Paratransit services provide specialized transportation for individuals with disabilities, offering door-to-door rides tailored to specific accessibility needs. Demand-responsive transit operates on flexible routes and schedules, allowing passengers to request pickups and drop-offs within a defined service area, often serving a broader population. Both models enhance mobility options but differ in target users and operational flexibility.
Table of Comparison
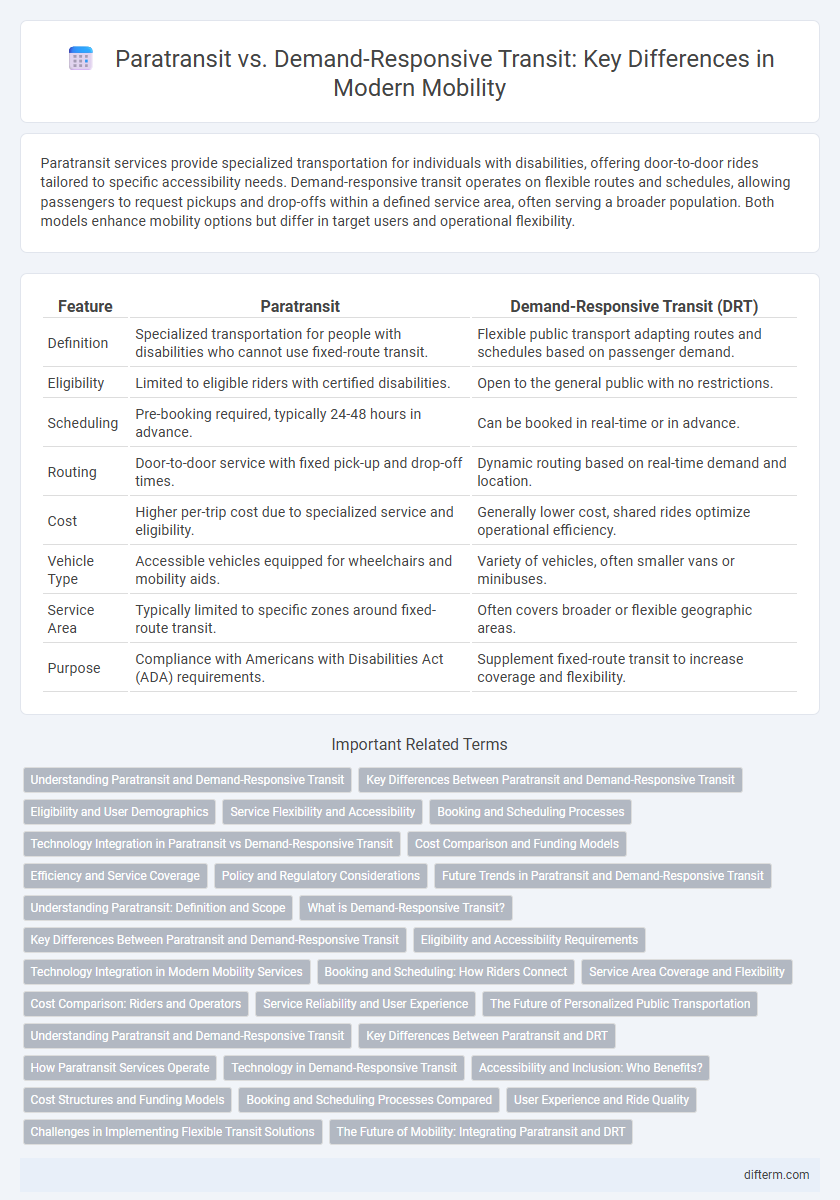
| Feature | Paratransit | Demand-Responsive Transit (DRT) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Specialized transportation for people with disabilities who cannot use fixed-route transit. | Flexible public transport adapting routes and schedules based on passenger demand. |
| Eligibility | Limited to eligible riders with certified disabilities. | Open to the general public with no restrictions. |
| Scheduling | Pre-booking required, typically 24-48 hours in advance. | Can be booked in real-time or in advance. |
| Routing | Door-to-door service with fixed pick-up and drop-off times. | Dynamic routing based on real-time demand and location. |
| Cost | Higher per-trip cost due to specialized service and eligibility. | Generally lower cost, shared rides optimize operational efficiency. |
| Vehicle Type | Accessible vehicles equipped for wheelchairs and mobility aids. | Variety of vehicles, often smaller vans or minibuses. |
| Service Area | Typically limited to specific zones around fixed-route transit. | Often covers broader or flexible geographic areas. |
| Purpose | Compliance with Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) requirements. | Supplement fixed-route transit to increase coverage and flexibility. |
Understanding Paratransit and Demand-Responsive Transit
Paratransit services provide specialized, door-to-door transportation designed primarily for individuals with disabilities who are unable to use fixed-route public transit, ensuring accessibility and compliance with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). Demand-responsive transit (DRT) offers flexible routing and scheduling based on passenger requests, serving a wider population including areas with low transit demand or during off-peak hours. Both systems enhance mobility by accommodating unique travel needs, but paratransit is strictly eligibility-based while demand-responsive transit operates more broadly to improve public transportation coverage.
Key Differences Between Paratransit and Demand-Responsive Transit
Paratransit services primarily cater to individuals with disabilities, offering door-to-door transportation tailored to specific eligibility requirements under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). Demand-responsive transit (DRT) provides flexible routing and scheduling for the general public, allowing passengers to request rides in real time via apps or call centers, optimizing route efficiency. Key differences include eligibility restrictions, service areas, and operational flexibility, with paratransit focusing on accessibility and demand-responsive transit emphasizing convenience for a broader user base.
Eligibility and User Demographics
Paratransit services primarily cater to individuals with certified disabilities who qualify under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), often encompassing elderly users and persons with mobility impairments. Demand-responsive transit (DRT) serves a broader demographic, including the general public, offering flexible routing and scheduling without strict eligibility criteria. Paratransit typically requires pre-registration and proof of eligibility, whereas DRT aims to enhance accessibility by adapting to diverse user needs in various urban and rural settings.
Service Flexibility and Accessibility
Paratransit offers highly flexible, door-to-door services tailored for individuals with disabilities, ensuring maximum accessibility for those unable to use fixed-route transit. Demand-responsive transit provides adaptable routing and scheduling but typically serves a broader population with less specialized accommodations. Both aim to enhance mobility, yet paratransit prioritizes personalized access while demand-responsive transit optimizes efficiency and coverage.
Booking and Scheduling Processes
Paratransit services require advanced booking well in advance, often 24 to 48 hours before the trip, ensuring operators can efficiently coordinate specialized vehicles for passengers with disabilities. Demand-responsive transit (DRT) offers more flexible scheduling, allowing riders to book trips closer to the travel time, sometimes within hours, through digital platforms or call centers. Both systems optimize route planning and resource allocation but differ significantly in their booking windows and response times, impacting user convenience and operational efficiency.
Technology Integration in Paratransit vs Demand-Responsive Transit
Paratransit services benefit from advanced technology integration such as real-time GPS tracking, automated dispatch systems, and mobile apps tailored for accessibility, enhancing ride scheduling and vehicle routing. Demand-responsive transit employs dynamic routing algorithms and data analytics to optimize efficiency and adapt to fluctuating demand patterns across urban areas. Both systems rely on cloud-based platforms for seamless communication between operators, drivers, and passengers, but paratransit prioritizes features that address specific mobility impairments and regulatory compliance.
Cost Comparison and Funding Models
Paratransit services typically incur higher operational costs per trip due to specialized vehicles and stricter regulatory requirements, whereas demand-responsive transit (DRT) benefits from flexible routing and lower overhead, reducing overall expenses. Funding models for paratransit often rely on federal mandates such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) allocations combined with local subsidies, while DRT programs frequently utilize a mix of public-private partnerships and dynamic fare structures to optimize cost recovery. Evaluating cost efficiency requires analyzing vehicle utilization rates, trip density, and integration with fixed-route transit to maximize resource allocation in both service types.
Efficiency and Service Coverage
Paratransit typically offers door-to-door service tailored for individuals with disabilities, providing high accessibility but often at higher operational costs and limited geographic coverage. Demand-responsive transit (DRT) optimizes routes based on real-time passenger requests, enhancing efficiency by reducing empty miles and expanding service coverage across broader areas. Integrating advanced booking systems and dynamic routing algorithms, DRT maximizes vehicle utilization while maintaining flexible service zones, outperforming traditional paratransit in scalability and cost-effectiveness.
Policy and Regulatory Considerations
Paratransit services are mandated under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), requiring transit agencies to provide comparable transportation for individuals with disabilities within specific service areas. Demand-responsive transit (DRT) operates under more flexible regulatory frameworks, often governed by local or regional policies that prioritize efficiency and cost-effectiveness without strict ADA constraints. Effective policy development must balance accessibility requirements, funding mechanisms, and operational standards to ensure equitable and sustainable mobility options for all users.
Future Trends in Paratransit and Demand-Responsive Transit
Future trends in paratransit and demand-responsive transit emphasize the integration of advanced technologies such as electric vehicles, real-time data analytics, and AI-driven routing to enhance efficiency and accessibility. Autonomous vehicle deployment and expanded on-demand service options are poised to reduce operational costs and improve rider experience for individuals with disabilities and those in underserved communities. Collaboration between public agencies and private mobility providers is expected to drive innovative solutions, fostering seamless multi-modal transportation networks that prioritize equity and sustainability.
paratransit vs demand-responsive transit Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com