Joystick control offers precise and intuitive maneuverability for power chairs, allowing users to make smooth directional changes with minimal effort. Touchpad control provides a modern, compact alternative that enables easy navigation through simple finger gestures, ideal for users seeking a sleek interface. Both control methods enhance mobility but cater to different preferences and levels of dexterity.
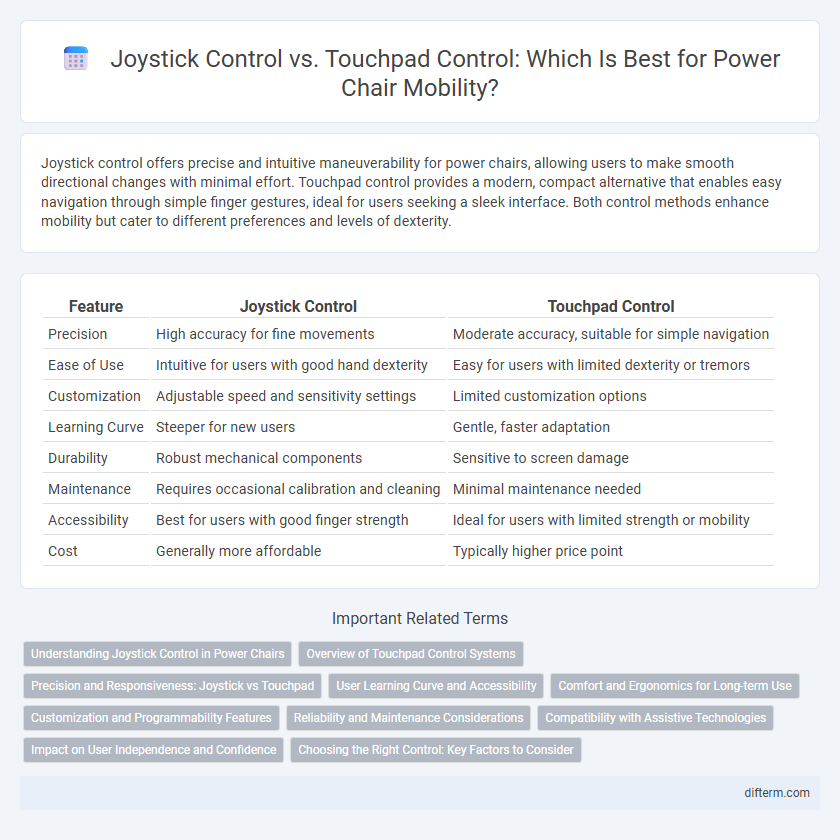
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Joystick Control | Touchpad Control |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | High accuracy for fine movements | Moderate accuracy, suitable for simple navigation |
| Ease of Use | Intuitive for users with good hand dexterity | Easy for users with limited dexterity or tremors |
| Customization | Adjustable speed and sensitivity settings | Limited customization options |
| Learning Curve | Steeper for new users | Gentle, faster adaptation |
| Durability | Robust mechanical components | Sensitive to screen damage |
| Maintenance | Requires occasional calibration and cleaning | Minimal maintenance needed |
| Accessibility | Best for users with good finger strength | Ideal for users with limited strength or mobility |
| Cost | Generally more affordable | Typically higher price point |
Understanding Joystick Control in Power Chairs
Joystick control in power chairs provides precise, multi-directional navigation through ergonomic hand movements, enabling users to maneuver smoothly in tight spaces. Unlike touchpad controls that rely on tapping and swiping gestures, joystick systems translate physical pressure into variable speed and direction, offering more intuitive responsiveness. Advanced joystick controls often feature customizable sensitivity settings and feedback mechanisms to enhance user comfort and safety during mobility.
Overview of Touchpad Control Systems
Touchpad control systems in power chairs utilize capacitive or resistive touch-sensitive surfaces to translate user finger movements into directional commands, offering precise and intuitive navigation. These systems often include customizable sensitivity settings and gesture recognition, enhancing accessibility for users with varying dexterity levels. Compared to traditional joystick controls, touchpad interfaces reduce physical exertion and can be seamlessly integrated into armrests or control panels, improving overall mobility experience.
Precision and Responsiveness: Joystick vs Touchpad
Joystick controls in power chairs offer superior precision and responsiveness due to their analog input, enabling users to make nuanced directional adjustments effortlessly. Touchpad controls, while intuitive, often lack the fine-tuned sensitivity of joysticks, leading to less accurate maneuvering in tight or complex environments. Users requiring high control accuracy and immediate feedback typically benefit more from joystick systems than touchpad alternatives.
User Learning Curve and Accessibility
Joystick control in power chairs offers intuitive directional input that typically results in a shorter user learning curve, especially for individuals with limited motor skills. Touchpad control requires users to adapt to gesture-based commands, which can increase complexity and extend the learning period, particularly for those unfamiliar with touchscreen technology. Accessibility favors joystick controls due to tactile feedback and straightforward operation, enhancing usability for a broader range of mobility-impaired users.
Comfort and Ergonomics for Long-term Use
Joystick control in power chairs offers precise maneuverability with minimal hand movement, reducing fatigue during extended use and promoting better wrist alignment for ergonomic comfort. Touchpad control requires consistent finger pressure and hand positioning, which can lead to strain and decreased comfort over long periods. Studies show joystick interfaces enhance user comfort and reduce musculoskeletal stress, making them preferable for long-term mobility management.
Customization and Programmability Features
Joystick controls for power chairs offer extensive customization and programmability options, allowing users to fine-tune sensitivity, speed, and directional input to match their specific mobility needs. Touchpad controls provide configurable settings but typically lack the depth of programmable features found in joystick interfaces, limiting personalized adjustments. Advanced joystick systems often integrate with software platforms for tailored profiles, enhancing user control and adaptability compared to the more static touchpad configurations.
Reliability and Maintenance Considerations
Joystick control systems in power chairs offer higher reliability due to their robust mechanical design and fewer susceptibility points, resulting in lower maintenance requirements over time. Touchpad controls, while providing intuitive user interfaces, often involve complex electronic components that can be more prone to wear and require frequent calibration or software updates. Maintenance teams favor joystick controls for their ease of troubleshooting and replacement, enhancing long-term operational durability in mobility devices.
Compatibility with Assistive Technologies
Joystick control in power chairs offers superior compatibility with a wide range of assistive technologies, including sip-and-puff systems and head controls, due to its standardized interface and customizable sensitivity settings. Touchpad controls, while intuitive for some users, often face limitations in integration with diverse assistive devices, reducing their effectiveness for individuals requiring advanced accessibility options. Selecting joystick controls can enhance user independence by providing seamless connectivity with environmental control units and communication aids.
Impact on User Independence and Confidence
Joystick control in power chairs offers precise maneuverability, fostering enhanced user independence by allowing smooth navigation in tight spaces. Touchpad control provides an intuitive interface, beneficial for users with limited hand dexterity, which boosts confidence through ease of operation. Both control methods significantly contribute to personalized mobility solutions, directly influencing user autonomy and self-assurance.
Choosing the Right Control: Key Factors to Consider
Choosing the right control for power chairs depends on user dexterity, precision needs, and environmental adaptability. Joystick controls offer fine maneuverability and responsiveness, ideal for users requiring precise navigation in tight spaces. Touchpad controls provide an intuitive interface with easier access for those with limited hand strength or coordination, enhancing overall comfort and usability.
Joystick control vs Touchpad control (power chairs) Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com