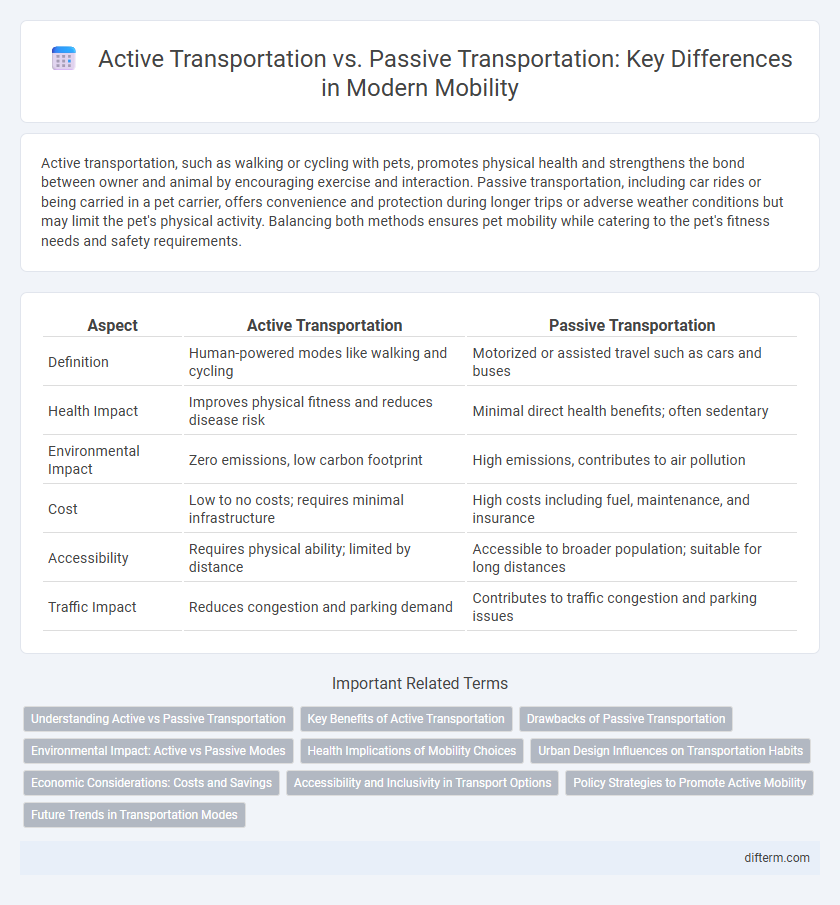
Active transportation, such as walking or cycling with pets, promotes physical health and strengthens the bond between owner and animal by encouraging exercise and interaction. Passive transportation, including car rides or being carried in a pet carrier, offers convenience and protection during longer trips or adverse weather conditions but may limit the pet's physical activity. Balancing both methods ensures pet mobility while catering to the pet's fitness needs and safety requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Active Transportation | Passive Transportation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Human-powered modes like walking and cycling | Motorized or assisted travel such as cars and buses |
| Health Impact | Improves physical fitness and reduces disease risk | Minimal direct health benefits; often sedentary |
| Environmental Impact | Zero emissions, low carbon footprint | High emissions, contributes to air pollution |
| Cost | Low to no costs; requires minimal infrastructure | High costs including fuel, maintenance, and insurance |
| Accessibility | Requires physical ability; limited by distance | Accessible to broader population; suitable for long distances |
| Traffic Impact | Reduces congestion and parking demand | Contributes to traffic congestion and parking issues |
Understanding Active vs Passive Transportation
Active transportation involves modes of travel that require physical effort, such as walking, cycling, and skateboarding, promoting health benefits and reducing environmental impact. Passive transportation, including cars, buses, and trains, relies on motorized vehicles, offering convenience but often contributing to traffic congestion and emissions. Understanding the distinctions between active and passive transportation aids urban planners in designing sustainable, efficient mobility systems that prioritize pedestrian-friendly infrastructure and reduce carbon footprints.
Key Benefits of Active Transportation
Active transportation, such as walking and cycling, promotes cardiovascular health by increasing physical activity and reducing risks of chronic diseases. It lowers environmental impact by decreasing greenhouse gas emissions and traffic congestion compared to passive modes like driving. Economic benefits include reduced healthcare costs and savings on fuel and vehicle maintenance, making active transportation a sustainable and cost-effective mobility choice.
Drawbacks of Passive Transportation
Passive transportation methods, such as cars and buses, contribute significantly to environmental pollution through greenhouse gas emissions, exacerbating climate change. Reliance on passive transportation often leads to increased traffic congestion and longer commute times, reducing overall urban mobility efficiency. Moreover, sedentary travel modes negatively impact public health by limiting physical activity, increasing risks of obesity and cardiovascular diseases.
Environmental Impact: Active vs Passive Modes
Active transportation, such as walking and cycling, significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to passive modes like driving and public transit powered by fossil fuels. Studies show that switching to active transportation can lower an individual's carbon footprint by up to 40%. Promoting infrastructure for biking and walking not only decreases air pollution but also mitigates traffic congestion and reduces reliance on non-renewable energy sources.
Health Implications of Mobility Choices
Active transportation methods such as walking, cycling, and scootering significantly improve cardiovascular health by increasing physical activity levels, reducing risks of obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. Passive transportation, including car travel and public transit, often promotes sedentary behavior, contributing to increased rates of chronic illnesses and mental health challenges. Choosing active transportation not only enhances individual fitness but also supports environmental sustainability and reduces air pollution-related health issues.
Urban Design Influences on Transportation Habits
Urban design significantly shapes transportation habits by promoting active transportation modes like walking and cycling through mixed-use developments and complete streets. High-density neighborhoods with accessible public transit and safe pedestrian infrastructure encourage residents to choose active over passive transportation, reducing car dependency and lowering urban carbon emissions. Integrating green spaces and connectivity enhances walkability, fostering healthier lifestyles and more sustainable urban mobility patterns.
Economic Considerations: Costs and Savings
Active transportation, such as walking and cycling, significantly reduces individual and public expenses by lowering healthcare costs and decreasing reliance on fossil fuels. Passive transportation modes, including cars and buses, involve higher costs for fuel, maintenance, and infrastructure, contributing to increased economic burdens. Investing in infrastructure supporting active transportation yields long-term savings through improved public health and reduced environmental impacts.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in Transport Options
Active transportation modes, such as walking and cycling, enhance accessibility by providing affordable and flexible options that accommodate diverse populations, including those with limited mobility or low income. Passive transportation, including private vehicles and public transit, often presents barriers due to costs, infrastructure limitations, and schedule constraints, disproportionately affecting marginalized communities. Prioritizing inclusive design and investment in active transportation infrastructure promotes equitable access and fosters social inclusion in urban mobility systems.
Policy Strategies to Promote Active Mobility
Policy strategies to promote active mobility prioritize infrastructure investments such as expanding pedestrian pathways and protected bike lanes, enhancing safety and accessibility for cyclists and walkers. Implementing traffic-calming measures and integrating multimodal transit options reduce reliance on private vehicles, encouraging healthier, sustainable travel behaviors. Urban planning policies that connect residential areas to workplaces and amenities via active transportation networks increase adoption rates and improve public health outcomes.
Future Trends in Transportation Modes
Future trends in transportation emphasize a significant shift towards active transportation modes such as walking, cycling, and e-scooters, driven by urbanization and environmental concerns. Integration of smart infrastructure and real-time data enhances safety and convenience for pedestrians and cyclists, promoting sustainable mobility. Innovations in wearable technology and connected devices further encourage active transportation by monitoring health metrics and optimizing travel efficiency.
active transportation vs passive transportation Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com