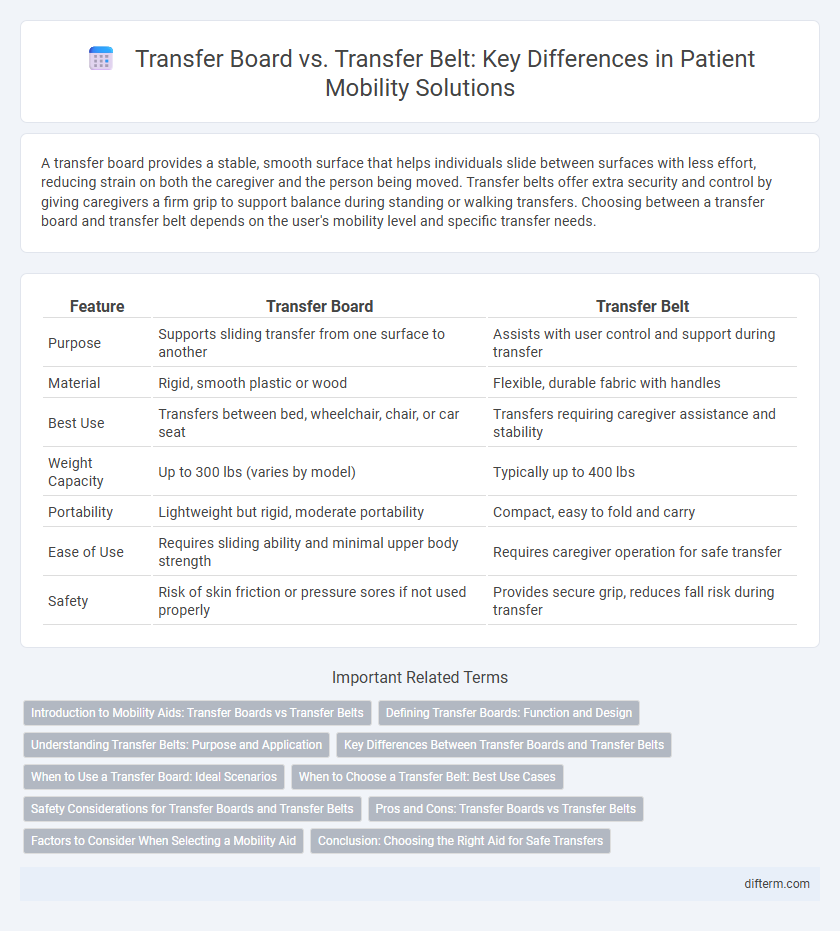
A transfer board provides a stable, smooth surface that helps individuals slide between surfaces with less effort, reducing strain on both the caregiver and the person being moved. Transfer belts offer extra security and control by giving caregivers a firm grip to support balance during standing or walking transfers. Choosing between a transfer board and transfer belt depends on the user's mobility level and specific transfer needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Transfer Board | Transfer Belt |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Supports sliding transfer from one surface to another | Assists with user control and support during transfer |
| Material | Rigid, smooth plastic or wood | Flexible, durable fabric with handles |
| Best Use | Transfers between bed, wheelchair, chair, or car seat | Transfers requiring caregiver assistance and stability |
| Weight Capacity | Up to 300 lbs (varies by model) | Typically up to 400 lbs |
| Portability | Lightweight but rigid, moderate portability | Compact, easy to fold and carry |
| Ease of Use | Requires sliding ability and minimal upper body strength | Requires caregiver operation for safe transfer |
| Safety | Risk of skin friction or pressure sores if not used properly | Provides secure grip, reduces fall risk during transfer |
Introduction to Mobility Aids: Transfer Boards vs Transfer Belts
Transfer boards and transfer belts are essential mobility aids designed to assist individuals with safe and efficient transfers between surfaces. Transfer boards provide a stable bridge for sliding from one seat to another, commonly used for wheelchair to bed or car transfers. Transfer belts, equipped with handles, offer caregivers secure control and support to aid in patient movement, reducing the risk of falls and injury during transfers.
Defining Transfer Boards: Function and Design
Transfer boards are flat, rigid devices designed to facilitate smooth lateral movement between surfaces such as beds, wheelchairs, or car seats, reducing friction and effort for individuals with limited mobility. Typically made from lightweight materials like wood or polyethylene, transfer boards feature a smooth, non-slip surface and beveled edges to ensure stability and safety during use. Unlike transfer belts, which provide physical support for caregivers during patient movement, transfer boards act as a stable bridge, enabling independent or assisted transfers.
Understanding Transfer Belts: Purpose and Application
Transfer belts serve as essential assistive devices designed to provide caregivers with a secure and ergonomic grip when moving or repositioning individuals with limited mobility, reducing strain and enhancing safety. Unlike transfer boards, which create a stable surface for sliding transfers between seating surfaces, transfer belts focus on stability and control during standing or pivot transfers. Their application is crucial in clinical and home care settings to prevent falls and support smooth, controlled movements during patient transfers.
Key Differences Between Transfer Boards and Transfer Belts
Transfer boards are rigid, flat surfaces designed to bridge gaps between seats, facilitating smooth lateral movement for individuals with limited mobility. Transfer belts are flexible, adjustable straps worn around the waist, providing caregivers with secure handholds to assist in lifting or stabilizing during transfers. While transfer boards enable independent sliding transfers, transfer belts primarily support caregiver-assisted lifts and stability during mobility transitions.
When to Use a Transfer Board: Ideal Scenarios
A transfer board is ideal for moving individuals with limited lower body strength but sufficient upper body control, such as transferring from wheelchair to bed or car seat. It provides a stable, smooth surface that minimizes friction and reduces the risk of falls during lateral transfers. Use a transfer board when the gap between surfaces is small and can be safely bridged without requiring significant standing or weight-bearing ability.
When to Choose a Transfer Belt: Best Use Cases
Transfer belts are ideal for assisting patients with limited lower body strength who require upright support during transfers or walking. They provide secure handholds for caregivers to maintain control while minimizing strain, making them suitable for short-distance transfers or ambulation. Unlike transfer boards, belts are preferred when patient mobility involves weight-bearing activities or gradual balance improvement.
Safety Considerations for Transfer Boards and Transfer Belts
Transfer boards reduce friction and risk of falls by providing a stable surface during patient transfers, but require proper positioning to prevent slipping hazards. Transfer belts enhance caregiver control and patient stability by allowing secure gripping points, minimizing the chance of sudden drops or imbalances. Both devices demand careful assessment of patient mobility, weight, and cognitive status to maximize safety and prevent injury during transfers.
Pros and Cons: Transfer Boards vs Transfer Belts
Transfer boards provide a sturdy surface that facilitates sliding between two points, minimizing the effort needed for transfers, especially over wider gaps or uneven surfaces. Transfer belts offer enhanced control and security by allowing caregivers to support and guide the individual more directly, reducing fall risk during mobility assistance. While boards excel in situations requiring smooth, low-friction transfers, belts are preferable for maintaining close support and stability in dynamic environments.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Mobility Aid
When selecting between a transfer board and a transfer belt, consider the user's level of upper body strength and balance, as transfer boards provide a stable surface for sliding, ideal for those with limited weight-bearing ability. The environment and available space also influence choice; transfer belts are more versatile in tight spaces and assist caregivers in controlling the user's movement safely. Additionally, assessing the caregiver's experience and the user's comfort and confidence with each device ensures a safer, more effective transfer process.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Aid for Safe Transfers
Transfer boards provide a stable, rigid surface ideal for bridging gaps between seats or surfaces, making them suitable for patients with sufficient upper body strength and balance. Transfer belts offer secure handholds and support for caregivers to assist patients with limited mobility, enhancing control and safety during transfers. Selecting the appropriate aid depends on the patient's physical capabilities, transfer environment, and caregiver involvement to ensure maximum safety and comfort.
Transfer board vs Transfer belt Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com