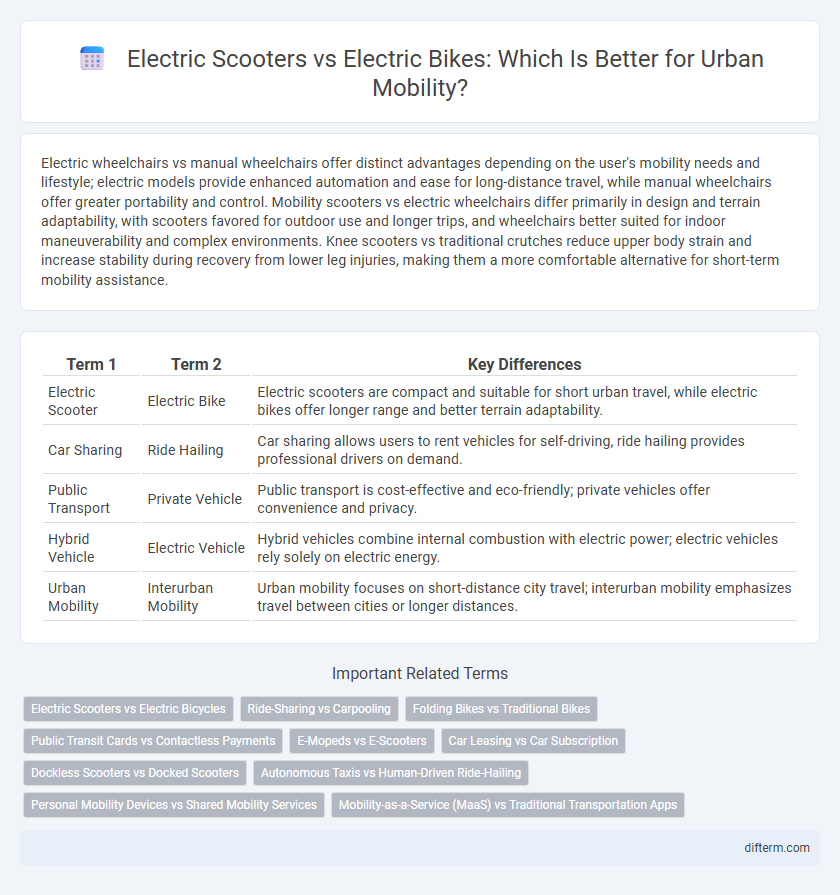
Electric wheelchairs vs manual wheelchairs offer distinct advantages depending on the user's mobility needs and lifestyle; electric models provide enhanced automation and ease for long-distance travel, while manual wheelchairs offer greater portability and control. Mobility scooters vs electric wheelchairs differ primarily in design and terrain adaptability, with scooters favored for outdoor use and longer trips, and wheelchairs better suited for indoor maneuverability and complex environments. Knee scooters vs traditional crutches reduce upper body strain and increase stability during recovery from lower leg injuries, making them a more comfortable alternative for short-term mobility assistance.
Table of Comparison
| Term 1 | Term 2 | Key Differences |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Scooter | Electric Bike | Electric scooters are compact and suitable for short urban travel, while electric bikes offer longer range and better terrain adaptability. |
| Car Sharing | Ride Hailing | Car sharing allows users to rent vehicles for self-driving, ride hailing provides professional drivers on demand. |
| Public Transport | Private Vehicle | Public transport is cost-effective and eco-friendly; private vehicles offer convenience and privacy. |
| Hybrid Vehicle | Electric Vehicle | Hybrid vehicles combine internal combustion with electric power; electric vehicles rely solely on electric energy. |
| Urban Mobility | Interurban Mobility | Urban mobility focuses on short-distance city travel; interurban mobility emphasizes travel between cities or longer distances. |
Electric Scooters vs Electric Bicycles
Electric scooters provide compact, lightweight urban mobility ideal for short-distance commuting, while electric bicycles offer extended range and superior pedal-assist power for varied terrains. Battery capacity in electric bicycles typically ranges from 400 to 700 watt-hours, enabling longer trips compared to electric scooters' 250 to 350 watt-hour batteries. Maintenance of electric scooters is generally simpler due to fewer moving parts, contrasting with the more complex drivetrain and tire maintenance required for electric bicycles.
Ride-Sharing vs Carpooling
Ride-sharing platforms like Uber and Lyft offer on-demand transport with flexible routes, while carpooling typically involves pre-arranged shared rides among regular commuters. Ride-sharing prioritizes convenience and immediate availability, leveraging mobile apps and dynamic pricing algorithms. Carpooling emphasizes cost savings, environmental benefits, and reduced traffic congestion through coordinated, often recurring trips using private vehicles.
Folding Bikes vs Traditional Bikes
Folding bikes offer superior portability and compact storage compared to traditional bikes, making them ideal for urban commuters with limited space. Traditional bikes provide better ride stability and performance, favored for longer distances and varied terrains. Choosing between folding and traditional bikes depends on balancing convenience and riding experience in mobility solutions.
Public Transit Cards vs Contactless Payments
Public transit cards offer a dedicated, reliable payment method tailored for frequent travelers, ensuring seamless access to buses, trains, and subways without the need for a bank account. Contactless payments leverage NFC-enabled devices like smartphones and credit cards, providing flexible, universal acceptance across various transit systems and retail environments. Both methods enhance commuter convenience but differ in infrastructure compatibility, security protocols, and user access preferences.
E-Mopeds vs E-Scooters
E-Mopeds offer greater speed and range compared to E-Scooters, making them suitable for longer urban commutes and moderate highway use. E-Scooters excel in portability and ease of maneuverability, ideal for short-distance travel and crowded city environments. Battery capacity and motor power significantly differentiate the two, influencing performance and user experience in electric mobility solutions.
Car Leasing vs Car Subscription
Car leasing offers long-term vehicle use with fixed monthly payments and ownership options at lease-end, while car subscription provides flexible, short-term access including insurance, maintenance, and vehicle swaps for a single monthly fee. Car subscriptions cater to consumers seeking convenience and variety without long-term commitments, contrasting with leasing's structured contract periods typically ranging from two to four years. Pricing models in car subscriptions often incorporate all-inclusive services, whereas leasing primarily requires upfront down payments and maintenance responsibilities.
Dockless Scooters vs Docked Scooters
Dockless scooters offer greater flexibility and convenience for short-distance urban travel compared to docked scooters, which require designated parking stations. Dockless models rely on GPS technology and mobile apps for locating and unlocking, increasing accessibility but posing challenges in public space management. In contrast, docked scooters provide structured parking to reduce clutter and improve organization, often supporting more consistent maintenance and charging.
Autonomous Taxis vs Human-Driven Ride-Hailing
Autonomous taxis utilize advanced AI and sensor technology to offer consistent, efficient rides with lower operational costs compared to human-driven ride-hailing, which relies on driver availability and variable human behavior. Safety metrics show autonomous vehicles can reduce accidents caused by human error, while human-driven services provide personalized interaction and adaptability to complex traffic scenarios. Fleet management for autonomous taxis benefits from centralized control and predictive maintenance, enhancing service reliability over traditional ride-hailing models.
Personal Mobility Devices vs Shared Mobility Services
Personal Mobility Devices, such as electric scooters and e-bikes, offer individualized control and convenience, empowering users with flexible, last-mile transportation solutions. Shared Mobility Services, including bike-sharing and ride-hailing platforms, enhance urban efficiency by reducing private car usage and promoting eco-friendly travel alternatives. The integration of both options supports sustainable mobility ecosystems by balancing personal freedom with collective resource optimization.
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) vs Traditional Transportation Apps
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) integrates various transportation modes into a single accessible platform, offering seamless trip planning, booking, and payment, unlike traditional transportation apps that typically focus on a single transit option such as ride-hailing or public transport. MaaS aims to optimize urban mobility by reducing dependency on private vehicles, enhancing sustainability, and improving user convenience through multimodal connectivity. Traditional transportation apps often lack this holistic approach, limiting user flexibility and comprehensive route customization within smart city ecosystems.
Certainly! Here is a list of micro niche "term1 vs term2" comparisons in the context of Mobility: Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com