Docked bikes require designated docking stations for parking and charging, offering organized storage and reducing street clutter. Dockless bikes provide greater flexibility by allowing users to pick up and drop off bikes anywhere within a service area, enhancing convenience and accessibility. Both systems contribute to urban mobility, but dockless bikes demand more robust GPS and app integration to manage bike locations effectively.
Table of Comparison
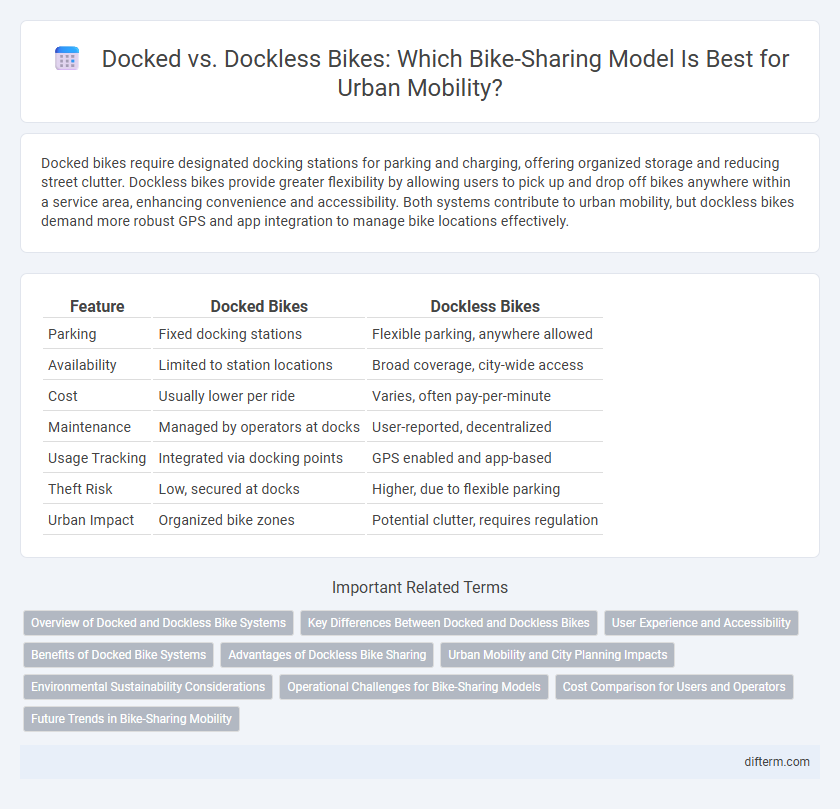
| Feature | Docked Bikes | Dockless Bikes |
|---|---|---|
| Parking | Fixed docking stations | Flexible parking, anywhere allowed |
| Availability | Limited to station locations | Broad coverage, city-wide access |
| Cost | Usually lower per ride | Varies, often pay-per-minute |
| Maintenance | Managed by operators at docks | User-reported, decentralized |
| Usage Tracking | Integrated via docking points | GPS enabled and app-based |
| Theft Risk | Low, secured at docks | Higher, due to flexible parking |
| Urban Impact | Organized bike zones | Potential clutter, requires regulation |
Overview of Docked and Dockless Bike Systems
Docked bike systems require users to pick up and return bikes at designated stations, offering secure parking and easy availability in high-demand areas. Dockless bike systems provide greater flexibility by allowing users to locate and leave bikes via GPS-enabled apps anywhere within a service zone, enhancing last-mile connectivity. Both systems leverage real-time data for efficient bike redistribution and maintenance, powering urban mobility solutions and reducing traffic congestion.
Key Differences Between Docked and Dockless Bikes
Docked bikes require fixed stations for parking and locking, promoting organized storage but limiting flexibility in pickup and drop-off locations. Dockless bikes utilize GPS technology and onboard locks, allowing riders to park freely within designated areas, enhancing convenience but potentially causing urban clutter. The maintenance and redistribution of dockless fleets rely heavily on real-time data analytics, contrasting with docked systems' predictable infrastructure-backed operations.
User Experience and Accessibility
Dockless bikes offer greater accessibility by allowing users to pick up and drop off bikes anywhere within a designated area, enhancing convenience and reducing the time spent searching for docking stations. Docked bikes provide a more structured user experience with designated parking spots that help maintain urban order and reduce sidewalk clutter. The balance between docked and dockless systems impacts overall mobility by offering flexibility for spontaneous trips while ensuring reliable infrastructure for regular commuters.
Benefits of Docked Bike Systems
Docked bike systems offer enhanced security by requiring bikes to be returned to designated stations, reducing theft and vandalism. These systems improve urban organization by providing fixed parking locations, minimizing sidewalk clutter and ensuring availability at key transit hubs. They also facilitate precise tracking and maintenance, leading to better bike durability and service reliability.
Advantages of Dockless Bike Sharing
Dockless bike sharing offers increased flexibility by allowing users to pick up and drop off bikes anywhere within designated zones, eliminating the need for fixed docking stations and promoting convenient last-mile connectivity. This system maximizes bike availability across urban areas, reducing congestion at docking points and adapting quickly to fluctuating demand patterns. Advanced GPS tracking and mobile app integration enhance user experience and operational efficiency, supporting sustainable and dynamic urban mobility solutions.
Urban Mobility and City Planning Impacts
Docked bikes require fixed stations that influence urban infrastructure design, limiting flexibility but enhancing organized parking and reducing clutter in high-density areas. Dockless bikes offer greater mobility and convenience by allowing users to pick up and drop off bikes anywhere, presenting challenges for city planners in managing public space and sidewalk accessibility. Effective urban mobility strategies must balance the spatial demands of docked systems with the spontaneous usage patterns of dockless bikes to optimize traffic flow and pedestrian safety.
Environmental Sustainability Considerations
Dockless bikes reduce the need for extensive docking infrastructure, minimizing urban space consumption and promoting flexible, eco-friendly transportation. However, improper parking and bike disposal in dockless systems can lead to environmental challenges such as clutter and waste. Docked bikes offer controlled parking and maintenance, ensuring longer bike lifespan and reducing environmental impact related to damaged or abandoned bikes.
Operational Challenges for Bike-Sharing Models
Docked bike-sharing systems face operational challenges including the need for fixed docking stations that require significant urban space and infrastructure investment, limiting flexibility in bike placement and affecting user accessibility. Dockless bike models encounter issues such as uneven bike distribution, increased risks of vandalism or theft, and challenges in managing fleet maintenance without centralized docks. Efficient rebalancing strategies and real-time monitoring are essential to optimize availability and minimize operational costs across both bike-sharing models.
Cost Comparison for Users and Operators
Dockless bikes generally offer lower upfront costs for users due to the absence of docking fees and greater flexibility in parking locations, while docked bikes require fixed stations that can increase rental costs. Operators of dockless systems face higher expenses related to bike redistribution, maintenance, and theft prevention, whereas docked bike systems benefit from controlled parking infrastructure that simplifies asset management and reduces operational losses. Cost efficiency for users and operators varies significantly based on urban density, maintenance strategies, and system scale, influencing long-term sustainability and pricing models in mobility networks.
Future Trends in Bike-Sharing Mobility
Dockless bikes are forecasted to dominate future bike-sharing mobility due to their flexibility and integration with smart city infrastructures, enabling dynamic redistribution through AI-powered algorithms. Docked bikes continue to offer reliable station-based access, supporting urban areas prioritizing fixed parking and reducing sidewalk clutter. Emerging trends emphasize hybrid models combining docked stability with dockless convenience, optimizing user experience and operational efficiency.
docked bikes vs dockless bikes Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com