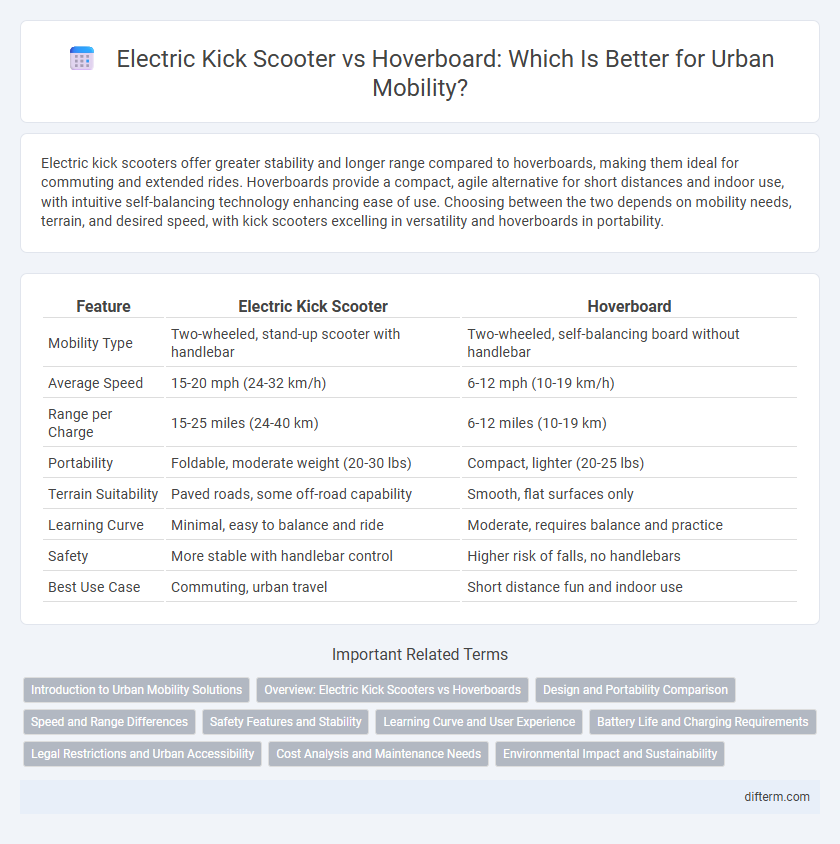
Electric kick scooters offer greater stability and longer range compared to hoverboards, making them ideal for commuting and extended rides. Hoverboards provide a compact, agile alternative for short distances and indoor use, with intuitive self-balancing technology enhancing ease of use. Choosing between the two depends on mobility needs, terrain, and desired speed, with kick scooters excelling in versatility and hoverboards in portability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Electric Kick Scooter | Hoverboard |
|---|---|---|
| Mobility Type | Two-wheeled, stand-up scooter with handlebar | Two-wheeled, self-balancing board without handlebar |
| Average Speed | 15-20 mph (24-32 km/h) | 6-12 mph (10-19 km/h) |
| Range per Charge | 15-25 miles (24-40 km) | 6-12 miles (10-19 km) |
| Portability | Foldable, moderate weight (20-30 lbs) | Compact, lighter (20-25 lbs) |
| Terrain Suitability | Paved roads, some off-road capability | Smooth, flat surfaces only |
| Learning Curve | Minimal, easy to balance and ride | Moderate, requires balance and practice |
| Safety | More stable with handlebar control | Higher risk of falls, no handlebars |
| Best Use Case | Commuting, urban travel | Short distance fun and indoor use |
Introduction to Urban Mobility Solutions
Electric kick scooters offer a practical and energy-efficient mode of transportation for short urban commutes, boasting speeds up to 15-25 km/h and ranges between 15-30 km per charge. Hoverboards provide a compact alternative with intuitive balance-based control, suitable for short distances typically up to 10-15 km and speeds around 10-15 km/h. Both devices contribute to reducing urban congestion and emissions, supporting sustainable mobility trends in densely populated cities.
Overview: Electric Kick Scooters vs Hoverboards
Electric kick scooters offer greater range and speed compared to hoverboards, making them better suited for longer commutes and urban travel. Hoverboards emphasize balance and portability, with a compact design ideal for short distances and maneuvering in tight spaces. Both modes of electric personal transport provide eco-friendly alternatives to gasoline-powered vehicles, but differ significantly in control mechanisms and user experience.
Design and Portability Comparison
Electric kick scooters feature a foldable frame and lightweight materials, making them highly portable and easy to carry on public transit or store in tight spaces. Hoverboards offer a compact, symmetrical design that allows for effortless balance but typically require a separate carrying case for convenient transport. In terms of design, scooters provide a handlebar for enhanced stability and control, while hoverboards focus on foot placement and body movement for navigation.
Speed and Range Differences
Electric kick scooters typically reach speeds of 15 to 20 mph with ranges between 15 to 30 miles per charge, making them suitable for longer commutes. Hoverboards usually offer lower speeds of around 6 to 12 mph and shorter ranges of 7 to 12 miles per charge, focused more on short-distance urban mobility. The speed and range differences stem from their design priorities, with scooters emphasizing efficiency and control, while hoverboards prioritize portability and balance.
Safety Features and Stability
Electric kick scooters offer enhanced safety features such as reliable braking systems, sturdy handlebars for better control, and built-in lights for visibility, making them more stable and easier to maneuver on various terrains. Hoverboards, while compact and convenient, often lack advanced safety mechanisms and have a higher risk of tipping due to their self-balancing design, which requires constant user adjustment. The stability of electric kick scooters generally surpasses hoverboards, providing a safer and more secure riding experience for urban mobility.
Learning Curve and User Experience
Electric kick scooters offer a more intuitive learning curve with straightforward balancing and acceleration, making them accessible for beginners and urban commuters. Hoverboards require a more nuanced sense of balance and coordination, often demanding extended practice to achieve stability and smooth control. User experience on kick scooters is typically enhanced by ergonomic handles and faster speeds, while hoverboards deliver a compact, hands-free ride that appeals to users seeking portability and maneuverability within short distances.
Battery Life and Charging Requirements
Electric kick scooters typically offer longer battery life, ranging from 15 to 30 miles per charge, compared to hoverboards which average around 7 to 12 miles. Charging times for electric kick scooters usually span 4 to 8 hours, whereas hoverboards generally require 2 to 4 hours to reach full charge. Battery capacity and efficiency play crucial roles in determining the range and usability, with electric kick scooters often equipped with higher-capacity lithium-ion batteries.
Legal Restrictions and Urban Accessibility
Electric kick scooters face clearer legal regulations, often requiring age limits, speed caps, and designated riding zones in urban areas, ensuring safer integration into city traffic. Hoverboards encounter stricter restrictions or bans in many cities due to safety concerns and limited control, reducing their accessibility on sidewalks and public roads. Urban accessibility favors electric scooters with their compact design, longer range, and compatibility with bike lanes, making them more practical for short-distance commuting.
Cost Analysis and Maintenance Needs
Electric kick scooters generally have higher upfront costs, ranging from $300 to $700, compared to hoverboards, which typically cost between $150 and $400. Maintenance for electric kick scooters involves regular tire checks, brake adjustments, and battery care, while hoverboards primarily require battery maintenance and occasional motor checks. Over time, scooters may incur higher maintenance expenses due to wear on mechanical parts, making hoverboards a more cost-effective option for minimal upkeep.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Electric kick scooters produce lower carbon emissions compared to hoverboards due to their more energy-efficient motors and longer battery life, contributing significantly to urban sustainability efforts. The sustainable materials used in scooter manufacturing, combined with higher durability and easier repairability, reduce environmental waste and promote circular economy principles. Hoverboards, while convenient, generally have higher battery replacement rates and less efficient energy consumption, leading to a greater overall environmental footprint.
Electric kick scooter vs hoverboard Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com