Implementing congestion pricing and enhancing multimodal connectivity encourage shifts away from private cars, yet funding and infrastructure upgrades remain significant challenges.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in Transportation
Public transit systems offer greater accessibility and inclusivity by providing affordable, specially equipped vehicles and infrastructure for individuals with disabilities, elderly passengers, and those without access to private cars. Unlike private vehicles, public transit reduces transportation barriers in urban and rural areas, fostering social equity and community engagement. Investments in multimodal integration and real-time information further enhance mobility options for diverse populations.
Safety Records and Concerns
Public transit systems demonstrate significantly lower accident rates compared to private vehicles, with the National Safety Council reporting transit is four times safer per mile traveled. Safety concerns for private vehicles often include distracted driving and impaired operation, contributing to higher fatality rates annually. Transit authorities implement rigorous safety protocols and advanced monitoring technologies to maintain secure environments for millions of daily commuters.
Technological Innovations Shaping Mobility
Technological innovations such as electric buses, real-time GPS tracking, and autonomous vehicle systems are rapidly transforming public transit by enhancing efficiency, reducing emissions, and improving passenger experience. Private vehicles are also evolving with the integration of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), electric drivetrains, and connected car technologies that promote safer and more sustainable driving. These advancements are reshaping the mobility landscape by facilitating smarter, greener transportation options across both public and private sectors.
Transit Infrastructure: Investment and Development
Investment in public transit infrastructure, such as dedicated bus lanes, modern rail systems, and real-time tracking technology, significantly enhances urban mobility and reduces traffic congestion. Development projects prioritizing transit hubs and multimodal connectivity improve access and encourage a shift from private vehicle use to sustainable transportation options. Robust funding and strategic planning in transit infrastructure are critical to supporting growing populations and achieving environmental goals.
Public Health Implications
Public transit reduces air pollution by lowering per capita emissions compared to private vehicles, significantly decreasing respiratory illnesses and cardiovascular diseases. Increased use of buses and trains encourages physical activity through walking to stops, improving overall community health outcomes. Crowded transit environments require enhanced sanitation and ventilation to mitigate communicable disease transmission risks among passengers.
Future Trends in Urban Transportation
Future trends in urban transportation emphasize the integration of public transit systems with emerging technologies such as electric buses, autonomous vehicles, and smart infrastructure to enhance efficiency and reduce emissions. Investment in multimodal transit solutions and real-time data analytics drives improved accessibility and encourages a shift away from private vehicle reliance. Cities increasingly prioritize sustainable mobility by expanding bike-sharing programs, enhancing pedestrian pathways, and developing transit-oriented developments that promote reduced car dependency.
Public transit vs private vehicle Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com