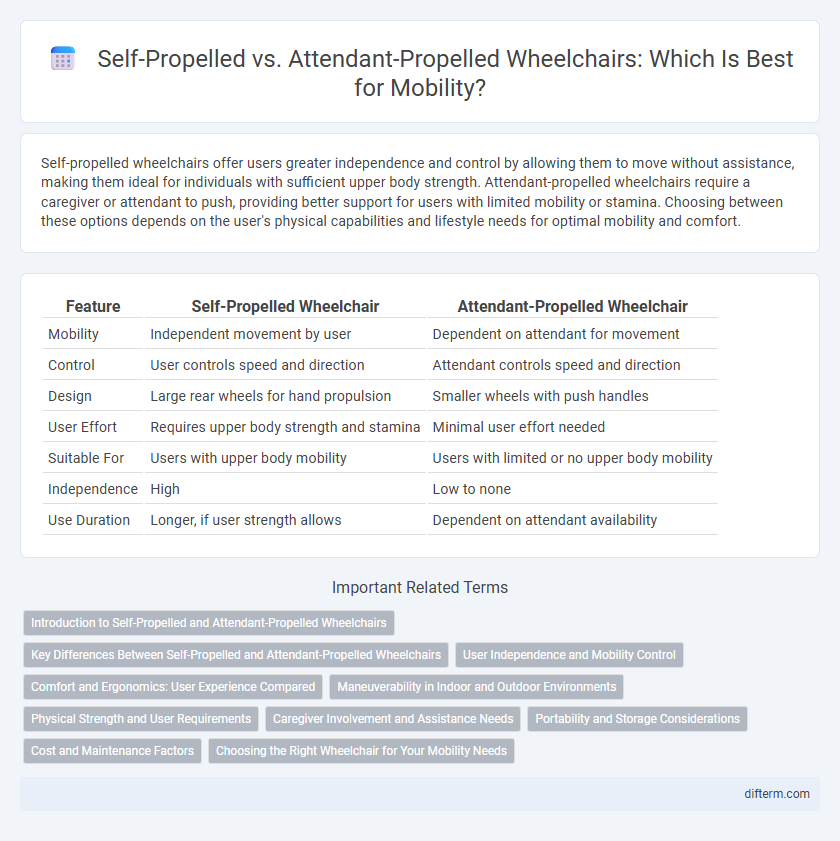
Self-propelled wheelchairs offer users greater independence and control by allowing them to move without assistance, making them ideal for individuals with sufficient upper body strength. Attendant-propelled wheelchairs require a caregiver or attendant to push, providing better support for users with limited mobility or stamina. Choosing between these options depends on the user's physical capabilities and lifestyle needs for optimal mobility and comfort.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Self-Propelled Wheelchair | Attendant-Propelled Wheelchair |
|---|---|---|
| Mobility | Independent movement by user | Dependent on attendant for movement |
| Control | User controls speed and direction | Attendant controls speed and direction |
| Design | Large rear wheels for hand propulsion | Smaller wheels with push handles |
| User Effort | Requires upper body strength and stamina | Minimal user effort needed |
| Suitable For | Users with upper body mobility | Users with limited or no upper body mobility |
| Independence | High | Low to none |
| Use Duration | Longer, if user strength allows | Dependent on attendant availability |
Introduction to Self-Propelled and Attendant-Propelled Wheelchairs
Self-propelled wheelchairs feature large rear wheels allowing users to independently maneuver by gripping and rotating the wheels, promoting autonomy and mobility. Attendant-propelled wheelchairs are designed with smaller rear wheels and push handles, enabling a caregiver or attendant to control movement and provide support. Selecting between these types depends on the user's physical strength, endurance, and need for independence in daily mobility.
Key Differences Between Self-Propelled and Attendant-Propelled Wheelchairs
Self-propelled wheelchairs feature large rear wheels that enable users to independently maneuver using hand rims, offering greater autonomy and physical engagement. Attendant-propelled wheelchairs rely on a caregiver or attendant to push, making them ideal for users with limited upper body strength or dexterity. Key differences include user independence, wheel size, and the necessity of external assistance for mobility.
User Independence and Mobility Control
Self-propelled wheelchairs provide users with enhanced independence and direct mobility control by allowing them to navigate without assistance, promoting autonomy in daily activities. Attendant-propelled wheelchairs require a caregiver for movement, limiting user autonomy but offering support for individuals with limited upper body strength or coordination. Choosing between these wheelchair types depends on the user's physical capabilities and the need for independence in mobility.
Comfort and Ergonomics: User Experience Compared
Self-propelled wheelchairs offer enhanced comfort and ergonomics by allowing users greater independence in controlling movement, promoting better posture through adjustable seating and customizable support features. Attendant-propelled wheelchairs prioritize ease of maneuverability for the caregiver but may compromise user comfort due to limited adjustment options and less individualized fit. Ergonomic design in self-propelled models often reduces strain and pressure points, improving overall user experience and long-term health outcomes.
Maneuverability in Indoor and Outdoor Environments
Self-propelled wheelchairs offer greater maneuverability in both indoor and outdoor environments due to user-controlled navigation and individualized speed adjustment. Attendant-propelled wheelchairs rely on external force, limiting responsiveness and adaptability on uneven terrain or tight indoor spaces. Enhanced maneuverability in self-propelled models improves autonomy and ease of movement across variable surfaces and spatial constraints.
Physical Strength and User Requirements
Self-propelled wheelchairs require considerable upper body strength and dexterity, allowing users to independently control and maneuver their mobility device, which benefits physically capable individuals seeking autonomy. Attendant-propelled wheelchairs depend on a caregiver or assistant for mobility, reducing the physical demands on the user but increasing reliance on the attendant's strength and availability. User requirements for self-propelled models emphasize endurance and arm function, while attendant-propelled designs prioritize comfort and ease of pushing for caregivers.
Caregiver Involvement and Assistance Needs
Self-propelled wheelchairs significantly reduce caregiver involvement by enabling users to independently maneuver, enhancing autonomy for individuals with sufficient upper body strength and coordination. Attendant-propelled wheelchairs demand continuous caregiver assistance for propulsion and navigation, increasing physical effort and time investment from caregivers. Choosing the appropriate wheelchair type directly impacts the level of caregiver support required and user mobility outcomes.
Portability and Storage Considerations
Self-propelled wheelchairs typically feature larger rear wheels that allow users to maneuver independently, but these wheels can make the chair bulkier and less compact for storage or transportation. Attendant-propelled wheelchairs often have smaller wheels and a lighter frame, enhancing portability and making them easier to fold and store in tight spaces such as car trunks or closets. When evaluating wheelchair options, considering the storage environment and transport method is crucial for selecting between self-propelled and attendant-propelled models.
Cost and Maintenance Factors
Self-propelled wheelchairs typically have higher initial costs due to reinforced frames and durable wheels designed for independent use, but they require less frequent maintenance compared to attendant-propelled models. Attendant-propelled wheelchairs are generally more affordable upfront, but their basic components may necessitate more regular repairs and adjustments because of increased wear from operator handling. Budgeting for long-term expenses is essential, with self-propelled wheelchairs offering better value through reduced maintenance frequency despite higher purchase prices.
Choosing the Right Wheelchair for Your Mobility Needs
Self-propelled wheelchairs offer users greater independence and flexibility by allowing them to control movement without assistance, making them ideal for individuals with sufficient upper body strength and stamina. Attendant-propelled wheelchairs are designed for users who rely on caregivers for mobility, providing enhanced comfort and support during longer trips or in environments where self-navigation is challenging. Selecting the right wheelchair depends on evaluating physical capabilities, lifestyle needs, and the typical environment in which the wheelchair will be used.
self-propelled wheelchair vs attendant-propelled wheelchair Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com